Abstract
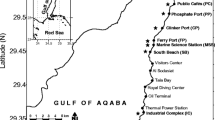
Red Sea corals have been found to be biomonitors of trace metal pollution. A comparative study was undertaken on three species from a polluted area near a desalination plant at Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) and from an unpolluted area. The results show that corals take-up trace elements from their aquatic environment and thereby act to record changes in the composition of that environment. Variations in the composition of skeletons and soft tissues of corals have been correlated with changes in sea water composition. Three coral species, Porites lutea, Goniastrea retiformis and Pocillopora verrucosa have been analysed for Hg, Cu, Zn, Pb, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cd, V, Al, Cr, Mg, B, Ca, and Sr in both skeletal and soft tissues. Results show that corals in the polluted areas have significantly higher concentrations of trace elements compared to that of corals from unpolluted areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard, L. A., Macintyze, I. G., and Pierce, J. W.: 1988, ‘Possible Environmental Index in Tropical Reef Corals’,Nature, Lond.252, 219–220.
Bray, R. C. and Clark, I.: 1971, ‘Vagaries in the Use of Isolated Intestibal Mucosal Cell Preparation with Particular Emphasis on Ca Uptake’, in G. Nicholls and R. H. Wasserman (eds.),Cellular mechanisms for Ca transfer and homeostasis, pp. 313–337.
Budemeier, R. W., Schnieder, R. C., and Smith, S. V.: 1981, ‘The Alkaline Earth Chemistry of Corals’, Proc. 4th Int. Coral Reef Symp., Vol. 2, pp. 81–85, University of the Philippines, Manila.
Butler, P. A., Andren, Bonde, G. J., Jernelov, A., and Reish, D. J., 1971, ‘Monitoring Organisms’, In FAO Technical Conference on Marine Pollution and its Effects on living Resources and Fishing, Rome 1970. Supplement 1: Report of the Seminar on methods of detection, measurement and monitoring of Pollutants in the marine environment, pp. 101–12,FAO Fisheries Reports No. 99, suppl. 1.
Chester, R. and Hughes, M. J.: 1967, ‘A Chemical Technique for the Separation of Ferromanganese Minerals, Carbonate Minerals and Absorbed Trace Elements from Pelagic Sediments’,Chem. Geol. 2, 249–62.
Crocket, J. H. and Winchester, J. W.: 1966, ‘Coprecipitation of Zn with Ca Carbonate’,Geochim. Cosinochim. Acts 30, 1093–1109.
Denton, G. R. W. and Burdon-Jones, C.: 1986, ‘Trace Metals in Corals from the Great Barrier Reef’,Mar. Pollut. Bull 17, 209–213.
Dodge, R. E., Jickells, T. D., Knap, A. H., Boyd, S., and Bak, R. P. M.: 1984, ‘Reef-Building Coral Skeletons as Chemical Pollution (Phosphorus) Indicators’,Mar. Pollut. Bull 15, 178–187.
Eisler, R.: 1981, ‘Trace Metal Concentration Marine Organism’, Pergamon Press, Londen, Oxford, p. 680.
El-Waked, S. K.; El-Sayed, M. K., and Hussain, S. A.: 1984, ‘Relative Abundance of Carbonate Minerals in Common Reef-Building Corals’, Proc. Sym. Coral Reef Environ. Red Sea, Jeddah, pp. 276–292.
Flor, T. H. and Moore, W. S.: 1977, ‘Radium/Calcium and Uranium/Calcium determinations for Western Atlantic Reef corals’, Proc. 3rd Int. Coral Reef Symp., Vol. 2, pp. 555–561.
Goreau, T. J.: 1977, ‘Coral Skeletal Chemistry: Physiological and Environmental Regulation of Stable Isotopes and Trace Metals inMontastrea annularis’,Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 196, 291–315.
Halim, Y., Awad, H., El-Sayed, M. Kh., El-Zorka, S., Hanna, R. G., Ormond, R., and Stiern, IJ.: 1987, ‘Review of the State of the Marine Environment, Red Sea and Gulf of Aden’,Gesamp Working Group 26, UNEP.
Hanna, R. G. M.: 1970, ‘Trace Element Partition Patterns in North Atlantic Deep-Sea Sediments’, M. Sc thesis, Liverpool University, U.K.
Hanna, R. G. M.: 1975, ‘Chemical formation Patterns of Deep Sea Sediments and Algae Grow in Area of Different Salinities’, Ph. D. thesis, Moscow, U.S.S.R.
Hanna, R. G. M.: 1986, ‘The Environmental Pollution of Littoral Area of the Red Sea’, Intergovernmental Report, Cairo, pp. 495.
Hanna, R. G. M.: 1988, ‘Red Sea Corals as Chemical Pollution Indicators’, (in prep.).
Haug, A. S., Melsom and S. Omang: 1974, ‘Estimation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Two Norwegan Fjord Areas by Analysis of the Brown AlgaeAscophyllum nodosum’,Environment Pollution 7, 179, 92.
Kinsman, D. J. J. and Holland, H. D.: 1969, ‘The Co-Precipitation of Cations with CaCo3 IV. The Co-Precipitation of Sr with Aragonite Between 16° and 96°C’,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 33, 1–17.
Vinogradov, A. P.: 1953, ‘The Elementary Chemical Composition of Marine Organisms’,Sears Found. Mar. Res., Yale Univ., Memoir No. 11, 647.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanna, R.G., Muir, G.L. Red sea corals as biomonitors of trace metal pollution. Environ Monit Assess 14, 211–222 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00677917
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00677917