Abstract
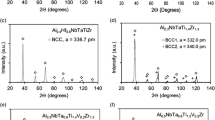
New high-strength, high-temperature Cu-Ni-Si alloys have been developed using additions of Cr, Zr, and/or Ti. These new alloys remain as precipitation hardenable as the base alloy, but the main strengthening phase may be different than Ni2Si (e.g., Cr2Ti). Substantial increases in mechanical strength were observed at both room and high temperature (773 K) when additions of Cr+Zr+Ti and Cr+Zr were made. Industrial testing of these alloys indicated a sevenfold increase in the lifetime of lateral blocks in continuous casting equipment of copper alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Tigeot,Revue de Metallurgie, Vol 64, 1967, p 773
J. Moisan and M. Perez,Revue de Metallurgie, Vol 77,1980, p 289
Z. Rdzawski and J. Stobrawa,Mater. Sci. Techn., Vol 9,1993, p 142
A. Popa, internal report, Metallurgical Research Institute, Bucha- rest, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Constantinescu, S., Popa, A., Groza, J.R. et al. New high-temperature copper alloys. JMEP 5, 695–698 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646904
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646904