Abstract
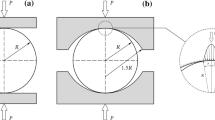
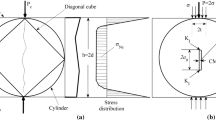
The effect of both size specimen and boundary conditions on the splitting tensile strength, determined from the Brazilian test, were studied experimentally. A total of 110 splitting tests of granite and mortar specimens were performed, using cylindrical and prismatic specimens of sizes between 17 mm and 300 mm. To analyze the effect of the boundary conditions, the specimens were tested with different widths of load bearing strip in the range of size recommended by the standards. The influence of the rupture mode (stable or unstable crack propagation) on the splitting tensile strength was also explored. The results of the tests were compared with the theoretical predictions obtained from a closed form analytical expression based on the cohesive crack model. The validity of the classical limit strength theory for larger size specimens was also analyzed. The results indicate that the splitting tensile strength depends strongly on specimen size and on the boundary conditions of the test. As the size of the specimen increases and the relative width of the bearing strip decreases, the splitting strength tends asymptotically to the minimum value coincident with the tensile strength. The dependence of the Brazilian test on the specimen size and boundary conditions closely follows the predictions of the cohesive crack model.
Résumé
L'influence de la taille et des conditions de bords sur la résistance mécanique à la traction indirecte (essai brésilien) ont été déterminés à partir des essais de compression diamétrale. On a essayé un total de 110 éprouvettes, en granite et en mortier. Les échantillons employés étaient prismatiques et cylindriques, de dimensions comprises entre 17 mm et 300 mm. Afin d'analyser l'effet des conditions d'essai, les échantillons ont été testés avec différentes largeurs d'appuis, dans l'intervalle conseillé par la norme. L'influence du mode de rupture (propagation stable ou instable) sur la résistance mécanique à la traction a été aussi testée. On a comparé les résultats des essais avec les prévisions théoriques obtenues moyennant une expression analytique fermée qui s'appuie sur le modèle de la fissure cohésive. La validité de l'approche de la contrainte limite a été analysée pour des éprouvettes de plus grande taille. Les résultats montrent que la résistance à la traction des éprouvettes est étrotement liée à la taille et aux conditions de l'essai. Quand la taille de l'éprouvette augmente et la largeur relative de l'appui diminue, la résistance atteint une limite qui correspond à la résistance à la traction. L'essai de compression indirecte (essai brésilien) dépend de la taille de l'éprouvette et des conditions de l'essai, en accord étroit avec les prévisions du modèle de la fissure cohésive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rocco, C., Guinea, G. V., Planas, J. and Elices, M., ‘Size effect and boundary conditions in the Brazilian test: theoretical analysis’,Mater. Struct. (Submited for publication), 1998.
Sabinis, G. M. and Mirza, S. M., ‘Size effects in model concrete's?’Journal of the Structural Division, ASCE 105 (ST6) (1979) 1007–1020.
Hasegawa, T., Shioya, T. and Okada, T., ‘Size effect on splitting tensile strength of concrete’, in Proceedings Japan Concrete Institute 7th Conference, June 1985, 309–312.
Kim, J. and Eo, S., ‘Size effect in concrete specimens with dissimilar initial cracks’,Magazine of Concrete Research 42 (1990) 233–238.
Bažant, Z. P., Kazemi, M. T., Hasegawa, T. and Mazars, J., ‘Size effect in Brazilian split-cylinder test: measurements and fracture analysis’,ACI Materials Journal 88 (3) (1991) 325–322.
Chen, W. F. and Yuan, R. L., ‘Tensile strength of concrete: the double punch tests’,Journal of the Structural Division ASCE 106 (ST8) (1980) 1673–1693.
Rocco, C., Guinea, G. V., Planas, J. and Elices, M., ‘Mechanisms of rupture in the Brazilian test’, to appear inACI Journal (1999).
ASTM C 496-85, ‘Standard Test Method for Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens’, Annual Book of ASTM Standards 4 (04. 02) (1986) 337–342.
RILEM Draft Recommendation, ‘Determination of fracture energy of mortar and concrete by means of three-point bend test on notched beams’,Mater. Struct. 18 (1985) 285–290.
Tada, H., Paris, P. and Irwin G., ‘The stress analysis of cracks handbook’, Del Research Corporation, St. Louis, Missouri (1985).
Guinea, G. V., Planas, J. and Elices, M., ‘A general bilinear fitting for the softening curve of concrete’,Mater. Struct. 27 (1994) 99–105.
Guinea, G. V., Planas, J. and Elices, M., ‘Measurement of the fracture energy using three-point bend test: Part 1-Influence of experimental procedures’,Mater. Struct. 25 (1992) 212–218
Planas, J., Elices, M. and Guinea, G. V., ‘Measurement of the fracture energy using three-point bend test: Part 2-Influence of bulk energy dissipation’, 305–312.
Elices, M., Guinea, G. V. and Planas, J., ‘Measurement of the fracture energy using three-point bend test: Part 3-Influence of cutting the P-δ tail’, 327–334.
Hillerborg, A., Modéer, M. and Petersson, P., ‘Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements’,Cement and Concrete Research 6 (1976) 773–782.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial Note Prof. M. Elices and Prof. J. Planas are RILEM Senior Members. Both participate in the work of RILEM Technical Committee QFS (Size effect and scaling of quasibrittle fracture) Prof. Elices also participates in RILEM TC 147-FMB (Fracture mechanics applications to anchorage and bond) and 148-SSC (Test methods for the strain softening response of concrete). Prof. G. Guinea is the 1994 Robert l'Hermite medallist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocco, C., Guinea, G.V., Planas, J. et al. Size effect and boundary conditions in the Brazilian test: Experimental verification. Mat. Struct. 32, 210–217 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481517
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481517