Abstract
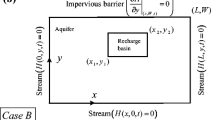
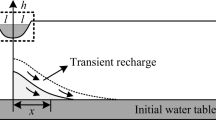
A problem of water-table fluctuation in a finite two-dimensional aquifer system in response to transient recharge from an overlying rectangular area is studied. An analytical solution is obtained by using the method of finite Fourier transform to predict the transient position of the water-table. The solution for constant rate of recharge is shown as a special case of the present solution. Effects of variation in the rate of recharge on the growth of two-dimensional groundwater mound is illustrated with the help of a numerical example.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
half width of the aquifer [L]
- B :
-
half length of the aquifer [L]
- D :
-
half width of the recharge basin [L]
- e :
-
specific yield
- h :
-
varying water-table height [L]
- h 0 :
-
initial water-table height [L]
- h :
-
weighted mean of the depth of saturation [L]
- K :
-
hydraulic conductivity [LT−1]
- L :
-
half length of the recharge basin [L]
- P(t) :
-
time varying rate of recharge [LT−1]
- P 1 +P 0 :
-
initial rate of time varying recharge [LT−1]
- P 1 :
-
final rate of time varying recharge [LT−1]
- t :
-
time of observation [T]
- x, y :
-
coordinate axes
- α :
-
decay constant [T−1]
References
Baumann, P., 1952, Groundwater movement controlled through spreading,Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng. Trans. 117, 1024–1074.
Bear, J., 1979,Hydraulics of Groundwater, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Glover, R. E., 1960, Mathematical derivations pertaining to groundwater recharge,U.S. Dept. Agr., Agr. Res. Serv., Ft. Collins, Colo. (mimeographed).
Hantush, M. S., 1967, Growth and decay of groundwater mounds in response to uniform percolation,Water Resour. Res. 3, 227–234.
Horton, R. E., 1940. Approach toward a physical interpretation of infiltration capacity,Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 5, 399–417.
Hunt, B. W., 1971, Vertical recharge of unconfined aquifers,J. Hydraulic Div. ASCE 97 [HY7], 1017–1030.
Marino, M. A., 1967. Hele-Shaw model study of the growth and decay of groundwater ridges,J. Geophys. Res. 72, 1195–1205.
Rao, N. H. and Sarma, P. B. S., 1981a, Groundwater recharge from rectangular areas,Groundwater 19(3), 271–274.
Rao, N. H. and Sarma, P. B. S., 1981b, Recharge from rectangular areas to finite aquifers,J. Hydrol. 53, 269–275.
Sneddon, I. N., 1974,The Use of Integral Transforms, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
Zomorodi, K., 1991, Evaluation of the response of a water-table to a variable recharge rate,Hydrol. Sci. J. 36, 67–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, S.N., Manglik, A. & Singh, R.N. Water table fluctuation in response to transient recharge from a rectangular basin. Water Resour Manage 8, 1–10 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872276
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872276