Abstract
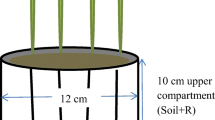
32P labelled fertilizers were used to measure native soil and fresh fertilizer phosphorus uptake byLolium perenne L. in greenhouse experiments. The P source evaluation was carried out for multiple rates of application for a standard P fertilizer (DAP) on low and medium soil P levels and for North Carolina rock phosphate (RP) at the medium soil P level only. At the low soil P level, the native P uptake increase was independent of P-DAP applied, and represented 19% of the nil P uptake. At the medium soil P level, the variability of the native soil as a nutrient P source depended on the phosphate fertilizer applied, and the rate of application. Consequently the amount of total P uptake could conceal differences in P fertilizer evaluations as the nutrient P source. Fresh P uptake increased linearly with the rates of P applied as standard or tested P fertilizer. The comparison of various P sources by means of fresh P uptake ratio (i.e. fresh P uptake from tested phosphate divided by fresh P uptake from standard phosphate) was independent of the rate of application. It was therefore suggested that various phosphorus sources be evaluated by measuring the fresh P uptake for a single rate of application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afnor 1982 Recueil de normes francaises. Matières fertilisantes et supports de culture. Alnor, Paris, 409 p.
Black C A and Scott C O 1956 Fertilizer evaluation: I. Fundamental principles. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 20, 176–179.
Bolland M D A and Bowden J W 1984 The initial and residual value for subterranean clover of phosphorus from crandallite rock phosphates, apatite rock phosphates and superphosphate. Fert. Res. 5, 295–307.
Bolland M D A and Gilkes R J 1987 How effective are calciphos and Phospal. Fert. Res. 12, 229–239.
Bouldin D R and Black C A 1960 Fertilizer evaluation. IV. Use of32P labeled fertilizers. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 24, 491–496.
Caldwell A C, Hustrulid A, Hammers F L and MacGregor J M 1954 The absorption of phosphorus from radioactive phosphate fertilizers applied to established meadows. I. Effect of source, rate and time of application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 18, 440–443.
Chien S H and Hammond L L 1978 A comparison of various laboratory methods for predicting the agronomic potential of phosphate rocks for direct application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 935–939.
Dean L A, Nelson W L, MacKenzie A J, Armiger W H and Hill W L 1947 Application of radioactive tracer technique to studies of phosphatic fertilizer utilization by crops. I. Greenhouse experiments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 12, 107–112.
Fardeau J C et Guiraud G 1972 Phosphore assimilable du sol et des engrais déterminé par la méthode de dilution isotopique. Phosphore et Agric. 60, 23–30.
Fardeau J C, Migadel F, Malja S et Gjermani A 1984 Efficacité d'un phosphate à faible teneur dans quelques sols d'Albanie. mesurée au moyen de32P.In Actes du 3ème Congrès International sur les Composés Phosphorés. pp 519–532 Imphos, Casablanca, Maroc.
Ghosh A K and Gilkes R J 1987 The initial and residual agronomic effectiveness of some Indian, USA and Australian Rock Phosphate. Fert. Res. 12, 201–218.
Hammond L L, Chien S H and Easterwood G W 1986 Agronomic effectiveness of Bayovar phosphate rock in soil with induced phosphorus retention. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 1601–1606.
John M K 1970 Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in soil and platn material with ascorbic acid. Soil Sci. 109, 214–220.
Krantz B A, Nelson W L, Welch C D and Hall N S 1949 A comparison of phosphorus utilization by crops. Soil Sci. 68. 171–177.
Kucey R M N and Bole J B 1984 Availability of phosphorus in moderatly and weakly acidic soils as determined by32P dilution, A value, and total P uptake methods. Soil Sci. 138, 180–188.
Morel Ch et Fardeau J C 1988 Détermination par tracage isotopique de la valeur fertilisante du phosphate aluminocalcique: comparaison avec d'autres formes. Agronomie 8, 47–54.
Nelson W L, Krantz B A, Colwell W E, Woltz W G, Hawkins A, Dean L A,MacKenzie A J and Rubins E J 1947 Application of radioactive tracer technique to studies of phosphatic fertilizer utilization by crops. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 12, 113–118.
Olsen S R, Cole C V, Watanabe F S and Dean L A 1954 Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circ. No939.
Smierzchalska K 1965 use of neutron irradiated phosphorus fertilizers in studies of their effectiveness.In Isotopes and Radiations in Soil-Plant Nutrition Studies. pp 471–479. Proc. Symp. Ankara, IAEA/FAO.
Spinks J W T and Barber S A 1948 Study of fertilizer uptake using radioactive phosphorus II. Sci. Agri. 28, 79–87.
Stelly M and Morris H D 1953 Residual effect of phosphorus on cotton on cecil soil as determined with radioactive phosphorus. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 17, 267–269.
Terman G L, Bouldin D R and Webb J R 1962 Evaluation of fertilizers by biological methods. Adv. Agron. 14, 265–319.
Terman G L and Allen S E 1969 Fertilizer and soil P uptake by maize, as affected by soil P level, granule size and solubility of phosphates sources. J. Agric. Sci. Camb. 73, 417–424.
Terman G L and Allen S E 1970 Fertilizer and soil P uptake by paddy rice as affected by soil P level, source and date of application. J. Agric. Sci. Camb., 75, 547–552.
Terman G L and Engelstad O P 1976 Agronomic Evaluation of Fertilizers: Principles and Practices. Bull. Y-21. TVA. Muscle Shoals, Alabama.
Welch C D, Hall N S and Nelson W L 1949 Utilization of fertilizer and soil phosphorus by soybeans. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 13, 231–235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morel, C., Fardeau, J.C. Native soil and fresh fertilizer phosphorus uptake as affected by rate of application and P fertilizers. Plant Soil 115, 123–128 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220702
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220702