Abstract
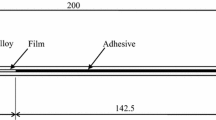
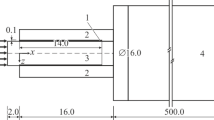
Mode I fracture behaviour of adhesively bonded double and cantilever beam (DCB) compact tension (CT) joints was studied using a rubber-modified epoxy (Araldite® GY260) as the adhesive. Adherends were prepared from a carbon fibre (CF)/epoxy composite or aluminium alloys. The crack path in the joints was studied based on the sign of the non-singularT-stress ahead of the crack tip by calculating the thermal residual stress in the joints using finite element analysis. The results indicate that the type of adherend materials influence the level of the thermal residual stress in the adhesive layer, which consequently causes different crack paths in the joints, i.e. a uniformly smooth fracture surface in both CT and DCB aluminium joints and a wavy crack growth in the DCB CF/epoxy composite joints. However, the fracture energies of different types of adhesive joints were almost identical to each other for bond thicknesst<0.2 mm, and a somewhat higher fracture resistance was obtained for the CF/epoxy DCB joints with large bond thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. R. AKISANYA and N. A. FLECK,Int. J. Fract. 58 (1992) 93.
M. CHARALAMBIDES, A. J. KINLOCH, Y. WANG and J. G. WILLIAMS,ibid. 54 (1992) 269.
N. A. FLECK, J. W. HUTCHINSON and Z. SUO,Int. J. Solids Struct. 27 (1991) 1683.
A. R. AKISANYA and N. A. FLECK,Int. J. Fract. 55 (1992) 29.
H. CHAI,ibid. 32 (1987) 211.
J. S. WANG and Z. SUO,Acta Metall. 38 (1990) 1279.
H. R. DAGHYANI, L. YE and Y.-W. MAI,J. Compos. Mater. (1996) in press.
H. C. CAO and A. G. EVANS,Mech. Mater. 7 (1989) 295.
M. D. THOULESS,Acta Metall. 38 (1990) 1135.
H. DAGHYANI, L. YE and Y.-W. MAI,J. Adhesion 53 (1995) 149.
Idem, ibid.,53 (1995) 163.
Idem, ibid., (1996) in press.
H. R. DAGHYANI, L. YE, Y.-W. MAI and J. WU,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 13 (1994) 1330.
R. F. WEGMAN, in “Surface Preparation Techniques for Adhesive Bonding” (Noyes, 1989) pp. 9–27.
J. DUNDURS,J. Appl. Mech. 36 (1969) 650.
M.-Y. HE and J. W. HUTCHINSON,J. Appl. Mech. 56 (1989) 270.
K. M. LIECHTI and Y. S. CHAI,ibid. 59 (1992) 295.
B. COTTERELL and J. R. RICE,Int. J. Fract. 16 (1980) 155.
“Fracture Strength in Clevage of Adhesives in Bonded Joints”, ASTM-D3433-75, Annual Book of ASTM Standards (American Society for Testing and Materials, Easton, MD, 1980).
Y.-W. MAI and A. S. VIPOND,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 13 (1978) 2280.
ADINA R and D, INC, USA (1992).
P. M. UNTERWEISER and H. M. COBB (eds), “Worldwide Guide to Equivalent Nonferrous Metals and Alloys”, 2nd Edn, (ASM International, 1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daghyani, H.R., Ye, L. & Mai, Y.W. Effect of thermal residual stress on the crack path in adhesively bonded joints. J Mater Sci 31, 2523–2529 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687277
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687277