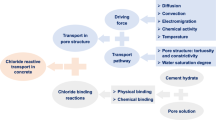
Abstract
A numerical model has been developed to simulate the transport of several ionic species across a saturated concrete or mortar sample. The chloride binding as well as the electrical coupling between the different ionic fluxes are included in the model by using the Nernst-Planck system of equations. This model highlights which parameters affect substantially chloride penetration into reinforced concrete structures and then shows that the use of Fick’s first law in a predictive model for chloride penetration is strongly challenged. The simulations are in good agreement with diffusion-cell experiments and membrane potential measurements.
Résumé
Un modèle numérique a été développé afin de simuler le transport de plusieurs espèces ioniques dans une éprouvette de béton ou de mortier saturée. La fixation des ions chlorures ainsi que le champ électrique créé par les divers flux ioniques sont modélisés à l’aide d’un système d’équations de Nernst-Planck. Le modèle permet, premièrement, de mettre en évidence les paramètres qui influencent le plus la pénétration des ions chlorures et, deuxièmement, il montre que l’utilisation de la 1e loi de Fick dans un modèle de prédiction de la pénétration des ions chlorures est fortement remise en cause. Les résultats sont en accord avec les expériences de diffusion et les mesures expérimentales du potentiel de membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nilsson, L. O., Poulsen, E., Sandberg, P. and Sørensen, H. E., ‘Chloride penetration into concrete—State-of-the-art’, HETEK Report No. 53, (Danish Road Directorate, 1996).
Marchand, J., Gérard, B. and Delagrave, A., ‘Ion Transport Mechanisms in Cement-Based Materials’, Report GCS-95-07, (Dept. of Civil Eng.—University of Laval, Quebec, 1995).
Boddy, A., Bentz, E., Thomas, M. D. A. and Hooton, R. D., ‘An overview and sensitivity study of a multimechanistic chloride transport model’,Cement and Concrete Research 29 (6) (1999) 827–837.
Clifton, R., ‘Predicting the service life of concrete’,ACI Materials Journal 90 (6) (1993) 611–617.
Bigas, J. P., ‘La diffusion des ions chlore dans les mortiers’, PhD Thesis (in French), Génie civil—INSA, Toulouse, (1994).
Achari, G., Chatterji, S. and Joshi, R. C. ‘Evidence of the concentration dependent ionic diffusivity through saturated porous media’, in RILEM International Workshop—Chloride penetration into concrete, (St Rémy-les-Chevreuses, 1995) 74–76.
Chatterji, S., ‘Transportation of ions through cement-based materials. 3. Experimental-evidence for the basic equations and some important deductions’,Cement and Concrete Research 24 (7) (1994) 1229–1236.
Goto, S. and Roy, D. M., ‘Diffusion of ions through hardened cement pastes’,Cement and Concrete Research 11 (5/6) (1981) 751–757.
Ushiyama, H. and Goto, S., ‘Diffusion of various ions in hardened Portland cement pastes’, in 6th Intl. Cong. Chem. Cement, (Moscow, 1974) 331–337.
Tang, L., ‘Chloride transport in concrete—Measurement and prediction’, PhD Thesis, Building Materials—Chalmers, Gothenburg, (1996).
Zhang, J. Z. and Buenfeld, N. R., ‘Presence and possible implications of a membrane potential in concrete exposed to chloride solution’,Cement and Concrete Research 27 (6) (1997) 853–859.
Arsenault, J., ‘Étude des mécanismes de transport des ions chlore dans le béton en vue de la mise au point d’un essai de migration’, PhD Thesis (in French), Génie civil—INSA, Faculté des Sciences et de Génie, Toulouse, Laval, (1999).
Rubinstein, I., ‘Electro-diffusion of ions’, Edn. (SIAM Studies in Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, 1990).
Helfferich, F., ‘Ion exchange’, Edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1962).
Atkins, P. W., ‘Physical chemistry’, 6th Edn., (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1998).
Tang, L., ‘Concentration dependence of diffusion and migration of chloride ions. Part 2. Experimental evaluations’,Cement and Concrete Research 29 (9) (1999) 1469–1474.
Truc, O., Ollivier, J. P. and Nilsson, L. O., ‘Numerical simulation of multi-species transport through saturated concrete during a migration test—MsDiff Code’, Accepted for publication inCement and Concrete Research, (2000).
Masi, M., Colella, D., Radaelli, G. and Bertolini, L., ‘Simulation of chloride penetration in cement-based materials’,Cement and Concrete Research 27 (10) (1997) 1591–1601.
Ames, W. F., ‘Numerical methods for partial differential equations’, 2nd Edn. (Academic Press, New York, 1977).
Larsen, C. K., ‘Chloride binding in concrete—Effect of surrounding environment and concrete composition’, Structural engineering—NTNU, Trondheim, (1998).
Francy, O., ‘Modélisation de la pénétration des ions chlorures dans les mortiers partiellement saturés en eau’, PhD Thesis (in French), Génie civil—Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, (1998).
Schmidt, F. and Rostasy, F. S., ‘A method of calculation of the chemical composition of the concrete pore solution’,Cement and Concrete Research 23 (5) (1993) 1159–1168.
Diamond, S., ‘Effects of two Danish flyashes on alkali contents of pore solutions of cement-flyash pastes’,Cement and Concrete Research 11 (3) (1981) 383–394.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial Note Prof. Jean-Pierre Ollivier is a RILEM Senior Member. He works at the LMDC, a RILEM Titular Member and participates in RILEM TCs 170-CSH (The structure of C-S-H) and 178-TMC (Testing and modelling chloride penetration in concrete). Prof. Lars-Olof Nilsson is a RILEm Senior Member.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truc, O., Ollivier, J.P. & Nilsson, L.O. Numerical simulation of multi-species diffusion. Mat. Struct. 33, 566–573 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480537
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480537