Abstract
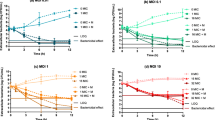
Intracellular penetration, accumulation and disposition are important parameters governing the activity of antibiotics against intracellular bacteria. Beta-lactams diffuse into but do not accumulate in phagocytes, probably because of their acidic character. Aminoglycosides are too polar to pass across membranes and are therefore only taken up slowly by endocytosis, which results in an exclusively lysosomal localization. Lincosaminides, macrolides and fluoroquinolones all accumulate in phagocytes, the two former classes of drugs showing both a cytosolic and a lysosomal localization. Fluoroquinolones appear to be entirely soluble in cells. Analysis of their activity in a model ofStaphylococcus aureus-infected J774 macrophages has revealed low activity of clindamycin, whereas macrolides, and even more so fluoroquinolones, easily reduce the original inoculum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moulder JW Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiological Reviews 1985, 49: 298–337.
Baillie AJ Intracellular infection and drug targeting. Pharmacy International 1984, 5: 168–172.
van den Broek PJ Antimicrobial drugs, microorganisms and phagocytes. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1989, 11: 213–245.
Tulkens PM: The design of antibiotics capable of an intracellular action: principles, problems and realizations. In: Buri, P. Gumma A (ed): Drug targeting. Elsevier, 1985, p. 179–193.
Bonventre PF, Imhoff JG Uptake of3H-dihydrostreptomycin by macrophages in culture. Infection and Immunity 1970, 2: 86–93.
Tulkens P, Trouet A The uptake and intracellular accumulation of aminoglycosides antibiotics in lysosomes of cultured fibroblasts. Biochemical Pharmacology 1978, 27: 415–424.
Tulkens PM Nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. Toxicology Letters 1989, 46: 107–123.
Aubert-Tulkens G, Van Hoof F, Tulkens P Gentamicin-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis in cultured rat fibroblasts. Laboratory Investigation 1979, 40:481–493.
Jacques P Endocytosis. In: Dingle JT, Fell HB (ed): Lysosomes in biology and pathology. Volume 2. North Holland, Amsterdam, 1969, p. 395–420.
Morin JP, Fillastre JP Aminoglycoside-induced lysosomal dysfunction in the kidney. In: Whelton A, Neu HC (ed): The aminoglycosides. Dekker, New York, 1982, p. 303–324.
Brown KN, Percival A Penetration of antimicrobials into tissue culture cells and leucocytes. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1978, 14, Supplement: 251–260.
Johnson JD, Hand WL, Francis JB, King-Thompson N, Corwin RW Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 1980, 95: 429–439.
Prokesh RC, Hand WL Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1982, 21: 373–380.
Forsgren A, Bellahsène A Antibiotic accumulation in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes and lymphocytes. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1985, 44, Supplement: 16–23.
Renard C, Vanderhaeghe HG, Claes PJ, Zenebergh A, Tulkens PM Influence of conversion of penicillin G into a basic derivative on its accumulation and subcellular localization in cultured macrophages. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1987, 31: 410–416.
Milne MD, Scribner BH, Crawford MA Non-ionic diffusion and the excretion of weak acids and bases. American Journal of Medicine 1958, 24: 709–729.
Waddell WJ, Bates RG Intracellular pH. Physiological Reviews 1969, 49: 285–329.
de Duve C, de Barsy Th, Poole B, Trouet A, Tulkens P, Van Hoof F Lysosomotropic agents. Biochemical Pharmacology 1974, 23:2495–2531.
Klempner MS, Styrt B Clindamycin uptake by human neutrophils. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1981, 144: 472–479.
Hand WL, King-Thompson NL, Steinberg TH Interactions of antibiotics and phagocytes. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1983, 12, Supplement C: 1–11.
Hand WL, Boozer RM, King-Thompson NL Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages of smokers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1985, 27: 42–45.
Martin JR, Johnson P, Miller MF Uptake, accumulation and egress of erythromycin by tissue culture cells of human origin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1985, 27: 314–319.
Carlier MB, Zenebergh A, Tulkens PM Cellular uptake and subcellular distribution of roxithromycin and crythromycin in phagocytic cells. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987, 20, Supplement B: 47–56.
Gladue RP, Bright GM, Isaacson RE, Newborg MF In vitro and in vivo uptake of azithromycin (CP-62, 993) in phagocytic cells: possible mechanism of delivery and release at sites of infection. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1989, 33: 277–282.
Easmon CSF, Crane JP Uptake of ciprofloxacin by macrophages. Journal of Clinical Pathology 1985, 38: 442–444.
Easmon CSF, Crane JP, Blowers A Effect of ciprofloxacin on intracellular organisms: in vitro and in vivo studies. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1986, 18, Supplement D: 43–48.
Trouet A, Tulkens P Intracellular penetration and distribution of antibiotics: the basis for an improved chemotherapy. In: Ninet L, Bost PE, Bouanchaud DH, Florent J (ed): The future of antibiotherapy and antibiotic research. Academic Press, London, 1981, p. 339–349.
Suter E Multiplication of tubercle bacilli within phagocytes cultivated in vitro, and effect of streptomycin and isonicotinic acid hydrazide. American Review of Tuberculosis 1952, 65: 775–776.
Mackaness GB, Smith N The bactericidal action of isoniazid, streptomycin and terramycin on extracellular and intracellular tubercle bacilli. American Journal of Tuberculosis 1953, 67: 322–340.
Mackaness GB The action of drugs on intracellular tubercle bacilli. Journal of Pathological Bacteriology 1952, 64: 429–446.
Jenkin C, Benacerraf B In vitro studies on the interaction between mouse peritoneal macrophages and strains ofSalmonella andEscherichia coli. Journal of Experimental Medicine 1960, 112: 403–417.
Chang YT Suppressive activity of streptomycin on the growth ofMycobacterium lepraemurium in macrophage cultures. Applied Microbiology 1969, 17: 750–754.
Horwitz MA, Silverstein SC Intracellular multiplication of legionnaires' disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampin. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1983, 71: 15–26.
Fitzgeorge RB, Gibson DH, Jepras R, Baskerville A Studies on ciprofloxacin therapy of experimental Legionnaires' disease. Journal of Infection 1985, 10: 194–203.
Vildé VL, Dournon E, Rajagopalan P Inhibition ofLegionella pneumophila multiplication within human macrophages by antimicrobial agents. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1986, 30: 743–748.
Sanchez MS, Ford CW, Yancey RJ Evaluation of antibacterial agents in a high-volume bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophilStaphylococcus aureus intracellular killing assay. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1986, 29: 634–638.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tulkens, P.M. Intracellular distribution and activity of antibiotics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 10, 100–106 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964420
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964420