Abstract
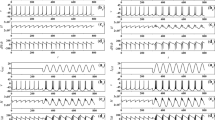
A new mathematical model to simulate the extracellular ECA (electrical control activity) of the human stomach by computer is proposed in the paper. In this model the ECA is generated by the electrical potential produced by an annular band polarised by electric dipoles and moving distally from the mid-corpus to the terminal antrum. The model is consistent with the function of the stomach and reproduces all the morphological characteristics (waveform, amplitude, duration, frequency) of the gastric ECA as obtained by experimentsin vivo. It is easy to simulate by computer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Couturier, D., Roze, C., Paolaggi, J. andDebray, C. (1972) Electrical activity of the normal human stomach.Am. J. Dig. Dis.,17, 969–976.
Diamont, N. E., Rose, P. K. andDavison, E. J. (1970) Computer simulating of intestinal slow-wave frequency gradient.,17, 299–310.
Johnson, L. R. L. (1981)Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. Raven Press, New York, 393–410.
Kelly, K. A., Coke, C. F. andElveback, L. E. (1969) Pattern of canine gastric activity.Am. J. Physiol.,217, 461–469.
Linkens, D. A. andDatardina, S. P. (1977) Frequency entrainment of coupled Hodgkin-Huxley type oscillators for modelling gastrointestinal electrical activity.IEEE Trans.,BME-24, 362–365.
Linkens, S. A. (1980) Electronic modelling of slow-waves and spike-activity in intestinal tissue.,BME-27, 351–357.
Milenov, K. (1968) On the rhythm of the electric and motor activities in intact stomachs and after transverse resections.Izv. Inst. Fisiol. (Sofia),11, 79–86.
Monges, H. andSalducci, J. (1969) Etude électromyographique de la motricité gastrique chez l’homme normal.Arch. Fr. Mal. App. Digestif,58, 517–530.
Nelsen, T. S. andBecker, J. C. (1968) Simulation of the electrical and mechanical gradient of the small intestine.Am. J. Physiol.,214, 749–757.
Sarna, S. K., Bowes, K. L. andDaniel, E. E. (1976) Gastric pacemakers.Gastroenterology,70, 226–231.
Sarna, S. K., Daniel, E. E. andKingma, Y. J. (1972) Simulation of the electric activity of the stomach by an array of relaxation oscillators.Am. J. Dig. Dis.,17, 299–310.
Smout, A. J. M., van der Schee, E. J. andGrashuis, J. L. (1980) What is measured in electrogastrography?,25, 179–187
Weber, J. andKohatsu, S. (1970) Pacesetter localiztion and electrical conduction patterns in the canine stomach.Gastroenterology,59, 717–726.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirizzi, N., Stella, R. & Scafoglieri, U. A model of extracellular waveshape of the gastric electrical activity. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 23, 33–37 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02444024
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02444024