Abstract
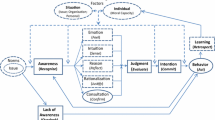
This paper reports on a survey that investigated the moral decision processes of accountants. A formal belief revision model is adapted and hypotheses based on theorizations from the cognitive-developmental school are tested. The moral decision processes of accountants are hypothesized to be influenced by professional expectations, organizational expectations and internalized expectations. Subjects provided specific demographic data and were asked to access the appropriateness of fourteen principles for making moral decisions in business. Subjects were also asked to indicate which of the fourteen approaches would be most appropriate for resolving each of five ethical situations that are representative of common ethical dilemmas in accounting.
Subjects' responses to the appropriateness of the fourteen principles are reduced to two dimensions using factor analysis. The factors are consistent and representative of important underlying dimensions of the stages of moral development. Demographic variables are correlated with the extracted factors using analysis of variance.
The results show that subjects consider interpersonal expectations and conformity to be more appropriate than approaches that are self-serving. These findings suggest that ethical decision processes of accountants are influenced by organizational support. Age, gender, and education were also found to influence the moral decision process. Overall, the findings are consistent with the expectations hypothesized from the cognitive-developmental school and suggest that the moral development of accountants is ongoing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, G. D.: 1985, ‘A Fresh Look at Standards of Professional Conduct’,Journal of Accountancy (Sept.), 91–106.
Arlow, P. and T. A. Ulrich: 1988, ‘A Longitudinal Survey of Business School Graduates' Assessments of Business Ethics’,Journal of Business Ethics 7, 295–302.
Arlow, P.: 1991, ‘Personal Characteristics in College Students' Evaluations of Business Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility’,Journal of Business Ethics 10, 63–69.
Armstrong, M. B.: 1987, ‘Moral Development and Accounting Education’,Journal of Accounting Education 5, 27–34.
Baumhart, R. C.: 1968,An Honest Profit: What Businessmen Say About Ethics in Business (Holt, Rinehart, and Winston, New York).
Campbell, D. J. and H. C. Stanley: 1966,Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Research (Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston).
Clart, J. W.: 1966,Religious and Moral Standards of American Businessmen (Southwestern Publishing Company, Cincinnati).
Claypool, G. A., D. F. Fetyko and M. A. Pearson, 1990, ‘Reactions to Ethical Dilemmas: A Study Pertaining to Certified Public Accountants’,Journal of Business Ethics 9, 699–706.
Gilligan, C., J. Ward, J. Taylor and B. Bardige: 1988,Mapping the Moral Domain (Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass).
Gilligan, C.: 1977, ‘In a Different Choice: Women's Conceptions of the Self and of Morality’,Harvard Educational Review 47, 481–517.
Gilligan, C.: 1982, ‘Adult Development and Women's Development: Arrangements for a Marriage’, in J. Giele (eds.),Women in the Middle Years (John Wiley & Sons, New York).
Hiltebeitel, K. M. and S. K. Jones: 1991, ‘Initial Evidence on the Impact of Integrating Ethics into Accounting Education’,Issues in Accounting Education 6(2), 262–275.
Hilebeitel, K. M. and S. K. Jones: 1992, ‘An Assessment of Ethics Instruction in Accounting Education’,Journal of Business Ethics 11, 37–46.
Institute of Management Accountants: 1982,Statement of Management Accounting No. 1-B, June 17.
Institute of Management Accountants: 1983,Statement of Management Accounting No. 1-C, June 1.
Johnson, R. A. and D. W. Wichern: 1982,Applied Multivariate Statistical Methods (Prentice Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs).
Jones, S. and L. Ponemon: 1993, ‘A Comment on A Multidemensional Analysis of Selected Ethical Issues in Accounting’,The Accounting Review 68(2), in press.
Kohlberg, L.: 1971,The Philosophy of Moral Development (Harper & Row Publishers, San Francisco).
Lewis, P. V.: 1989, ‘Ethical Principles for Decision Makers: A Longitudinal Study’,Journal of Business Ethics 8, 271–276.
Loeb, S. E.: 1970, ‘A Behavioral Study of CPA Ethics’, Ph.D. Dissertation (University of Wisconsin).
Loeb, S. E.: 1984, ‘Codes of ethics and Self-regulation for Non-public Accountants: A Public Policy Perspective’,Journal of Accounting and Public Policy, Spring, 1–8.
Petrick, J. A., R. A. Wagley and T. J. Von der Embse: 1991, ‘Structured Ethical Decision Making: Improving the Prospects of Managerial Success in Business’,Sam Advanced Management Journal 56, 28–34.
Ponemon, L.: 1990, ‘Ethical Judgments in Accounting: A Cognitive-Developmental Perspective’,Critical Perspectives on Accounting 1, 191–215.
Ponemon, L. and Glazer, A.: 1990, ‘Accounting Education and Ethical Development: The influence of liberal Learning on Students and Alumni in Accounting Practice’,Issues in Accounting Education 5(2), 195–208.
Rest, J. R.: 1979a,Development in Judging Moral Issues (University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis).
Rest, J. R.: 1979b,Revised Manual for the Defining Issues Test (University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis).
Reidenbach, E. R. and D. P. Robin: 1991, ‘A Conceptual Model of Corporate Moral Development’,Journal of Business Ethics 10, 273–284.
Sas Institute Inc.: 1989,SAS/STAT Users Guide, Version 6, Fourth Edition, Volume 1 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC).
Schlachter, P. J.: 1990, ‘Organizational Influences on Individual Ethical Behavior in Public Accounting’,Journal of Business Ethics 9, 839–853.
Sorensen, J. E.: 1967, ‘Professional and Bureaucratic Organization in the Public Accounting Firm’,Accounting Review (July), 553–565.
St. Pierre, K. E., E. S. Nelson and A. L. Gabbin: 1990, ‘A Study of the Ethical Development of Accounting Majors in Relation to Other Business and Nonbusiness Disciplines’,The Accounting Educators' Journal (Summer), 23–35.
Wood, A. M.: 1985, ‘What Must be Done: A Report from the POB’,Journal of Accountancy (Aug.), 142–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, S.K., Hiltebeitel, K.M. Organizational influence in a model of the moral decision process of accountants. J Bus Ethics 14, 417–431 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872084
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872084