Abstract
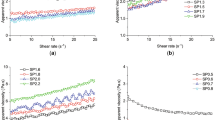
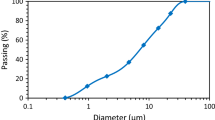
Shear stress and shear rate data obtained for cement pastes were correlated by means of different rheological models. Pastes were prepared from a commercial Portland cement 325 at different water/cement ratios ranging from 0.34 to 0.42. Tests were performed at 25°C using a rotating coaxial cylinder viscometer. The investigation was accomplished by means of a hysteresis-cycles procedure. On the basis of the goodness of fit, the Herschel-Bulkley model seemed to be very effective for application to cement pastes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ivanov, Ya., ‘Rheology of cement pastes’,Univ. Trieste, Fac. Ing., Ist. Chim. Appl. Ind., No. 111 (1981) pp. 1–67.
Lapasin, R., ‘Rheology of cement pastes’,Il Cemento 79 (4) (1982) p. 243.
Tattersall, G.H. and Banfill, P.F.G.,The Rheology of Fresh Concrete (Pitman, London, 1983) 254–304.
Lapasin, R., Papo, A. and Rajgelj, S., ‘Flow behaviour of fresh cement pastes. A comparison of different rheological instruments and techniques’,Cem. Concr. Res. 13 (3) (1983) p. 349.
Caufin, B. and Papo, A., ‘Rheological behaviour of fresh cement pastes’,Zement Kalk Gips,37 (12) (1984) p. 656.
Lapasin, R., Papo, A. and Rajgelj, S., ‘The phenomenological description of the thixotropic behaviour of fresh cement pastes’,Rheol. Acta 22 (4) (1983) 410.
Cheng, D.C.-H. and Evans, F., ‘Phenomenological characterization of the rheological behaviour of inelastic reversible thixotropic and anti-thixotropic fluids’,Br. J. Appl. Phys. 16 (1965) 1036.
Caufin, B. and Papo, A., ‘The influence of the hydration process on the rheology of cement pastes’,Zement Kalk Gips 39 (7) (1986) p. 389.
Eyring, H., ‘Viscosity, plasticity and diffusion as examples of absolute reaction rates’,J. Chem. Phys. 4 (1936) 283.
Atzeni, C., Massidda, L. and Sanna, U., ‘Comparison between rheological models for Portlant cement pastes’,Cem. Concr. Res. 15 (3) (1985) 511.
Casson, N.,Rheology of Dispersed Systems (Pergamon, London, 1959) 84–104.
Herschel, W.H. and Bulkley, R., ‘Measurement of consistency as applied to rubber-benzene solutions’,Proc. ASTM 26 (1926) 621.
Jones, T.E.R. and Taylor, S., ‘A mathematical model for the flow curve of cement paste’,Mag. Concr. Res. 29 (1977) 207.
Williamson, R.V., ‘The flow of pseudoplastic materials’,ind. Eng. Chem. 21 (1929) 108.
Vom Berg, W., ‘On the flow behaviour of cement pastes. Influence of the granulometric composition of cement and of the concentration of solids’,Mag. Concr. Res. 31 (1979) 211.
Sisko, A.W., ‘The flow of lubricating greases’,Ind. Eng. Chem. 50 (1958) 1036.
Robertson, R.E. and Stiff, H.A., ‘An improved mathematic model for relating shear rate in drilling fluids and cement slurries’,Soc. Petr. Eng. J. 16 (1976) 31.
Shangraw, R., Grim, W. and Mattocks, A.M., ‘An equation for non-Newtonian flow’,Trans. Soc. Rheol. 5 (1961) 247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papo, A. Rheological models for cement pastes. Materials and Structures 21, 41–46 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472527
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472527