Abstract
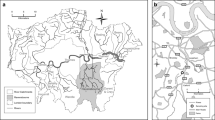
Bed sediments were collected from the entire region of the Ganges basin and some parts of the Brahmaputra. In addition, selected stations were sampled for suspended sediments as well. The samples were analysed for a number of heavy metals (Fe, Mn, Ni, Cr, Cu, and Zn) by the thin-film energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence technique. There are pronounced temporal and spatial variations in the heavy metals distributions. Suspended sediments are 5–10 times richer than the bed sediments. None of the tributaries contribute significant heavy metal load, but around urban areas in Yamuna (tributary of Ganges), very high levels due to the distribution from the drainage network are observed. Compared to the Brahmaputra, the distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in the Ganges sediments are more erratic and highly variable. All the metals considered show high correlation among themselves. Given the high flux of suspended sediments from the Himalayan rivers (nearly 20% of the global flux), the worldwide budget for heavy metal transport may need to be suitably revised.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Flanagan, F. J., 1973, 1972 values for international geochemical reference samples. Geochim. et. Cosmochim. Acta v. 37, p. 1189–1198.
Forstner, U., and G. T. W. Wittmann, 1981, Metal pollution in the aquatic environment; Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 486 p.
Garrels, R. M., F. T. Mackenzie, and C. Hunt, 1975, Chemical cycles and the global environment—assessing human influences: CA, William Kaufman Co. 206 p.
Gibbs, R. J., 1977, Transport phases of transition metals in the Amazon and Yukon Rivers. Geol. Soc. Am. Bul., v. 88, p. 829–843.
Martin, J. M. and M. Meybeck, 1979, Elemental mass balance of material carried by major world rivers: Mar Chem., v. 7, p. 173–206.
Martin, J., G. Kulbicki, and A. J. Degroot, 1973, Terrigenous supply of radioactive and trace elements to the oceans. Hydrogeochem., v. 1, p. 463–483, Clarke and Co., N.Y.
Millimann, J. D., and R. H. Meade, 1983, World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. Jour. Geol., v. 91, p. 1–21.
Ramamoorthy, S., and B. R. Rust, 1978, Heavy metal exchange processes in sediment-water systems. Env. Geol., v. 2, p. 165–172.
Sarin, M. M., D. V. Borole, and S. Krishnaswami, 1979, Geochemistry and geochrology of sediments from Bay of Bengal and equatorial Indian oceans: Proc. Ind. Ac. Sc., v. 88A, p. 131–154.
Singh, S. K., and V. Subramanian, 1984, Hydrous Fe and Mn oxides-scavengers of heavy metals in the aquatic environment: CRC-Critical Review. Envt. Control, v. 14, p. 13–69.
Subramanian, V., 1978, Input by Indian rivers into the world oceans: Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci., v. 87A, p. 77–78.
Subramanian, V., R. Sitaswad, and L. U. Joshi, 1985a, Rate of sedimentation in Jamuna river around Delhi using Pb210-Ra226 method: Journ. Radio. Analytical Chem., v. 90, p. 271–276
Subramanian, V., L. Van't dack, and R. Van Grieken, 1985b, Chemical composition of river sediments from the Indian subcontinent: Chem. Geol. v. 48, p. 271–279.
Subramanian, V., J. Richey, and N. Abbas, 1985c, Preliminary studies on the distribution of organic C and N in Ganges and Brahmaputra particulates.In E. Degens, ed., River transport of mineral and carbon Hamburg, Univ. Hamburg Press, v 3, p. 513–518.
Trefry, J. H., and B. J. Presley, 1976, Heavy metal transport from the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico.In H. L. Windom and R. A. Duce, eds. Marine pollutant transfer: Lexington, Mass., Lexington Books, p. 39–76.
Van Dyck, P. M., and R. E. Van Grieken, 1980, Absorption correction via scattered radiation in energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis for samples of variable composition and thickness: Anal. Chem. v. 52, p. 1859–1864.
Van Grieken, R. E., L. Van't dack, Costa Dantes, and H. De Silveira Dantes, 1979, Soil analysis by thin-film energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence: Anal. Chim. Acta., v. 108, p. 93–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramanian, V., Van Grieken, R. & Van't Dack, L. Heavy metals distribution in the sediments of ganges and Brahmaputra rivers. Environ. Geol. Water Sci 9, 93–103 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02449940
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02449940