Summary
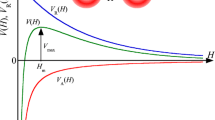
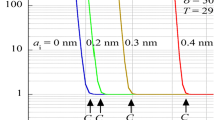
From a knowledge of the interactions between colloidal particles differing in both size and surface potential, the colloidal stability of polydisperse systems has been calculated. For dispersions having some stability, aGaussian distribution of radii or surface potential about a mean value results in a less stable dispersion than the corresponding monodisperse system. The difference between the stability of a polydisperse and a monodisperse system increases with increasing variation in surface potential and particle size about their mean values. Stability ratios for some latex dispersions have been recalculated allowing for the known size distributions of the particles and the effects on the interpretation of graphs of log (stability ratio) versus log (electrolyte concentration) have been noted.
Zusammenfassung
Im ersten Teil der Arbeit wurde die Stabilität von Dispersionen berechnet, deren Partikel sich sowohl in der Größe als auch im Oberflächenpotential unterscheiden. Dispersionen, in denen die Radien und die Oberflächenpotentiale der Teilchen nach einerGauβschen Verteilung variieren, sind weniger stabil als entsprechende monodisperse Systeme mit konstantem Oberflächenpotential. Je stärker die Unterschiede im Oberflächenpotential und in der Teilchengröße sind, desto größer wird auch der Unterschied in der Stabilität. Im zweiten Teil der Arbeit wurden Stabilitätsquotienten für einige Latexdispersionen umgerechnet unter Berücksichtigung der Teilchengrößenverteilung. Die Beziehung log (Stabilitätsquotient) gegen log (Elektrolytkonzentration) wurde ausführlich diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hogg, R., T. W. Healy, andD. W. Fuerstenau, Trans. Faraday Soc.62, 1638 (1966).
Weise, G. R. andT. W. Healy, Trans. Faraday Soc.66, 490 (1970).
Derjaguin, B. V. andL. Landau, Acta Physiochim.14, 633 (1941).
Verwey, E. J. W. andJ. Th. G. Overbeek, Theory of Stability of Lyophobic Colloids (Amsterdam 1948).
Ottewill, R. H. andJ. N. Shaw, Disc. Faraday Soc.42, 154 (1966).
Watillon, A. andA. -M. Joseph-Petit, Disc. Faraday Soc.42, 143 (1966).
Hamaker, H. C., Physica4, 1058 (1937).
Fuchs, N., Z. Physik89, 736 (1934).
McGown, D. N. L. andG. D. Parfitt, J. Phys. Chem.71, 449 (1967).
Weigner, G., Kolloid-Z.8, 227 (1911).
Smoluchowski, M., Physik-Z.17, 557 (1917); Z. Physik Chem.92, 227 (1911).
Muller, H., Kolloid-Z.88, 1 (1920).
Reference 4. Pages 175, 176 and 177.
Reerink, H. andJ. Th. G. Overbeek, Disc. Faraday Soc.18, 74 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, W.D. Coagulation of polydisperse colloidal systems. Kolloid-Z.u.Z.Polymere 250, 38–45 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01508209
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01508209