Abstract
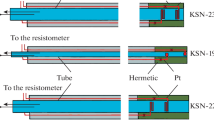
A determination of the absolute specific conductance of KCl solutions is demonstrated. The measurement is based on the conductance cell with a well defined geometry, having a difference in the removable center tube of accurately measured dimensions. The specific conductance of the solution is obtained from the measured resistances of the cell with and without the center tube and the measured l/A ratio of the center tube. Specific conductances obtained using the cell agree with the previously accepted standards for 0.1 demal and 0.01 demal solutions within 0.02%. Results are also presented for solutions based on molality. The temperature control, bridge, and detector technology used to obtain results of this accuracy are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Kohlrausch and W. A. Nippoldt,Gott. Nach. 415, (1868);Ann. Physik 138, 280, 370 (1869); F. Kohlrausch, L. Holborn, and H. Dieselhorst,Weid. Ann. 64, 625 (1898).
G. Jones and B. C. Bradshaw,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, 1780 (1933).
NBS Circular C459,Announcement of Changes in Electrical and Photometric Units, (1949).
“The International Practical Temperature Scale for 1968,”Metrologia 5, 35 (1969).
Standard Solutions Reproducing the Conductivity of Electrolytes, International Recommendation No. 56, Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale (OIML), 1st edn., June 1980 (Bureau International de Métrologie Légale, Paris, 1981).
Y. C. Wu, W. F. Koch, W. J. Hamer, and R. L. Kay,J. Solution Chem. 16, 985 (1987).
H. C. Parker and E. W. Parker,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 46, 312 (1924).
G. Jones and R. C. Josephs,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 50, 1049 (1928).
P. H. Dike,Rev. Sci. Instruments 2, 379 (1931).
H. W. Lamson,Rev. Sci. Instruments 9, 272 (1938).
R. A. Robinson and R. H. Stokes,Electrolyte Solutions, 3rd edn., (Butterworths, London, 1959).
Y-C. Chiu and R. M. Fuoss,J. Phys. Chem. 72, 4123 (1968).
J. C. Justice,J. Chim. Phys. 65, 353 (1968).
Rostock, cited by G. J. Janz and R. P. T. Tompkins,J. Electrochem. Soc. 55C, 124 (1977).
J. Barthel, F. Feuerlein, R. Neueder, and R. Wachter,J. Solution Chem. 9, 209 (1980).
P. Saulnier and J. Barthel,J. Solution Chem. 8, 847 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y.C., Pratt, K.W. & Koch, W.F. Determination of the absolute specific conductance of primary standard KCl solutions. J Solution Chem 18, 515–528 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664234
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664234