Summary
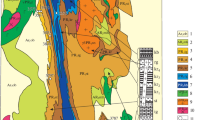
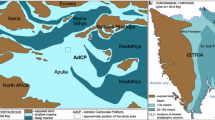
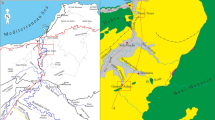
An extensive carbonate platform of predominately Middle Miocene age (Marmarica Formation) occupies the larger part of the northern plateau of the Western Desert of Egypt. The Marmarica Formation (up to 150m thick) exposed on the cliffs facing the Mediterranean coast consists mainly of alternating limestones and dolostones. Deposition took place in a shallow and normal marine environment. The limestones are dominated by algal boundstone, crossbedded packstone and bioturbated wackestone facies. The occurrence of the crossbedded packstone facies throughout the Marmarica Formation indicates that a shallow marine environment prevailed.
Lithification of the precursor carbonates took place mainly in a meteoric environment. Replacement dolomitization ranged from fabric destructive to retentative and from fabric selective to pervasive. The presence of an abundant open marine fauna, the lack of evaporites, coupled with the contents of Sr and Na suggests that dolomitization took place in solutions more dilute than normal sea water.
The limestone and dolostone facies cannot be separated into distinct types based on their major or trace element chemistry. Only Mn and Sr seem to be facially controlled. Both elements are particularly enriched in the lagoonal facies compared with the organic buildup facies. The difference in the Mn content is attributed to their proximity to continental areas at the time of deposition. The differences in Sr values are interpreted by an originally differing mineralogy (calcite versus aragonite) and different rates of diagenesis. Dolomitization did not appear to influence the Mn content as substantially as the Sr content. The amount of the acid insoluble residue is controlled by the distribution of Si, Ti, Al, Fe, k, Rb and Zr.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annoscia, E. (1969): The bryofauna of Mesomiocenic Al Jaghbub Formation in Eastern Cyrenaica (Libya).—Proc. 3rd African Micropal. Colloq. 37–97, 2 Pls., 4 Figs., Cairo
Badiozamani, K. (1973): The Dorag dolomitization model-application to the Middle Ordvician of Wisconsin.—J. Sed. Petrol.43/4, 965–984, 14 Figs., 5 Tables, Tulsa
Bathurst, R.G.C. (1975): Carbonate sediments and their diagenesis 2nd ed., 658 p., 359 Figs., 25 Tables, Amsterdam, (Elsevier)
Bencini, A. &Turi, A. (1974): Mn distribution in the Mesozoic carbonate rocks from Lima Valley, Northern Apennies.—J. Sed. Petrol.44/3, 774–782, 2 Figs., 3 Tables, Tulsa
Brand, U. &Veizer, J. (1980): Chemical diagenesis of multicomponent carbonate system-1 trace elements.—J. Sed. Petrol.,50/4, 1219–1236, 13 Figs., 5 Tables, Tulsa
Coniglio, M., James, N.P. &Aissaoui, D.M. (1988): Dolomitiztion of Miocene carbonates, Gulf of Suez, Egypt.—J. Sed. Petrol.58/1, 100–119, 16 Figs., 2 Tables, Tulsa
Cosgrove, M.E. &Sulaiman, M.A. (1973): A rapid method for the determination of quartz in sedimentary rocks by X-ray diffraction incorporating mass absorption correction.—Clay Minerals,10, 51–55, 1 Fig., 1 Table, London
Dunham, R.J. (1962): Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional textures.—InW.E. Ham (ed.) Classification of Carbonate Rocks a symposium.—Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. Memoir1, 108–121, 7 Pls, Tulsa
El-Shahat, A. &West, I.M. (1983): Early and late lithification of aragonitic bivalve beds in the Purbeck Formation (Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous) of Southern England.—Sediment. Geol.35, 15–41, 8 Figs., 3 Tables, Amsterdam
El-Shazli, M.M., El-Fayoumi, I.F. &Misak, R.F. (1974): Stratigraphic microfacies of the geological succession in El Dabaa-Ras El Hekma area ‘Western Mediterranean Coast, Egypt’.—Mans. Sci. Bull.4, 149–168, 10 Pls, 10 Figs., El-Mansoura
Flügel, E. (1982) Microfacies analysis of limestone.—663 p., 53 Pls., 78 Figs., 58 Tables, Berlin (Springer)
Folk, R.L. &Land, L.S. (1975): Mg/Ca ratio and salinity, two controls over crystallization of dolomite.—Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. Bull.59/1, 60–68, 2 Figs., Tulsa
Friedman, G.M. (1965): Terminology of crystallization textures and fabrics in sedimentary rocks.—J. Sed. Petrol.35/3, 643–655, 11 Figs., Tulsa
Gindy, A.R. (1971): The stratigraphic succession of the exposed coastal Miocene sediments north of Salum town, its diagenesis and correlation with that of the Siwa depression, Western Desert of Egypt.—Proc. Egypt. Acad. Sci. (For 1970).23, 9–28, 2 Pls. 2 Figs., 3 Tables, Cairo
— (1987): The relative diagenetic order of preservation of skeletal structures in fossil debris of a Miocene coquina near Salum, Egypt.—N. Jb. Paläont. Mh.1987/1, 27–42, 5 Figs., 2 Tables, Stuttgart
Gindy, A.R. &El-Askary, M.A. (1969): Stratigraphy, structure and origin of Siwa depression, Western Desert of Egypt.—Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. Bull.53/3, 603–625, 9 Figs., Tulsa
Heckel, P.H. (1974): Carbonate buildups in the geologic record: A review. In: L. F. Laporte (Ed.) Reefs in time and space.—Soc. Econ. Paleontol. Mineral. Spec. Publ.18, 90–154, 9 Figs., 1 Tables, Tulsa.
Hsü, K.J., Ryan, W.B.F. &Cita, M.B. (1973): Late Miocene desiccation of the Mediterranean.—Nature,242, 239–243, London
Ismail, M.M. &Selim, A.A. (1969): Stratigraphy of the Salum area, Western Desert.—Bull. Fac. Sci. Alexandria Univ.9, 309–330, 19 Figs., Alexandria, Egypt
Ismail, M.M., Salim, A.A. &Taha, A.A. (1977): Matruh-Barrani carbonate sediments petrography and diagenesis.—Bull. Fac. Sci., K.A. University,1, 145–160, 1 Pl., 2 Figs., 3 Tables, Jedda, Saudi Arabia
Kinsman, D. J.J. (1969): Interpretation of Sr2+ concentrations in carbonate minerals and rocks.—J. Sed. Petrol.39/2 486–508, 4 Figs., Tulsa
Land, L.S. (1970): Phreatic versus vodose meteoric diagenesis of limestones: evidence from a fossil water table.—Sedimentology,14, 175–185, 6 Figs., 2 Tables, Amsterdam
— (1973): Holocene meteoric dolomitization of Pleistocene limestones, North Jamica.—Sedimentology,20, 411–424, 3 Figs., 7 Tables, Amsterdam
Land, L.S. &Hoops, G.K. (1973): Sodium in carbonate sediments and rocks: a possible index to the salinity of diagenetic solutions.—J. Sed. Petrol.43/3, 614–617, 4 Tables, Tulsa
Longman, M.W. (1980): Carbonate diagenetic textures from nearsurface diagenetic environments.—Bull. Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. Bull.64/4, 461–487, 18 Figs., Tulsa
Matthews, R.K. (1967): Diagenetic fabrics in biosparites from the Pleistocene of Barbados, West Indies.—J. Sed. Petrol.37/4, 1147–1153, 10 Figs., Tulsa
Qing, H. &Mountjoy, E.W. (1989): Multistage dolomitization in Rainbow Buildups, Middle Devonian Keg River Formation, Alberta, Canada.—J. Sed. Petrol.59/1, 114–126, 18 Figs., 2 Tables, Tulsa
Randazzo, A.F. &Zachos, L.G. (1984): Classification and description of dolomite fabrics of rocks from the Floridan aquifer, U.S.A..—Sed. Geol.37/3, 151–162, 8 Figs., 1 Table, Amsterdam
Said, R. (1962): The geology of Egypt.—377 p., 17 Pls., 71 Figs., 17 Tables, Amsterdam, Elsevier
Salem, R. (1976): Evolution of Eocene-Miocene sedimentation patterns in parts of northern Egypt.—Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. Bull.60, 34–64, 19 Figs., Tulsa
Sarkar, S.;Bhattacharyya, A. &Chanda, S.K. (1980): Recognition of hardgrounds and emersion surfaces: a new criterion.—J. Sed. Petrol.50/1, 83–89, 7 Figs., Tulsa
Selim, A.A. (1977): Diagenesis of the Middle Miocene limestones of the Salum area, Western Desert, Egypt.—Bull. Fac. Sci. K.A. University.1, 129–144, 3 Pls., 1 Fig., 1 Table, Jedda
Steinen, R.P. (1974): Phreatic and vadose diagenetic modification of Pleistocene limestone: petrographic observations from subsurface of Barbados, West Indies.—Am. Ass. Petrol. Geol. Bull.58/6, 1008–1024, 19 Figs., 2 Tables, Tulsa
Steinen, R.P. &Matthews, R.K. (1973): Phreatic vs. vadose diagenesis stratigraphy and mineralogy of a cored borehole on Barbados, W.I..—J. Sed. Petrol.43/4, 1012–1020, 2 Figs., 1 Table, Tulsa
Stoffers, P.;Summerhayes, C.P. &Dominik, J. (1980): Recent pelletoidal carbonate sediments off Alexandria, Egypt.—Marine Geol.34, M1-M8, 3 Figs., 2 Tables, Amsterdam
Tennant, C.B. &Berger, R.W. (1957): X-ray determination of dolomite-calcite ratio of carbonate rocks.—Am. Mineral.42, 23–29
Turekian, K.K. &Wedepohl, K.H. (1961): Distribution of the elements in some major rock units of the earth's crust.—Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer.,72/2, 175–192, 1 Table, New York
Veizer, J. (1976): Diagenesis of pre-Quaternary carbonates as indicated by tracer studies.—J. Sed. Petrol.47/2, 565–581, 13 Figs., Tulsa
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Shahat, A. Middle Miocene carbonates from the Northern Plateau of the Western Desert (Egypt): Petrography and geochemistry. Facies 28, 67–76 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539728
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539728