Abstract
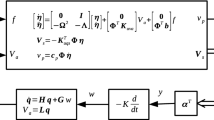
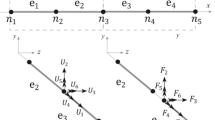
An integrated design procedure which is composed of structural design, control design, and actuator locations design is proposed in this paper. First, a composite objective function, formed by a structural and a control objective, is optimized in steady state through the homogenization design method. Then an independent modal space control algorithm (IMSC) is performed on this optimal structure to reduce the dynamic response. Finally, to minimize the control force while still obtaining the same modal response for the controlled modes, the optimal choice for actuator locations is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balas, M.J. 1978: Feedback control of flexible systems.IEEE Trans. Auto. Control Vol. AC23, 673–679
Balas, M.J. 1979: Direct velocity feedback control of large space structures.J. Guid., Control & Dyn. 2, 252–253
Baruh, H.; Meirovitch, L. 1981: On the placement of actuators in the control of distributed-parameter systems.AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS, 22nd Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conf., pp. 611–620
Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. 1988: Generating optimal topologies in structural design using homogenization method.Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 71, 197–224
Bendsøe, M.P.; Rodrigues, H.C. 1991: Integrated topology and boundary shape optimization of 2-D solids.Comp. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 87, 15–34
Díaz, A.R.; Kikuchi, N. 1992: Solution to shape and topology eigenvalue optimization problems using homogenization method.Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg. 35, 1487–1502
Hale, A.L.; Lisowiki, R.J.; Dahl, W.E. 1985: Optimal simultaneous structural and control design of maneuvering flexible spacecraft.J. Guid., Control & Dyn. 8, 86–93
Johnson, T.L. 1981: Principles of sensor and actuator location in distributed systems.Proc. Int. Symp. on Engineering Science and Mechanics, Tainan, Taiwan,50, pp. 1–14
Kajiwara, I.; Tsujioka, K.; Nagamatsu, A. 1994: Approach for simultaneous optimization of a structure and control system.AIAA J. 32, 866–873
Kamat, M.P.; Venkayya, V.B.; Khot, N.S. 1983: Optimization with frequency constraints limitations.J. Sound & Vib. 91, 147–154
Lindberg, R.E.; Longman, R.W. 1984: On the number and placement of actuators for independent modal space control.J. Guid., Control & Dyn. 7, 215–221
Martin, J.C.E. 1978: Optimal allocation of actuators for distributed-parameter system.ASME J. Dyn. Systems, Measurement and Control 100, 227–228
Meirovitch, L.; Baruh, H. 1980: Control of self-adjoint distributed-parameter systems.J. Guid., Control & Dyn. 5, 60–66
Miller, D.F.; Shim, J. 1987: Gradient-based combined structural and control optimization.J. Guid., Control & Dyn. 10, 291–298
Ou, J.-S.; Kikuchi, N. 1996: Optimal design of controlled structures.Struct. Optim. 11, 19–28
Phillips, C.L.; Harbor, R.D. 1987:Feedback control systems. Prentice Hall
Rofooei, F.R.; Tadjbakhsh, I.G. 1993: Optimal control of structures with acceleration, velocity, and displacement feedback.J. Eng. Mech. 119, 1993–2011
Rozvany, G.I.N.; Zhou, M. 1991: The COC algorithm. Part I: cross-section optimization or sizing; Part II: topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization.Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 89, 281–336
Rozvany, G.I.N.; Zhou, M. 1992: Extensions of new discretized optimality criteria to structures with passive control.Proc. 4th AIAA/USAF/NASA/OAI Symp. on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization (held in Cleveland, OH), pp. 288–297. Washington D.C.: AIAA
Soong, T.T. 1990:Active structural control: theory and practice. New York: Wiley
Suzuki, K.; Kikuchi, N. 1991: A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization.Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 93, 291–318
Venkayya, V.B.; Tichler, V.A. 1985: Frequency control and its effect on the dynamic response of flexible structures.AIAA J. 23, 1768–1774
Yang, J.N.; Akbarpour, A.; Ghaemmagham, P. 1987: New optimal control algorithms for structural control.ASCE J. Eng. Mech. 113, 1369–1386
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part of this paper was presented in the First World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization (held in Goslar, Germany, May 28–June 2, 1995).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, J.S., Kikuchi, N. Integrated optimal structural and vibration control design. Structural Optimization 12, 209–216 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197358
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197358