Abstract
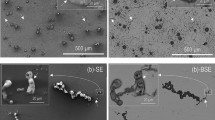
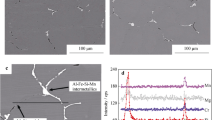
The effect of rapid solidification on the corrosion behaviour in aerated 0.001 M NaCl solution of Mg-Al alloys containing 9.6 to 23.4wt% AI has been investigated in comparison with chill-cast material. Polarization studies show that rapid solidification decreases corrosion current by up to two orders of magnitude corresponding to a corrosion rate of 6 to 11 mil y−1. Increasing the aluminium content in solid solution by rapid solidification gave rise to a steep increase in pitting potential between 10 and 23 wt% Al and resulted in development of an anodic plateau at ∼ 30μAcm−2 attributable to magnesium depletion for the alloy surface and formation of a protective film. Chemical analysis of the electrolyte as a function of dissolution time for the rapidly solidified material indicated that initially only magnesium dissolved and that this dissolution of magnesium ceased within 2 to 5 min. The results indicate the formation of an aluminium-enriched interdiffusion zone at the surface underlying a more stable surface oxide than for ingot-processed Mg-Al-based alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. R. Bothwell, in “The Corrosion of the Light Metals”, edited by R. T. Foleyet al. (Wiley, New York, 1967) p. 259.
E. F. Emley, in “Principles of Magnesium Technology” (Pergamon, Oxford, 1966) p. 670.
R. S. Busk, in “Magnesium Products Design” (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1987) p. 498.
M. Pourbaix, in “Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions” (Pergamon, Oxford, 1966) p. 139.
R. E. Lewis, A. Joshi andH. Jones, in “Processing of Structural Metals by Rapid Solidification”, edited by F. H. Froes and S. J. Savage (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1987) p. 367.
S. K. Das andC. F. Chang, in “Rapidly Solidified Crystalline Alloys”, edited by S. K. Das (The Metallurgical Society of RIME, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 1985) p. 137.
C. F. Chang, S. K. Das andD. Raybould, in “Rapidly Solidified Materials”, edited by P. W. Lee and R. S. Carbonara (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1986) p. 129.
S. K. Das, C. F. Chang andD. Raybould,Light Metal Age December (1986) 5.
F. Hehmann, R. G. J. Edyvean, H. Jones andF. Sommer, Conference Proceedings PM Aerospace Materials '87, edited by B. Williams and G. Dowson (Metal Powder Report Publishing Services, Shrewsbury, UK, 1988) pp. 46–1.
F. Hehmann, “Rasch Erstarrh magnesium Mischkoistalle und ihr Umwandlungs — und korrosionsver-halten”, Fortschoitt — Berichte VDI, Reihe 5, Nr. 155 (VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf, 1989).
H. Kaiser, in “Korrosion der Metalle” (Advanced Course, edited by H. Kaesche, University of Erlangen, Nürnberg, West Germany, 1984) pp. 4–7.
S. Akavipat, E. B. Hale, C. E. Habermann andP. L. Hagans,Mater. Sci. Engng 69 (1985) 311.
N. D. Tomashov, in “Theory of Corrosion and Protection of Metals” (MacMillan, New York, 1966) p. 493.
B. Mazurkiewicz,Corr. Sci. 23 (1983) 687.
J. I. Gardiazabal andJ. R. Galvele,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127 (1980) 255.
H. Gerischer andH. Rickert,Z. Metallkde 46 (1955) p. 681.
R. P. Tischer andH. Gerischer,Z. Electrochem. 62 (1958) p. 50.
H. Gerischer,Korrosion 14 (1962) 59.
H. Kaiser,Werkstoffe und Korrosion, to be published.
B. Kabius, Thesis, University of Erlangen (1987).
A. J. Forty andG. Rowlands,Phil. Mag. A 43 (1981) 171.
P. Durkin andA. J. Forty,ibid. 45 (1981) 95.
R. C. Weast, in “CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics”, 66th Edn (CRC, Florida, 1986) p. 46.
F. H. Wölbier,Diffusion Defect Data 50 (1987) 170.
W. A. Fernando, in Naval Surface Weapons Center Report TR 85-88 (Dahlgren, Virginia, 1985) p. I9.
H. Sugawara andH. Ebiko,Corros. Sci. 7 (1967) 513.
H. Kaiser, “Alloy Dissolution”, in “Corrosion Mechanisms” (Dekker, New York, 1987) p. 85.
H. W. Pickering andC. Wagner,J. Electrochem. Soc. 114 (1967) 698.
A. P. Pchelnikov, L. I. Krasinskaya, A. D. Sitnikov andV. V. Losev,Elektrokhimiya 11 (1975) 37.
H. W. Pickering andP. J. Byrne,J. Electrochem. Soc. 118 (1971) 209.
C. Wagner,ibid. 103 (1956) 571.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermann, F., Sommer, F., Jones, H. et al. Corrosion inhibition in magnesium-aluminium-based alloys induced by rapid solidification processing. J Mater Sci 24, 2369–2379 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01174498
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01174498