Abstract
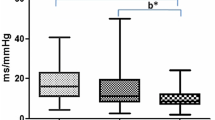
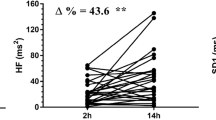
Our aim was to develop a signal analysis method for revealing interrelationships between heart rate and blood pressure and for displaying the influence of autonomic nervous control on these signals in a chronic lamb model. A chronically instrumented neonatal lamb model was made to record ECG and direct arterial blood pressure (N=15). Continuous two-minute recordings of blood pressure (BP) and ECG were digitised. The instantaneous heart rate signal (IHR) was derived from the ECG. The IHR and BP signals were bandpass filtered. Autospectra, cross-spectra, coherence spectra and phase spectra for the signals were computed to study the relative magnitudes and inter-relationships of the cardiovascular signals under normal conditions and during beta-adrenergic blockade. It was noted that both in the BP and IHR there were oscillations at the frequency of <0·1 Hz and also at the respiratory rate around 0·6 Hz. Beta-blockade reduced the oscillations of the IHR in <30-day-old lambs. It did not affect the coherence spectra or the phase lag between the signals. During quiet sleep the variability of blood pressure was decreased. In over-30-day-old-lambs the beta-blockade did not affect the variabilities of the cardiovascular parameters. These findings indicate that in neonatal lambs the sympathetic control system is a major regulator of cardiovascular interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akselrod, S., Gordon, D., Ubel, F. A., Shannon, D. C., Barger, A. C. andCohen, R. J. (1981) Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control.Science,213, 220–222.
Akselrod, S., Gordon, D., Madwed, J. B., Snidman, N. C., Shannon, D. C. andCohen, R. J. (1985) Hemodynamic regulation: investigation by spectral analysis.Am. J. Physiol.,249, H867-H875.
Bainbridge, F. A. (1920) The relation between respiration and the pulse rate.J. Physiol.,54, 192–202.
Berson, A. S. (1970) Analog-to-digital conversion for medicine. InClinical electrocardiography and computers.Caceres, C. A. (Ed.), New York 21–35.
Clement, D. L., de Pue, N., Jordaens, L. J. andPacket, L. (1985) Adrenergic and vagal influences on blood pressure variability.Clin. Exp. Hypertens. (A),7, (2–3), 159–166.
Dawes, G. S., Johnston, B. M. andWalker, D. W. (1980) Relationship of arterial blood pressure and heart rate in fetal newborn and adult sheep.J. Physiol.,309, 405–417.
de Boer, R. W., Karemaker, J. M. andStrackee, J. (1985) Relationships between short-term blood-pressure fluctuations and heart-rate variability in resting subjects I: a spectral analysis approach.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,23, 352–358.
Downing, S. E., Talner, N. S., Campbell, G. H., Hollborn, K. M. andWay, H. B. (1969) Influence of sympathetic nerve stimulation on ventricular function in the newborn lamb.Circ. Res.,25, 417–418.
Fiser, B., Honzikova, N. andPenaz, J. (1978) Power spectra of spontaneous variations of indirectly recorded blood pressure, heart rate and acral blood flow.Automedica,2, 143–147.
Grönlund, J., Metsäla, T., Antila, K., Oja, R., Halkola, L., Siimes, A. andVälimaki, I. (1985) Quantification of interrelations between heart rate, respiration, and arterial blood pressure by cross-spectral analysis in neonatal lambs. Proc. XIV ICMBE and VII ICMP,Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,23, Suppl., Part 1, 509–510.
Hyndman, B. W., Kitney, R. I. andSayers, B. McA. (1971) Spontaneous rhythms in physiological control systems.Nature,233, 339–341.
Jenkins, G. M. andWatts, D. G. (1969)Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden-Day, San Francisco, USA.
Jones, J. V. andSleight, P. (1981) Reflex control of the circulation in hypertensive humans. InDisturbances in neurogenic control of the circulation. American Physiological Society, USA, 161–175.
Kitney, R. I. (1979) A nonlinear model for studying oscillations in the blood pressure system.J. Biomed. Eng.,2, 89–99.
Kitney, R. I., Linkens, D., Selman, A. andMcDonald, A. (1982) The interaction between heart rate and respiration: Part II—Nonlinear analysis based on computer modelling.Automedica,4, 141–153.
Langhorst, P., Schultz, B., Lambertz, M., Schultz, G. andCamerer, H. (1980) Dynamic characteristics of the ‘unspecific brain stem system’. InCentral interaction between respiratory and cardiovascular control systems.Koepchen, H. P., Hilton, S. M. andTrzebski, A. (Eds.), Springer, Berlin, 30–41.
Lindqvist, A., Oja, R., Hellman, O. andVälimäki, I. A. T. (1983) Impact of thermal vasomotor control on the heart rate variability of newborn infants.Early Human Dev.,8, 37–47.
Macy, J. (1965) Analog-digital conversion systems. InComputers in biomedical research, vol. 2.Stacy, R. W. andWadman, B. D. (Eds.), Academic Press, New York, 3–34.
Mancia, G., Ferrari, A., Gregorini, L., Parati, G., Pomidossi, G., Bertinieri, G., Grassi, G., di Rienzo, M., Pedotti, A. andZanchetti, A. (1983) Blood pressure and heart rate variabilities in normotensive and hypertensive human beings.Circ. Res.,53, 96–104.
Prechtl, H. F. R. (1974) The behavioral states of the newborn infant.Brain Res.,76, 185–212.
Rabiner, L. B. andGold, B. (1975)Theory and application of digital signal processing. Prentice-Hall Inc., USA, 356–435.
Rabiner, L. B., McGonegal, C. A. andPaul, D. (1979) FIR windowed filter design program—WINDOW. InPrograms for digital signal processing. Digital Signal Processing Committee (Ed.), IEEE Press, New York, 5.2–00052.
Sayers, B. (1973) Analysis of heart rate variability.Ergonomics,16, 17–32.
Sayers, B. McA. (1980) Signal analysis of heart rate variability. InThe study of heart rate variability.Kitney, R. I., Rompelman, O. (Eds), Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Scher, A. M. andYoung, A. C. (1963) Servoanalysis of carotid sinus reflex effects on peripheral resistance.Circ. Res.,12, 152–156.
Siimes, A. S. I., Välimaki, I. A. T., Sarajas, H. S. S., Sakone, K. andOja, R. T. (1984) Heart rate variation in relation to age and sleep state in neonatal lambs.Acta Physiol. Scand., Suppl. 537, 7–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grönlund, J.U., Antila, K.J., Siimes, A.S.I. et al. Beta-adrenergic control and inter-relationships between heart rate and blood pressure in neonatal lambs. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 27, 163–170 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446226
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446226