Abstract
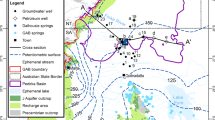
Hydrogeological studies at Figeh Springs were directed to determine groundwater flow paths, research, storage and discharge units, and the maximum reliable yield. The project was designed to provide information upon which to base pumpage to augment low-season flows from the spring which is the major water supply for the city of Damascus, Syria.
As a basis for conclusions and recommendations, work included extensive surface geologic mapping, air photographic interpretation, a detailed well and spring inventory, and a quality of water sampling program. Geologic structural work included mapping and jointing, faulting, and folding, and an analysis of their impact on groundwater movement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnow, Ted, 1959, Groundwater geology of Bexar County, Texas: Texas Water Comm. Bull. 5911.
Barraclough, J. T., and O. T. March, 1962, Aquifers and quality of groundwater along the Gulf Coast of Western Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Rpt. Inv. no. 28, 27 p.
Bazin, F. (SOGREAH), 1973, Etude hydrologique et hydrogeologique de la Source Figeh, rapport final, A. Cartes; R. 11.422.
Bazin, F. (SOGREAH), 1973, Etude hydrologique et hydrogique de la Source Figeh; R. 11.343.
Bazin, F. (SOGREAH), 1973, and others, 1973, Etude hydrologique et hydrogeologique de la Source Figeh, rapport final; R. 11.422.
Beckman, H. C., and N. S. Hinchey, 1944, The large springs of Missouri: second ser.: Mississippi Geol. Survey.
Biju-Duval, B., J. Letouzey, L. Montadert, P. Courrier, J. F. Mugnoit, and J. Sancho, 1974, Geology of the Mediterranean Sea Basins.In C. A. Burk, and C. L. Drake, The Geology of Continental Margins: New York, Springer-Verlag, p. 695–721.
Bishop, E. W., 1956, Geology and groundwater resources of Highlands County, Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Rept. Inv. 15.
Bogli, A., J. C. Schmid (translator), 1980, Karst hydrology and physical speleology: Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 284 p.
Brakensiek, D. L., H. S. Osborn, and W. J. Rawls, 1979, Field manual for research in agricultural hydrology: Science and Education Administration United States Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No. 224, 547 p.
Bretz, J. H., 1956, Caves of Missouri: Missouri Geological Survey and Water Resources, 490 p.
Burdon, D. J., 1954, Geological features of the Barada Valley in relation to the proposed storage reservoirs: Technical FAO United Nations Report No. 337 to the Government of Syria.
Burdon, D.J., 1959, The groundwater resources of the Damascus Basin—A preliminary report: Department of Irrigation and Hydraulic Power, Ministry of Public Works, Government of Syria, 19 p.
Burdon, D.J., 1961, Groundwater development and conservation in Syria; Expanded Technical Assistance Plan Rept. No. 1270: FAO, United Nations, Rome, 84 p.
Burdon, D.J., and C. Safadi, 1963, Ras-El-Ain (the great karst spring of Mesopotamia): Jour. Hydrology, vol. 7, no. 1.
Bredehoeft, J. E., and G. F. Pinder, 1968, Application of a digital computer for aquifer evaluation: Water Resources Research, v. 4, no. 5, p. 1069–1093.
Cherry, R. N., J. W. Stewart, and J. A. Mann, 1970, General hydrology of the Middle-Gulf area, Florida: Florida Bureau of Geol. Rept. Inv. 56, 96 p.
Chouker, F., 1982, Report on: Hydrogeological & geophysical work on the wells of the reserve captation caisson of Figeh Spring: Vocational Unit for Hydro & Engineering Geophysics, Damascus University, Syria, 9 p.
Coleman, R. G., 1974, Geologic background of the Red Sea,in Burk, C. A., and Drake, C. L., The Geology of Continental Margins: New York, Springer-Verlag, p. 743–751.
Conseils Et Installations Informatiques, Republic Arabe Syrienne, 1978, Source Figeh, Resultats des mesures de 1975 a 1976: Republique Arabe Syrienne, Establissment Public des Eaux de Figeh, p. 1–225.
Desart, J. E., C. A. Pascale, and H. Trapp, Jr., 1977, Water resources inventory of northeast Florida: U.S. Geol. Survey Water Resources Inv. 77–84.
Deutsch, M., D. R. Wiesnet, and A. Rango, eds., 1981, Satellite hydrology, Fifth Annual William T. Pecora Memorial Symposium, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, June 10–15, 1979: American Water Resources Association, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 730 p.
Dilamarter, R. R., and S. C. Csallany, 1977, Hydrologic problems in karst regions: Western Kentucky University, 481 p.
Doyle, F. L, and others, 1975, Environmental geology, and hydrology Huntsville and Madison County, Alabama: Alabama Geol. Survey Atlas Ser. 8, 118 p.
Dubertret, L., 1949, Carte Geologique au 50,000e du Liban. Feuille de Zebdan; et Notice Explicative, Beyrouth.
Dunham, R. J., 1962, Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture.In W. E. Ham, ed., Classification of Carbonate Rocks—A Symposium, AAPG Memoir One: Am. Assoc. Petroleum Geologist, Tulsa, Okla., p. 108–121.
Ferguson, G. E., C. W. Lingham, S. K. Lovee, and R. O. Vernon, 1947, Springs of Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Bull. v. 31.
Ferris, J. G., D. B. Knowles, R. H. Brown, R. W. Stallman, 1962, Theory of aquifer tests: U.S. Geol. Survey Water-Supply Paper 1536-E, 73 p.
Fetter, J. W., Jr., 1980, Applied hydrogeology: Columbus, OH. Charles E. Merrill Publishing Company, Columbus, OH, 488 p.
Gartza, S., 1962, Recharge, discharge, and changes in groundwater storage in the Edward and associate limestones, San Antonio area, Texas, a progress report on studies, 1955–1959: Texas Water Comm. Bull. 6201.
Gartza, S., 1966, Groundwater resources of San Antonio area, Texas, a progress on studies: Texas Dept. Water Resources Rept. 34.
Gearhart-Owen Industries, Inc., 1975, Portable logging systems operator manual model 3200/3500 P.L.S.: Gear-hart-Owen Industries, Inc., Fort Worth, TX, p. 2-1 to 2-42.
Girdler, R. W., 1978, Comparison of the East African rift system and the Permian Oslo rift.in I. B. Rambert, and E. R. Newman, eds., Tectonics and geophysics of continental rifts: Boston, D. Reidel Publishing Co., p. 329–345.
Gospodaric, R., and P. Habic, 1976, Underground water tracing, investigations in Slovenia 1972–1975: Institute for Karst Research, Ljublijana, Yugoslavia, 309 p.
Grantham, R. G., and C. B. Sherwood, 1968, Chemical quality of waters of Broward County, Florida: Florida Geol. Surv. Rept. Inv. 51, 52 p.
Greene, F. C., and W. B. Howe, 1952, Geological section of Pennsylvanian rocks exposed in the Kansas City area: Missouri Bur. Geology and Mines, Info. Cir. No. 8.
Guyod, H., 1966, Interpretation of electric and gamma ray logs in water wells: The Well Log Analyst, Jan.–March 1966, reprinted by Gearhart-Owens, Fort Worth, TX, 16 p.
Guyton, W. F. & Assoc., 1979, Geohydrology of Comal, San Marcos, and Heuco Springs: Texas Dept. Water Resources, Rept. 235.
Haan, C. T., 1977, Statistical methods in hydrology: Ames, Iowa, IA State Univ. Press.
Ham, W. E., ed., 1962, Classification of carbonate rocks, a symposium, Denver, Colorado, April 27, 1961: The American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir 1, Tulsa, OK, 279 p.
Heath, R. C., and W. E. Clark, 1971, Potential yield of groundwater on the Fair Point Peninsula, Santa Rose County, Florida: Florida Geol. Sur. Rept. Inv. 7, 82 p.
Herak, M., and V. T. Stringfield, eds., 1972, Karst important regions of the northern hemisphere: Amsterdam, Elsevier Pub. Co., 551 p.
Huber, R. (SOGREAH), 1973, Etude hydrologique et hydrologique de la Source Figeh, Annexes de la, 10 inches.
Interpretation of Records of 1975 through 1978, vol. I, Text and vol. II, Annexes.
Jakucs, L., B. Balkay (translator), 1977, Morphogenetics of karst regions: variants of karst evolution: New York, Halsted Press-John Wiley & Sons, 284 p.
Johnson Division, UOP, Inc., 1975, Groundwater and wells: Saint Paul, Minnesota, Johnson Division, UOP, Inc., 440 p.
Kanaan, W., 1982, Calculation of stability of boreholes at the project Al Fije Spring.In Assessment of pilot development project 28 July 1982–8 August, 1982: Tuscaloosa, Alabama, P. E. LaMoreaux and Associates, p. 16–22.
Kaufman, M. I., 1967, Hydrologic effects of groundwater pumpage in the Peace and Alafia River Basins, Florida 1934–1965: Florida Geol. Survey Rept. Inv. 49, 32 p.
Klein, H., and J. E. Hull, 1978, Biscayne aquifer, southeast Florida: U.S. Geol. Survey Water-Resource Inv. 78-107, 52 p.
Klein, H., M. C. Schroeder, and W. F. Lichtler, 1964, Geology and groundwater resources of Glades and Henry Counties, Florida Geol. Survey Rept. Inv. 37.
Klein, H., and C. B. Sherwood, 1961, Hydrologic conditions in the vicinity of levee 30, northern Dade County, Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Rept. Inv. 24, 24 p.
LaMoreaux, P. E., 1979, Remote-sensing techniques and the detection of karst: Assoc. of Eng. Geol. vol. XVI, no. 3.
LaMoreaux, P. E. and Associates, 1982, Assessment of pilot development project report, 28 July–8 August, 1982, with a section on Calculation of stability of boreholes at the project Al-Fije Spring, by Walid Kanaan for Establissement Public des Eaux de Figeh: Tuscaloosa, AL, P. E. LaMoreaux and Associates, 22 p.
LaMoreaux, P. E., H. E. LeGrand, and V. T. Stringfield, 1975, Progress of knowledge about hydrology of carbonate terranes: Union Geol. Sci., Paris, ser. B., no. 3, p. 41–52.
LaMoreaux, P. E., and others, 1963, Stratigraphic and structural guides to the development of water wells and well fields in a limestone terrane: Internal. Assoc. Sci. Hydol. Comm. Subterranean Waters pub. no. 52, p. 363–375.
LaMoreaux and others, 1970, Hydrology of limestone terranes with annotated bibliography of carbonate rocks: Alabama Geol. Survey Bull. 94A, 242 p.
LaMoreaux and others, 1975, Hydrology of limestone terranes: Alabama Geol. Survey Bull. 94B, 168 p.
Lattman, L. H., and R. R. Parizek, 1964, Relationship between fracture traces and the occurrence of ground water in carbonate rocks: Jour. Hydrology, v. 2, p. 73–91.
Lee, W., 1913, The geology of the Rolla Quadrangle, vol. XII, second series: Missouri Bureau Geology and Mines.
LeGrand, H. E., V. T. Stringfield, and P. E. LaMoreaux, 1976, Karst hydrology and water resources (reprint).In Water Resources Publication: 46 p.
Lichtler, W. F., 1972, Appraisal of water resources in the east central Florida region: Florida Geol. Survey Rept. Inv. 61.
Livingston, P., A. N. Sayre, and W. N. White, 1936, Water resources of the Edwards Limestone in the San Antonio area, Texas, U.S. Geol. Survey Water-Supply Paper 773-B, p. 59–113.
Linsley, R. K., Jr., M. A. Kohler, and J. L. H. Paulhus, 1975, Hydrology for engineers: Tokyo, McGraw-Hill, 482 p.
Logatchev, N. A., 1978, Main features of evolution and magnetism of continental rift zones in the Cenozoic.in I. B. Ramberg, and E. R. Newman, eds., Tectonics and geophysics of continental rifts: Boston, D. Reidel Publishing Co., p. 351–366.
Lohman, S. W., 1979, Groundwater hydraulics: U.S. Geol. Survey Professional Paper 708, 70 p.
Marsh, O. T., 1962, Geology of Tertiary rocks in Escambia and Santa Rosa Counties, western Florida: U.S. Geol. Survey Prof. Paper 450-D, p. D59–D61.
Meinzer, O. E., 1923a, The occurrence of groundwater in the United States: U.S. Geol. Survey Water-Supply Paper 489, 321 p.
Milanovic, P. T., J. J. Buhac (translator), 1981, Karst hydrology: Littleton, CO, Water Resources Publications, 434 p.
Miske, A. F., 1982, Pumping from Ain Harouch and Side Spring during the hydrologic year 1981–1982: Technical report to Republic Arabe Syrienne, Establissment Public des Eaux de Figeh, 32 p.
Moore, J. D., and F. Hinkle, 1975, High-yield wells and springs along lineaments intercepted from ERTS Imagery (abs.): Abs. and Programs Internat. Congress on Karst Hydrology, p. 66.
Moser, P. H., and others, 1972, Environmental geology and hydrology, Madison County, Alabama, Maysville area: Alabama Geol. Survey Interim Report, 32 p.
Muller, D. A., and R. D. Price, 1979, Groundwater availability in Texas: Texas Dept. Water Resouces Rpt. 238.
Muskgrove, R. H., J. T. Barraclough, and R. G. Grantham, 1965, Interim report on the water resources of Escambia and Santa Rosa Counties, Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Rept. Inv. 40.
Navara, J. G., 1979, Atmosphere, weather and climate: London, W. B. Saunders Company, p. 422–424.
Nefedov, K. E., and T. A. Popova, V. S. Kothekar (translator), 1972, Deciphering of groundwater from aerial photographs: New Delhi, India, Amerind Publishing Co., Pvt. Ltd., 191 p.
Newton, J. G., 1976, Early detection and correction of sinkhole problems in Alabama, with preliminary evaluation of remote sensing applications: Alabama Highway Dept. HPR Report 76, 83 p.
Parker, G. G., 1951, Geologic and hydraulic factors in the perennial yield of the Biscayne aquifer: Am. Water Works Assoc. Jour., v. 43.
Picket, G. R., 1977, Resistivity, Radioactivity and Acoustic Logs.in L. W. LeRoy, D. O. LeRoy, and J. W. Raese, eds., Subsurface geology: Golden, CO, Colorado School of Mines Press., p. 304–333.
Pinder, G. F., 1970a, A digital model for aquifer evaluation: U.S. Geol. Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, Book 7, 18 p.
Pinder, G. F., 1970b, An iterative digital model for aquifer evaluation: U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Rept., 44 p.
Plumley, W. J., G. A. Risley, R. W. Graves, Jr., and M. E. Kaley, 1962, Energy index for limestone interpretation and classification of carbonate rocks—a symposium: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir One, p. 85–107.
Ponikarov, V. P., ed., A. V. Vinogradskey (translator), 1968, The geological map of Syria, scale 1:50,000, with explanatory notes: Minestry of Industry, Syriani Arab Republic, 120 p.
Powell, W. J., C. W. Copeland, and J. A. Drahovzal, 1970, Delineation of linear features and application to reservoir engineering using Apollo 9 multispecial photography: Alabama Geological Survey Info. Ser. 41, 37 p.
Powell, W. J., and P. E. LaMoreaux, A problem of subsidence in a limestone terrane at Columbiana, Alabama: Alabama Geol. Survey Cir. 56, 30 p.
Prickett, T. A., and C. G. Lonnquist, 1971, Selected digital computer techniques for groundwater resource evaluation: Illinois State Water Survey Bull. 55, 62 p.
Rees, R., and A. W. Buckner, 1980, Occurrence and quality of groundwater in the Edwards-Trinity (Plateau) Aquifer in the Trans-Pecos Region of Texas: Texas Dept. Water Resources Rept. 255.
Riggs, H. C., 1972, Low flow investigation: U.S. Geol. Survey Techniques of Water Resources Inv., Book 4.
Schlumberger, Limited, 1972, Principles, v. 1 of Log interpretation: New York, Schlumberger Limited, 112 p.
Schlumberger Limited, 1974, Applications, v. 2 of Log interpretation: New York, Schlumberger Limited, 116 p.
Schlumberger Limited, 1972, Charts, part of Log interpretations: New York, Schlumberger Limited, 92 p.
Schroeder, M. C., H. Klein, and N. D. Hoy, 1958, Biscayne Aquifer of Dade and Broward Counties, Florida: Florida Geol. Sur., Rept. Inv. 17, 56 p.
Sellards, E. H., 1908, The underground water supply of central Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Bull. v. 1.
Sarrano, A. (SOGREAH), 1973, Etude hydrologique et hydrogeologique de la Source Figeh, Annexe 11.
Smith, D. I., D. P. Drew, 1975, Limestones and caves of the Mendip Hills: Pub. by David and Charles, North Pomfret, Vermont, 424 p.
Smith, W. L., 1977, Remote-sensing application for mineral exploration: Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross, 391 p.
SOGREAH, Nouvelle Adduction D'Eau De Damas, September 1975, R. 11.558A.
SOGREAH, Rapport Final Swi U Etude Des Perimetres de Protection de Sources de Figeh et Boukein; March 1980; R. 33.0327.
SOGREAH, Rapport Sur Ces Travaux de leve' geologique detaille'—Gallerie Amenee. v. 1.
Soil Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture (1967), Snow survey and water supply forecasting, section 22 of SCS National Engineering Handbook: Soil Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture, 198 p.
Sonderegger, J. L., 1970, Hydrology of limestone terranes photogeologic investigations: Alabama Geol. Survey Bull. 94C.
Stringfield, V. T., 1976, Relation of surface water hydrology to the principal artesian aquifer in Florida and southern Georgia: U.S. Geol. Survey Prof. Paper 501-C, p. C164–C169.
Stringfield, V. T., 1966, Artesian water in Tertiary limestone in the southeastern states: U.S. Geol. Survey Prof. Paper 517.
Stringfield, V. T., and H. E. LeGrand, 1966, Hydrology of limestone terranes in the Coastal Plain of the southeastern United States: Geol. Soc. America Special Paper 93, 46 p.
Stringfield, V. T., H. E. LeGrand, and P. E. LaMoreaux, 1977, Hydrology of limestone terranes; development of karst and its effects on the permeability and circulation of water in carbonate rocks, with special reference to the southeastern states: Alabama Geol. Survey Bull. 94G, 68 p.
Sweeting, M. M., ed., 1973, Karst landforms: New York, Columbia University Press, 362 p.
Sweeting, M. M., 1981, Karst geomorphology, Benchmark Papers in Geology, v. 59: Stroudsburg, PA, Hutchison Ross Publishing Company, 427 p.
Texas Water Commission, 1959, Groundwater geology of Bexar County, Texas: Texas Water Comm. Bull. 5911.
Theis, C. V., 1935, Relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using groundwater storage: Am. Geophys. Union Trans., pt. 2, p. 519–524.
Thomas, G. E., 1961, Grouping of carbonate rocks into textural and porosity units for mapping purposes.In Wm. E. Ham, eds., Classification of carbonate rocks—a symposium: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir One, p. 193–225.
Tolson, J. S., and F. L. Doyle, eds., 1977, Karst hydrology, memoirs of the 12th Congress of the Internat. Assoc. Hydrogeologists: Univ. of Alabama Press in Huntsville, 578 p.
Trescott, P. C., 1973, Iterative digital model for aquifer evaluation: U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report, 63 p.
UNESCO, 1972, Glossary and multilingual equivalents of karst terms: FAO, Paris, 72 p.
Vardin, P. (SOGREAH), 1973, Etude hydrologique et hydrogeologique de la Source Figeh, Annexe 12.
Vernon, R. O., 1951, Geology of Citrus and Levy Counties, Florida: Florida Geol. Survey Bull. 33, 256 p.
Van Hinte, J. E., 1976, A cretaceous time scale: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletins, v. 60, no. 4, p. 498–516.
Walker, L. E., 1979, Occurrence, availability, and chemical quality of groundwater in the Edwards Plateau Region of Texas, Texas Dept. Water Resources Rept. 235.
Waltham, A. C., 1974, Limestones and caves of northwest England: Newton Abbott, Devon, England, David & Charles, 477 p.
Walton, W. C., 1970, Groundwater resource evaluation: New York, McGraw-Hill Book Company, 664 p.
Ward, R. C., 1974, Principles of hydrology: London, McGraw-Hill Book Co., (UK) Limited, 367 p.
Warren, W. M., 1974, Retention basin failures in carbonate terranes: U.S. Geol. Survey Water Resources Bull., v. 10, no. 1, p. 22–31.
Werran, M. A., 1944, Artesian water in southeastern Georgia, with special reference to the coastal area: Georgia Geol. Survey Bull. 49.
White, W. A., 1970, The geomorphology of the Florida Peninsula, Florida Geol. Survey Bull. 51, 164 p.
Wilson, J. L., 1975, Carbonate facies in geologic history: Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 471 p.
Windley, B. F., 1977, The evolving continents: New York, John Wiley & Sons, p. 225–295.
Yevjevich, V., ed., 1976, Karst hydrology and water resources, Proceedings of the U.S.—Yugoslavia Symposium, Dubrovnik, June 2–7, 1975: Fort Collins, CO, Water Resources Publications, v. 1 & 2, 873 p.
Yevjevich, V., ed., 1981, Karst water research needs: Littleton, CO, Water Resources Publications, 266 p.
Zarjanov, K. H., and others, 1968, The geologic map of Syria with explanatory notes: Syria Arab Republic, Dept. of Geology and Mineral Research, 120 p.
Zoetl, J. G., 1974, Karst hydrogeologie: Wien, Austria, Springer-Verlag, 291 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamoreaux, P.E., Hughes, T.H., Memon, B.A. et al. Hydrogeologic assessment—Figeh Spring, Damascus, Syria. Environ. Geol. Water Sci 13, 73–127 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01664696
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01664696