Abstract
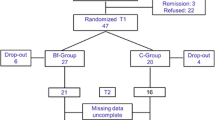
The purpose of this study was twofold: (a) to compare the effects of three behavioral strategies for the relief of migraine, and (b) to examine different combinations of the treatments to assess the effectiveness of multimodal biofeedback with this problem. Twenty-four volunteer migraine sufferers not on medication, and with at least weekly occurrence of headaches, participated in the study. Results indicated that (a) subjects who learned temporal cooling, frontalis relaxation, and progressive muscular relaxation exhibited the best success with headache relief; (b) control subjects, who did not show the same psychophysiological changes as experimental subjects, reported no headache relief; and (c) subjects in the group with only relaxation exercises performed similarly to control subjects and reported no headache relief.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, A. B. (1975). An experimental test of assumptions relating to the use of electromyographic biofeedback as a general relaxation training technique.Psychophysiology, 12 656–662.
Benson, H., Klemchuk, H. P., & Graham, J. R. (1974). The usefulness of the relaxation response in the therapy of headache.Headache, 14 49–52.
Bild, R., & Adams, H. E. (1980). Modification of migraine headaches by cephalic blood volume pulse and EMG biofeedback.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 48 51–57.
Blanchard, E. B., Andrasik, F., Ahles, T. A., Teders, S. J., & O'Keefe, D. (1980). Migraine and tension headache: A meta-analytic review.Behavior Therapy, 11 613–631.
Blanchard, E. B., Theobald, D. E., Williamson, D. A., Silver, B. V., & Brown, D. A. (1978). Temperature biofeedback in the control of migraine headaches: A controlled evaluation.Archives of General Psychiatry, 35 581–588.
Diamond, S., & Baltes, B. J. (1973). The diagnosis and treatment of headache.Chicago Medican School Quarterly, 32 1–4.
Friar, L. R., & Beatty, J. (1976). Migraine: Management by trained control of vasoconstriction.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 44 46–53.
Holroyd, K. A., Andrasik, F., & Noble, J. (1980). A comparison of EMG biofeedback and a credible pseudotherapy in treating tension headache.Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 3 29–39.
Kewman, D., & Roberts, A. H. (1980). Skin temperature biofeedback and migraine headaches. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 5, 327–345.
Lake, A., Raney, J., & Papsdorf, J. D. (1979). Biofeedback and rational-emotive therapy in management of migraine headache.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 12 127–140.
Lashley, J. K., & Elder, S. T. (1982). Selected case studies in clinical biofeedback.Journal of Clinical Psychology 1982,38 530–540.
Lazarus, A. (1970).Daily living: Coping with tension and anxieties. Chicago: Instructional Dynamics.
Miller, N. E. (1978). Biofeedback and visceral learning.Annual Review of Psychology, 29 373–404.
Mullinix, J., Norton, B., Hack, S., & Fishman, M. (1978). Skin temperature biofeedback and migraine.Headache, 17 242–244.
Olton, D. S., & Noonberg, A. R. (1980).Biofeedback: Clinical applications in behavioral medicine. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Sargeant, J. D., Green, E. E., & Walters, E. D. (1972). The use of autogenic feedback training in a pilot study of migraine and tension headaches.Headache, 12 120–124.
Sargeant, J. D., Green, E. E., & Walters, E. D. (1973). Preliminary report on the use of autogenic feedback training in the treatment of migraine and tension headaches.Psychosomatic Medicine, 35 129–135.
Shedivy, D. I., & Kleinman, K. M. (1977). Lack of correlation between frontalis EMG and either neck EMG or verbal ratings of tension.Psychophysiology, 14 182–186.
Sturgis, E. T., Adams, H. E., & Brantley, P. J. (1981). The parameters, etiology, and treatment of migraine headaches. In S. N. Haynes & L. Gannon (Eds.),Psychosomatic disorders: A psychophysiological approach to etiology and treatment. New York: Praeger Press.
Taub, E. (1977). Self-regulation of human tissue temperature. In G. E. Schwartz & J. Beatty (Eds.),Biofeedback: Theory and research. New York: Academic Press.
Turin, A., & Johnson, W. G. (1976). Biofeedback therapy for migraine headaches.Archives of General Psychiatry, 33 517–519.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gamble, E.H., Elder, S.T. Multimodal biofeedback in the treatment of migraine. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation 8, 383–392 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998748
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998748