Summary
In a field experiment initiated at the Central Soil Salinity Research Institute, Karnal in 1974 involving rice wheat cropping sequence and NPK fertilizer use on sodic soil (pH 9.2, ESP 32.0), an attempt was made to evaluate the available P and K status of the soil and their uptake by the crops during 1982–83 and 83–84.
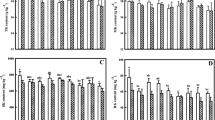
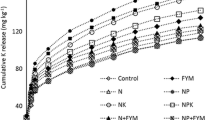
Application of P to either or both the crops significantly enhanced the yields of rice and improved available P status of the soil. Wheat yields remained unaffected. Fertilizer N reduced P content in rice but increased P uptake in crops and considerably brought down available P to a level (4.5 ppm) where rice plants showed reduced tillering and phosphorus deficiency. Application of K did not affect the yield of either crop but enhanced its available status in soil and uptake by the crops. Contribution of the non-exchangeable K towards total potassium removal was about 93% in the absence of applied K which decreased to 87% with the use of K. Application of K to both crops resulted in lesser uptake from non-exchangeable form as compared to its application to either crop. Laboratory studies carried out on soils of the experimental plots showed that cumulative K release measured after five successive extractions was higher in K-treated soils as compared to untreated ones. The major difference was only in the first extraction representing the exchangeable K after which release became independent of the available K of the soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chhillar R K and Swarup A 1984 Effect of continuous cropping and fertilizer use on soil properties and yields of rice and wheat in sodic soil. Indian J. agric. Sci. 54, 461–466.
Cooke G W, Mattingley G E G and Williams P J B 1958 Changes in the soil of long continued field experiment at Saxmundham, Suffolk. J. Soil Sci. 9, 298–305.
Goswami N N and Banerjee N K 1978 Phosphorus, potassium and other macro elements.In Soils and Rice. International Rice Resaerch Institute, Manila, Philippines. pp 561–580.
Jackson M L 1967 Soil Chemical Analysis, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.
Krishnamoorthy C H and Venkateswarlu 1976 Nutrient availability, concepts and relationships.In Soil Fertility — Theory and Practice. Ed J S Kanwar. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi pp 68.
Lutz J A Jr and Jones G D 1971 Crop yields and available P and K in soil as affected by sixteen annual application of N, P and K fertilizers. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 19 269–274.
Olsen S R, Cole C V, Watanabe F S and Dean L A 1954 Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Circ. 939, US Dept. Agric.
Powell R D and Webb J R 1974 Effects of high rates of fertilizer N, P and K on corn (Zea mays L.). Leaf nutrient concentrations. Commun. Soil Sci. Pl. Anal. 5, 93–104.
Singh D and Ghosh A B 1984 Removal of non-exchangeable potassium through intensive cropping in greenhouse study with alluvial soils. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci 32, 303–308.
Swarup A and Ghosh A B 1978 Effect of intensive fertilizer use based on soil tests on the available potassium status in soil and potassium content of crops. India J. Agron. 23 289–294.
Swarup A and Ghosh A B 1979 Effect of intensive cropping and manuring on soil properties and crop yields. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 49, 938–944.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swarup, A., Chhillar, R.K. Build up and depletion of soil phosphorus and potassium and their uptake by rice and wheat in a long-term field experiment. Plant Soil 91, 161–170 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181784
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181784