Abstract
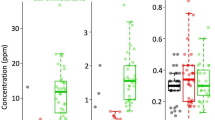
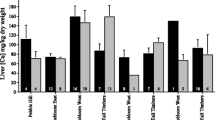
The feasibility of using Buzzards found dead as indicators of environmental contamination was tested. Liver, kidney, and tibia specimens were examined for the presence of Cd, Cu, Pb, Mn, and Fe, which were used as markers. All buzzards submitted to the Veterinary Institute in 1992 were examined for cause of death and condition. Results showed that more than half had been poisoned or shot. As the condition of the birds worsened, fat reserves were depleted before protein reserves. Concentrations of the heavy metals rose in liver and kidney as nutrient reserves fell. Since the content of heavy metal per organ was not related to body condition, content was considered a better measure for biomonitoring. The concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb, Mn, or Fe measured in buzzards were not toxic. In several places buzzards had recently ingested relatively large amounts Cd and/or Pb. Buzzards with high contents of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Mn were found in areas having more than average contamination. The North-South gradient in aerosol deposition and soil content of heavy metals (especially Cd & Pb) was reflected in the Buzzard. We concluded that the Buzzard is a suitable and cost-effective biomonitor, to investigate the bioavailability of ecocontaminants in large areas, to signal gross changes in food webs, and to monitor raptor persecution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Anonymous (1992): Milieudiagnose 1991: I Integrale rapportage lucht-, bodem- en grondwaterkwaliteit ‘pilot’ studie. III Bodem- en grondwaterkwaliteit. Nat. Inst. Publ. Health Environm. Hygiene, Bilthove.
Baars, A. J., &H. Over (1989): Wild bird mortality in the Netherlands, 1975–1989. CDI-DLO, Lelystad and Neth. Soc. Protect. Birds, Zeist.
Becker, P. H., R. W. Furness &D. Henning (1993): Mercury dynamics in young Common Tern (Sterna hirundo) chicks from a polluted environment. Ecotoxicol. 2: 33–40.
Beek, H. van, H. C. A. Greefkes &A. J. Baars (1987): Determination of copper, iron, manganese, lead and cadmium in automatically wet-digested animal tissue by graphite-furnace atomic-absorption spectrometry with Zeeman background correction. Talanta 34: 580–582.
Bijlsma, R. G. (1993): Ecologische atlas van Nederlandse roofvogels: 137–199, Haarlem.
Breukel, R. M. A., &W. G. van Gogh (1990): Cadmium in de Maas. Min. Traff. Waterways, D.B.W./RIZA, Lelystad, rep. 90.010.
Cheney, M. A., C. S. Hacker &G. D. Schroder (1981): Bioaccumulation of lead and cadmium in the Louisiana Heron (Hydranassa tricolor) and the Cattle Egret (Bubulcus ibis). Ecotoxicol. Environm. Safety 5: 211–224.
Clausen, B., &C. Wolstrup (1979): Lead poisoning in game from Denmark. Danish Rev. Game Biol. 11: 2–22.
Ditto,,K. Elvestad &O. Karlog (1982): Lead burden in Mute Swans from Denmark. Nordic Vet. Med. 34: 83–91.
Cramp, S. (1980): Handbook of the birds of Europe, the Middle East and North Africa. Vol. 2: Hawks to Buzzards: 177–190, Oxford.
Diem, K. (1982): Wissenschaftliche Tabellen. Geigy Teilband Statistik, Basel.
Eggenhuizen, G. &K. Breek (1995): De fabel van de buizerd, de torenvalk en de regenworm. De Takkeling 3: 42–44.
Eilinder, C. G. (1986): Iron. In:Friberg L., G. F. Nordberg &V. Vouk, Handbook on the toxicology of metals. II: 2 276–297, Amsterdam.
Esselink, H., F. M. van der Geld, L. P. Jager, G. A. Posthuma-Trumpie, P. E. F. Zoun &A. J. Baars (1995): Biomonitoring heavy metals using the Barn owl (Tyto alba guttata): sources of variation especially relating to body condition. Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 28: 471–486.
Frank, A. (1986): In search of biomonitors for cadmium: cadmium content of wild Swedish fauna during 1973–1976. Sci. Total Environm. 57: 57–65.
Garcia-Rodriquez, T., M. Ferrer, J. C. Carillo &J. Castroviejo (1987): Metabolic responses ofButeo buteo to long-term fasting and refeeding. Compar. Biochem. Physiol. 87A: 381–386.
Glutz von Blotzheim, U. N., K. M. Bauer &E. Bezzel (1971): Handbuch der Vögel Mitteleuropas. Band 4. Frankfurt a. M.
Hontelez, L. C. M. P., H. M. van den Dungen &A. J. Baars (1992): Lead and cadmium in birds in The Netherlands: a preliminary survey. Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 23: 453–456.
Hutton, M. (1981): Accumulation of heavy metals and selenium in three seabird species from the United Kingdom. Environm. Poll. A 26: 129–145.
Karlog, O., K. Elvestad &B. Clausen (1983): Heavy metals (cadmium, copper, lead and mercury) in Common Eiders (Somateria mollissima) from Denmark. Nordic Vet. Med. 35: 448–451.
Leeters, E. E. M. J., J. G. Hartholt, W. de Vries &L. J. M. Boumans (1994): Effects of aerial deposition on 150 forest stands in the Netherlands. Assessment of the chemical composition of foliage, soil, soil solution, ground water on a national scale. DLO-Staring Centre, Wageningen, rep. 69. 4.
Lumeij, J. T., I. Westerhof, T. Smit &T. J. Spierenburg (1993): Diagnosis and treatment of poisoning in raptors from the Netherlands: Clinical case reports and review of 2,750 postmortem cases, 1975–1988. In:Redig, P. T. et al., Raptor Biomedicine: 233–238, Minneapolis.
Ma, W. C. (1987): Heavy metal accumulation in the mole,Talpa europaea, and earthworm as an indicator of metal bioavailability in terrestrial environments. Bull. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 39: 933–938.
Ditto (1989): Effect of soil pollution with metallic lead pellets on lead bioaccumulation and organ/body mass alterations in small mammals. Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 18: 617–622.
Ditto,W. D. Denneman &J. H. Faber (1991): Hazardous exposure of ground-living small mammals to cadmium and lead in contaminated terrestrial ecosystems. Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 20: 266–270.
Moriarty, F. (1988): Ecotoxicology, the study of pollutants in ecosystems. London.
Piersma, T. (1984): Estimating energy reserves of Great Crested GrebesPodiceps cristatus on the basis of body dimensions. Ardea 72: 119–126.
Ditto,N. Davidson &P. Evans (1984): Estimation of the protein reserves of waders: the use and misuse of standard muscle volume. Wader Study Group Bull. 42: 19–22.
Saric, M. (1986): Managanese. In:Friberg, L., G. F. Nordberg, V. Vouk, Handbook on the toxicology of metals, II:354–386. Amsterdam.
Scanlon, P. F. (1982): Wet and dry weight relationships of Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) tissues. Bull. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 29: 615–617.
Scheuhammer, A. M. (1987): The chronic toxicity of aluminum, cadmium, mercury, and lead in birds: a review. Environm. Poll. 46A: 263–295.
Sovon (1987): Atlas van de Nederlandse vogels. Arnhem.
Straalen, N. M. van (1988): Ecotoxicologische theorievorming over opname, effecten en doorgifte van stoffen in dierpopulaties. Milieu 2: 40–45.
Szefer, P. (1983): Investigations of trace metals in Long-tailed Duck (Clangula hyemalis L.) from the Gdansk Bay. Sci. Total Environm. 29: 269–276.
Talmage, S. S., &B. T. Walton (1991): Small mammals as monitors of environmental contaminants. Rev. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 119: 47–145.
Ternes, W., B. Peterat &H. A. Rüssel-Sinn (1986): Belastung der Greifvögel Norddeutschlands mit den Schwermetallen Blei, Cadmium und Quecksilber. Proc. Tagung Vogelkrankheiten: 187–194. München.
Texeira, R. M. (1979): Atlas van de Nederlandse Broedvogels. Deventer.
Vries, W. de &E. E. M. J. Leeters (1994): Effects of aerial deposition on 150 forest stands in the Netherlands. Chemical composition of the humus layer, mineral soil and soil solution. DLO-Staring Centre, Wageningen, rep. 69.1.
Wolkers, H., T. Wensing &G. W. T. A. Groot Bruinderink (1994): Heavy metal contamination in organs of red deer (Cervus elaphus) and wild boar (Sus scrofa) and the effect on some trace elements. Sci. Total Environm. 144: 191–199.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jager, L.P., Rijnierse, F.V.J., Esselink, H. et al. Biomonitoring with the BuzzardButeo buteo in the Netherlands: Heavy metals and sources of variation. J Ornithol 137, 295–318 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01651071
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01651071