Summary
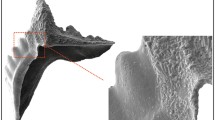
Scanning Electron Microscopy on conodonts from the Middle Triassic “Trochitenkalk” from Northwest Germany with CAI values ranging from 1 to 5 revealed structural alterations during progressive diagenesis. Conodonts with low CAI values of 1.5 already show syntaxial recrystallization of apatite on the conodont surface. Aggrading crystallization of the internal structure occurs in conodonts with CAI=5. The usually short-prismatic and blocky syntaxial crystallites become increasingly longer and an overall increase in crystallite size takes place. Conodonts from the telemagmatically heated sediments overlying the intrusive body of the Vlotho Massiv are often corroded, i.e., they have pocked, frosted to pitted surfaces with dolomite rhomb overgrowths, indicating contact with ascending dolomitizing brines.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Aldridge, R.J., Briggs, D.E.G., Clarkson, E.N.K. &Smith, M.P. (1986): The affinities of conodonts—New evidence from the Carboniferous of Edinburgh, Scotland.—Lethaia19, 279–291, 9 Figs, Oslo
Barnes, C.R. & Slack, D.J. (1975): Conodont ultrastructure: The subfamily Acanthodontine.—R. Ont. Mus. Life Sci. Contrib.105, 21 p.
Belka, Z. (1990): Thermal maturation and burial history from Conodont Color Alteration data, Holy Cross Mountains, Poland.—Cour. Forsch.-Inst. Senckenberg118, 241–251, 4 Figs, Frankfurt
Bender, P. & Königshof, P. (1994): Regional maturation patterns of the Devonian strata in the eastern Rheinisches Schiefergebirge (Lahn-Dill area) based on conodont colour alteration (CAI). —Cour. Forsch.-Inst. Senckenberg168,-WilliZiegler-Festschrift I-, 335–345, 6 Figs. Frankfurt
Brauckmann, F.J. (1984): Hochdiagenese im Muschelkalk der Massive von Bramsche und Vlotho.—Bochumer geol. u. geotechn. Arb.,14, 195p., 54 Figs., 45 Tables, Bochum
Bruckschen, P., Neuser, R.D. &Richter, D.K. (1990a): Cement Stratigraphy in Mesozoic Carbonates (mol, jox) of the Weserbergland (Early → Deep burial → Post-tectonic diagenesis). —TERRA Abstracts2, 37, Oxford (Blackwell)
Bruckschen, P., Nöth, S. &Richter, D.K. (1990b). Tempered microdolomites in crinoids: a new criterion for high-grade diagenesis.—Carbonates and Evaporites,5/2, 197–207, 9 Figs., 1 Table, Troy, New York
Budurov, K. &Stefanov, S. (1973): Etliche neue Plattformconodonten aus der Mitteltrias Bulgariens.—C.R. Acad. Bulg. Sci.26, 803–806, 1 Pl., Sofia
Buggisch, W. (1986): Diagenese und Anchimetamorphose auf grund der Conodontenfarbe (CAI) und “Illitkristallinität” (IC). Methodische Untersuchungen und Daten zum Oberdevon der Dillmulde (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge).—Geol. Jb. Hessen114, 181–200, 2 Pls., 6 Figs., Wiesbaden
Burnett, R.D. (1988): Physical and chemical changes in conodonts from contact-metamorphosed limestones.—Irish J. Earth Sci.9, 79–119, 7 Pls., 23 Figs. Dublin
Dean, M.T. (1992): Conodont colour maturation indices for the Carboniferous of west-central Scotland.—In:Parnell, J. (ed.) Basins on the Atlantic Seaboard: Petroleum Geology, Sedimentology and Basin Evolution. 3–21, Spec. Publ., Geol. Soc., London62, London
Deaton, B.C., Nestell, M. &Balsam, W.L. (1996): Spectral Reflectance of Conodonts: A Step Toward Quantitative Color Alteration and Thermal Maturity Indexes.—AAPG Bull.80/7, 999–1007, Tulsa, Oklahoma
Deutloff, O., Teichmüller, R., Teichmüller, M. &Wolf, M. (1980): Inkohlungsuntersuchungen im Mesozoikum des Massivs von Vlotho (Niedersächsisches Tektogen).—N. Jb. Geol. Paläont. Mh.1980/6, 321–341, 4 Figs., 3 Tables, Stuttgart
Epstein, A.G., Epstein, J.B. & Harris, L.D. (1977): Conodont color alteration—an index to organic metamorphism.—U.S. Geol. Surv., Prof. Pap.995, 27p., 20 Figs., 1 Table, Washington
Fuchs, A. (1989): Zur Bestimmung der Versenkungstemperatur im Ordovizium Thüringens und Skandinaviens mit Hilfe der Conodontenfarbe.—N. Jb. Geol. Paläont. Mh.1989/7, 390–399, 3 Figs., Stuttgart
Helsen, S. (1994): Micromorphological changes in Pridolian Lochkovian conodonts from the lowgrade metamorphised Naux Limestone (Ardennes, France).—Bull. de la Soc. belge de Geol.T103/1–2, 205–217, 4 Pls., 1 Fig., 1 Table, Liege
Helsen, S. &Königshof, P. (1994): Conodont thermal alteration patterns in Palaeozoic rocks from Belgium, northern France and western Germany.—Geol. Mag.31/3, 369–386, 6 Figs., London
Gawlick, H.J. &Königshof, P. (1993): Diagenese, niedrig- und mittelgradige Metamorphose in den südlichen Salzburger Kalkalpen. Paläotemperaturabschätzungen auf der Grundlage von Conodont-Color-Alteration-Index (CAI) Daten.—Jb. Geol. Bundesanst. Wien136/1, 39–48, Wien
Harris, A.G., Harris, L.D. & Epstein, J.B. (1978): Oil and gas from Palaeozoic rocks in the Appalachian Basin: maps for assessing hydrocarbon potential and thermal maturity (conodont color alteration isograd and overburden isopachs).— U.S. Geol. Surv. Misc. Invest. Ser., MapI-917-E scale 1∶250000, Washington DC
Harris, A.G., Rexroad, C.B., Lierman, R.T. &Askin, R.A. (1990): Evaluation of a CA1 anomaly, Putnam County, Central Indiana, USA: Possibility of a Mississippian Valley-type hydrothermal system.—Cour. Forsch.-Inst. Senckenberg,118, 253–266, 4 Figs., 2 Tables, Frankfurt
Janssen, Ch., Friedel, C.-H. &Paech, H.-J. (1988): Zur Schieferung in devonischen Riffkarbonaten.—Z. geol. Wiss.16/2, 721–737, 5 Pls., 3 Figs., Berlin
Jeppsson, L. (1979): Conodont element function.—Lethaia12, 153–171. 10 Figs., 1 Table, Oslo
Jeppsson, L., Fredholm, D. &Mattiasson, B. (1985): Acetec acid and phosphatic fossils—a warning.—J. Palaeont.59/4, 952–956, 2 Figs., Tulsa/Oklahoma
Königshof, P. (1992): Der Farbänderungsindex von Conodonten (CAI) in paläozioschen Gesteinen (Mitteldevon bis Unterkarbon) des Rheinischen Schiefergebirges—eine Ergänzung zur Vitrinitreflexion.—Cour. Forsch.-Inst. Senckenberg146, 118p, 9Pls., 29 Figs. 5 Tables. Frankfurt
Königshof, P. & Werner, R. (1994): Zur Bestimmung der Versenkungstemperaturen im Devon der Eifeler Kalkmulden-Zone mit Hilfe der Conodontenfarbe.—Cour. Forsch.-Inst. Senckenberg168,—Willi Ziegler-Festschrift I-,255–265, 1 Pl., 2 Figs., 1 Table, Frankfurt
Kovacs, S. &Arkai, P. (1987): Conodont alteration in metamorphosed limestones from northern Hungary, and its relationship to carbonate texture, illite crystallinity and vitrinite reflectance.—In:Austin, R.L. (ed.), Conodonts: Investigative Techniques and Applications. British Micropalaeont. Soc. Ser., 209–229, 5 Pls., 1 Fig., 3 Tables. Chichester (Ellis Horwood)
Kozur, H. (1971): Die Eunicida und Phyllodocida des Mesozoikums. —Freiberger Forsch. HefteC 267, 73–89, 15 Pls., Leipzig
Kozur, H. (1972): Die Conodontengattung Metapolygnathus und ihr stratigraphischer Wert.—Geol. Paläont. Mitt., Innsbruck2, 37p., 7 Pls., 1 Table, Innsbruck
Lindström, M. &Ziegler, W. (1971): Feinstrukturelle Untersuchungen an Conodonten. 1. Die Überfamilie Panderodontacea.—Geol. Palaeontol.5, 9–33, 6 Figs., 8 Tables, Marburg/L.
Mayr, U., Uyeno, T.T. &Barnes, Ch.P. (1978): Subsurface stratigraphy, conodont zonation, and organic metamorphism of the Palaeozoic succession, Bjorne Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, District of Franklin.—Geol. Surv. Can. Pap.F78/1A, 393–398, 2 Figs., Calgary
Mundry, E. (1971): Der Temperaturverlauf im Dach des Bramscher Massivs nach der Wärmeleitungstheorie.—Fortschr. Geol. Rheinld. u. Westf.18, 539–546, 5 Figs., Krefeld
Nöth, S. (1991): Die Conodontendiagenese als Inkohlungsparameter und ein Vergleich unterschiedlich sensitiver Diagenese-indikatoren am Beispiel von Triassedimenten Nord- und Mitteldeutschlands.—Bochumer geol. u. geotech. Arb.37, 169p, 3 Pls., 46 Figs., 14 Tables, Bochum
Nöth, S., Bruckschen, P. &Richter, D.K. (1991): Conodont color alteration and microdolomie composition—implications to the Muschelkalk limestones (Upper Triassic) overlying the Upper Cretaceous intrusive body of the Vlotho Massif (Weserbergland, Northwest Germany), Geologie en Mijnbouw70, 265–273. 8 Figs., Amsterdam
Nöth, S. &Richter, D.K. (1992): Infrared spectroscopy of Trassic conodonts: a new tool of assessing conodont diagenesis. —Terra Nova4, 668–675 9 Figs., 1 Table, Oxford
Nowlan, G.S. &Barnes, N.E.S. (1987): Application of conodont color alteration indices to regional and economic geology:— In:Austin, R.L. (ed.) Conodonts: Investigative Techniques and Applications, British Micropalaeont. Soc. Ser., 188–202, 1 Pl., 2 Figs., Chichester (Ellis Horwood)
Piftzner, H., Vahl, J., Werner, H. &Ziegler, W. (1968): Zur chemischen Zusammensetzung und Mikromorphologie der Conodonten.—Palaeontographica. Abt. A,128, 115–152 10 Pls., 10 Figs., 8 Tables, Stuttgart
Raven, J.G.M. &Van der Pluijm, B.A. (1986): Metamorphic fluids and transtension in the Cantabrian Mountains of northern Spain: an application of the conodont color alteration index.—Geol. Mag.123, 673–681, London
Rejebian, V.A., Harris, A.G. &Huebner, J.S. (1987): Conodont colour and textural alteration: An index to regional metamorphism, contact metamorphism and hydrothermal alteration.— Geol. Soc. of Amer. Bull.99/4, 471–497. 4 Figs., 2 Tables, Boulder/Colorado
Sansom, I.J., Smith, M.P., Armstrong, H.A. &Smith, M.M. (1994): Dentine in conodonts.—Nature368, 591
Schönlaub, H.P., Flajs, G. &Thallmann, F. (1980): Conodontenstratigraphie am Steierischen Erzberg (Nördliche Grauwackenzone).—Jb. Geol. Bundesanst.123/1, 169–229, 7 Pls., 11 Figs., Wien
Stadler, G. &Teichmüller, R. (1971): Zusammenfassender Überblick über die Entwicklung des Bramscher Massivs und des Niedersächsischen Tektogens.—Fortschr. Geol. Rheinld. u. Westf.18, 547–564, 1 Pl., 3 Figs., Krefeld
Winter, J. (1977): “Stabile” Spurenelemente als Leit-Indikatoren einertephrostratigraphischen Korrelation (Grenzbereich Unter-/Mitteldevon, Eifel-Belgien).—Newsl. Stratigr.,6/3, 152–170, 4 Pls., 5 Figs., Berlin, Stuttgart
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nöth, S. Conodont color (CAI) versus microcrystalline and textural changes in upper triassic conodonts from Northwest Germany. Facies 38, 165–173 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02537363
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02537363