Abstract
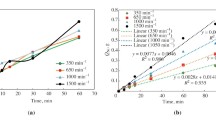
Iron cylinders with molybdenum capped ends are rotated at speeds of 260, 570, and 835 rpm in liquid copper and Cu-Fe alloys maintained at 1220°, 1300°C, and 1370°C under argon at 1 atm pressure. The dependence of the dissolution rate of the cylinders on the concentration of iron in the bulk liquid is observed. The solution-rate constants defined by an approximate form of the Berthoud equation vary from 7 × 10-3 to 30 × 10-3 cm.s-1. There is a linear relation between the logarithm of the rate constant and the reciprocal of absolute temperature for each rotational speed. The rate constant is found to vary with the 0.85 to the 0.96 power of the Reynolds number in the range 6500 〈 Re 〈 22000. This suggests that the dissolution process is diffusion controlled. The dependence of the dissolution rate on the activity of iron in the bulk liquid is observed. Oxygen increases markedly the dissolution rate, whereas sulfur does not.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. G. Ward and J. W. Taylor:J. Inst. Metals, 1957, vol. 86, pp. 36–42.
J. M. Lommel and B. Chalmers:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1959, vol. 215, pp. 499- 508.
J. K. Jackson and R. E. Grace:Physical Chemistry of Process Metallurgy, part 1, pp. 633–44, Interscience Publishers, New York, 1961.
D. A. Stevenson and J. Wulff:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1961, vol. 221, pp. 279–85.
P. M. Shurygin and V. D. Shantarin:Phys. Met. Metallog., 1963, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 81–86.
F. W. Hinzner and D. A. Stevenson:J. Phys. Chem., 1963, vol. 67, pp. 2424- 29.
M. Miyake:Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1964, vol. 28, pp. 111–16.
R. G. Olsson, V. Koump, and T. F. Perzak:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1965, vol. 233, pp. 1654–57.
R. G. Olsson, V. Koump, and T. F. Perzak:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 426–29.
M. Kosaka and S. Minowa:Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1967, vol. 53, pp. 1467–77.
T. F. Kassner:J. Electrochem. Soc, 1967, vol. 114, no. 7, pp. 689–94.
W. D. Forgeng, Jr. and R. E. Grace:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 1249–52.
T. L. Sri Krishna, M. A. Dayananda, and R. E. Grace:Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 3355–59.
E. A. Moelwyn-Hughes:The Kinetics of Reactions in Solutions, 2nd ed., p. 374, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1947.
M. Eisenberg, C. W. Tobias, and C. R. Wilke:Chem. Eng. Progr., Symp. Ser., 1955, vol. 51, no. 16, pp. 1–16.
T. H. Chilton and A. P. Colburn:Ind. Eng. Chem., 1934, vol. 26, pp. 1183–87.
V. G. Levich:Physicochemical Hydrodynamics, p. 69, Prentice-Hall, New York, 1962.
L. S. Darken and R. W. Gurry:Physical Chemistry of Metals, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1953; a, p. 469; b, p. 462;c, p. 408.
J. P. Morris and G. R. Zellars:AIME Trans., 1956, vol. 206, pp. 1086–90.
R. Ohno:Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1969, vol. 33, pp. 1053–59.
R. Ohno:Trans. Japan Inst. Metals, 1970, vol. 11, pp. 195–99.
M. Hansen:Constitution of Binary Alloys, 2nd ed., p. 581, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1958.
T. Ejima and M. Kameda:Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1969, vol. 33, pp. 96- 103.
J. F. Elliott, M. Gleiser, and V. Ramakrishna:Thermochemistry for Steel- making, p. 640, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Cambridge, Mass., 1963.
L. S. Darken:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 80–89.
R. Hultgren, R. L. Orr, P. D. Anderson, and K. K. Kelley:Selected Values of Thermodynamic Properties of Metals and Alloys, p. 107, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1963.
K. Monma and H. Suto:Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1960, vol. 24, pp. 377–79.
K. Monma and H. Suto:Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi, 1960, vol. 24, pp. 374–77.
J. F. Elliott and M. Gleiser:Thermochemistry for Steelmaking, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Reading, Mass., 1960; a, p. 177; b, p. 178; c, p. 179; d, p. 245.
O. Kubaschewski and J. A. Catterall:Thermochemical Data of Alloys, p. 178, Pergamon Press, London, 1956.
H. H. Kellogg:Can. Met. Quart., 1969, vol. 8, pp. 3–23.
W. A. Fischer and D. Janke:Z. Metallkunde, 1971, vol. 62, pp. 747–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohno, R. Rates of dissolution of rotating iron cylinders in liquid copper and cu-fe alloys. Metall Trans 4, 909–915 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645588
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645588