Abstract
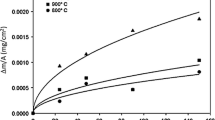
Several commercially available Ni-base superalloys were exposed isothermally in air at temperatures between 750° and 1000°C and also under cyclic conditions at 1000°C. The kinetics of oxidation were determined and the scales were analyzed by electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Thin adherent chromia-rich scales formed on the alloys at 750°C after 1000 hr. Although Waspaloy showed the lowest weight gain in this test, it also showed the deepest internal corrosion due to oxidation of the grain-boundary carbides. At temperatures up to 1000°C the external scales were also chromia-rich but there was greater internal corrosion. Titanium in the alloys oxidized, diffusing through the chromia scale to form faceted rutile (TiO2) grains at the surface as well as forming TiO2 and TiN internally. The amount of rutile at the oxide surface increased with temperature and alloy Ti concentration. Alumina formed as discrete internal oxides below the chromia scale, although Astroloy when oxidized isothermally at 1000°C developed a semicontinuous internal layer of alumina due to its higher Al content. Under cyclic conditions Astroloy formed a thicker, less-protective scale of transition oxides probably due to its lower Cr content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. L. Smialek and G. H. Meier, inSuperalloys II, C. T. Sims, N. S. Stoloff, and W. C. Hagel, eds. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987), chap. 11, High-Temperature Oxidation, p. 293.
C. S. Tedmon,J. Electrochem. Soc. 113, 766 (1966).
R. Prescott and M. J. Graham,Oxid. Met. 38, 233 (1992).
C. S. Giggins and F. S. Pettit,Trans. TMS AIME 245, 2495 (1969).
G. M. Ecer and G. H. Meier,Oxid. Met. 13, 119 (1979).
C. S. Giggins and F. S. Pettit,J. Electrochem. Soc. 118, 1782 (1971).
F. Abe, H. Araki, H. Yoshida, and M. Okada,Oxid. Met. 27, 21 (1987).
J. Litz, A. Rahmel, and M. Schorr,Oxid. Met. 30, 95 (1988).
J. Litz, A. Rahmel, M. Schorr, and J. Weiss,Oxid. Met. 32, 167 (1989).
N. Hussain, K. A. Shahid, I. H. Khan, and S. Rahman, Oxid. Met.41, 251 (1994).
F.-R. Chien and R. Brown,J. Mat. Sci. 27, 1514 (1992).
J. H. Chen, Thesis of Certificate of Post Graduate Studies at the Dept. of Materials Sci. and Met., University of Cambridge, June (1994).
M. Legall, A. M. Huntz, B. Lesage, C. Monty, and J. Bernardini,J. Mat. Sci. 30, 201 (1995).
K. P. Lillerud and P. Kofstad,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127, 2397 (1980).
J. Unnam, R. N. Shenoy, and R. K. Clark,Oxid. Met. 26, 231 (1986).
W. C. Hagel and A. U. Seybolt,J. Electrochem. Soc. 108, 1146 (1961).
D. R. Gaskell, inIntroduction to Metallurgical Thermodynamics (McGraw-Hill International Book Company, 1981), p. 287.
G. Y. Lai, inHigh-Temperature Corrosion of Engineering Alloys (ASM International, 1990), chap. 5, p. 73.
R. Mevrel,Mat. Sci. and Technol. 3, 531 (1987).
H. E. Evans and R. C. Lobb,Corr. Sci.,24, 209 (1984).
C. E. Lowell, J. L. Smialek, and C. A. Barrett, in High Temperature Corrosion, R. A. Rapp, ed. (San Diego, Cal., March 2–6, 1981), p. 219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J.H., Rogers, P.M. & Little, J.A. Oxidation behavior of several chromia-forming commercial nickel-base superalloys. Oxid Met 47, 381–410 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02134783
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02134783