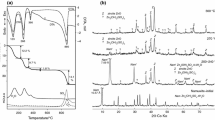
Abstract
The thermal decomposition of iron(II) sulphate heptahydrate was carried out in air under dynamic conditions in the presence of lithium, sodium, potassium and rubidium carbonates. The decomposition path in the presence of lithium carbonate differs from that in the presence of the other carbonates. In the presence of lithium carbonate, the heptahydrate loses all the water molecules before entering into reaction with the carbonate. The anhydrous sulphate then reacts with the carbonate, presumably to form iron(II) carbonate, which in turn undergoes decomposition — oxidation via magnetic oxide to ferric oxide. In the case of the other carbonates, iron(II) sulphate enters into reaction with the carbonate in question even before dehydration is complete, to form ferrous carbonate, which in turn reacts with the moisture still present to form green iron(II) hydroxide. This compound then undergoes decomposition — oxidation reactions via magnetic oxide to ferric oxide.
Zusammenfassung
Die thermische Zersetzung von Eisen(II)-sulfat-Heptahydrat wurde in Luft unter dynamischen Bedingungen in Gegenwart von Lithium-, Natrium-, Kalium und Rubidiumcarbonat ausgeführt. In Gegenwart von Lithiumcarbonat verläuft die Zersetzung auf einem anderen Wege als in Gegenwart der anderen untersuchten Carbonate. In Gegenwart von Lithiumcarbonat verliert das Heptahydrat alle Wassermoleküle, bevor es mit dem Carbonat in Reaktion tritt. Das wasserfreie Sulfat reagiert mit dem Carbonat vermutlich unter Bildung von Eisen(II)-carbonat, das oxydativ über Magnetit zu Eisen(III)-oxid zersetzt wird. Im Falle der anderen Carbonate tritt Eisen(II)-sulfat mit dem betreffenden Carbonat noch vor der völligen Beendigung der Dehydratation unter Bildung von Eisen(II)-carbonat in Reaktion, das daraufhin mit noch vorhandenem Wasser zu grünem Eisen(II)-hydroxid weiterreagiert. Diese Verbindung zersetzt sich oxydativ über Magnetit zu Eisen(III)-oxid
Резюме
В динамических услов иях и в атмосфере возд уха проведено термическ ое разложение гептагидрата сульфа та двухвалентного же леза в присутствии карбона тов лития, натрия, калия и рубиди я. Разложение сульфат а в присутствии карбона та лития отличается от разложения в прису тствии других карбон атов. В присутствии карбона та лития гептагидрат теряет все молекулы в оды перед тем как всту пить в реакцию с карбонато м. Безводный сульфат затем реагир ует с карбонатом, обра зуя главным образом карб онат двухвалентного железа, который подве ргается дальнейшему окислительно-восста новительному разложению до окиси т рехвалентного желез а через промежуточную стади ю образования магнитной окиси желе за. При наличии других карбонатов сульфат двухвалентн ого железа перед дегидратацией вступает в реакцию с к арбонатом, образуя карбонат дву хвалентного железа, который затем реагирует с находяще йся там влагой с образование м зеленой гидроокиси двухвалентного желе за. Это соединение подвергается реакци и разложения окислен ия через промежуточную стадию образования м агнитной окиси железа до конеч ного продукта окиси трехв алентного железа.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. S. R. Swamy, T. P. Prasad andB. R. Sant, J. Thermal Anal., 15 (1979) 307.
idem., ibid., 16 (1979) 471.
M. S. R. Swamy andT. P. Prasad, J. Thermal Anal., 19 (1980) 297.
N. Sh. Safiullin, E. B. Gitis andN. M. Panasenko, J. Appl. Chem. U.S.S.R., 42 (1969) 1843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors express their sincere thanks to Dr. B. R. Sant for his keen interest in this work and for his valuable suggestions. They also express their gratitude to Professor P. K. Jena, Director, for his permission to publish the results. One of us (MSRS) also thanks the Director for a Senior Fellowship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swamy, M.S.R., Prasad, T.P. Thermal decomposition of iron(II) sulphate heptahydrate in the presence of alkali metal carbonates. Journal of Thermal Analysis 25, 347–354 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01912959
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01912959