Abstract
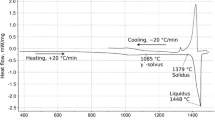
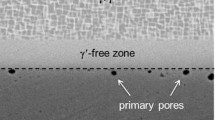
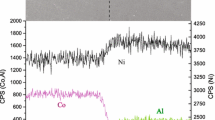
Interdiffusion in Ni-rich, Ni-Cr-Al diffusion couples was studied after annealing at 1100 and 1200 °C. Recession of γ′ (Ni3Al structure), β (NiAl structure), or α (bcc) phases was also measured. Aluminum and chromium concentration profiles were measured in the γ (fcc) phase for most of the diffusion couples. The amount and location of Kirkendall porosity suggests that Al diffuses more rapidly than Cr which diffuses more rapidly than Ni in the γ phase of Ni-Cr-Al alloys. The location of maxima and minima in the concentration profiles of several of the diffusion couples indicates that both cross-term diffusion coefficients for Cr and Al are positive and that DCrAl has a greater effect on the diffusion of Cr than does DA1Cr on the diffusion of Al. The γ/γ + β phase boundary has also been determined for 1200 °C through the use of numerous γ/γ+ β diffusion couples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Shankar, D.E. Koenig, and L.E. Dardi:J, Met., 1981, vol. 33, pp. 13–20.
D.K. Gupta and D. S. Duvall: inSuperalloys 1984, M. Gell, C. S. Kortovich, R.H. Bricknell, W.B. Kent, and J. F. Radavich, eds., TMS-AIME, New York, NY, 1984, pp. 711–20.
P. Tomaszewicz and G. R. Wallwork:Rev. High Temp. Mater., 1982, vol. 5, pp. 49–91.
M. A. Gedwill: NASA TM-81567, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, DC, 1980.
S. Stecura: NASA TM-86905, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, DC, 1985.
J.A. Nesbitt and R.W. Heckel:Thin Solid Films, 1984, vol. 119, pp. 281–90.
G. W. Goward: inSource Book on Materials for Elevated Temperature Applications, E. F. Bradley, ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1979, pp. 369-86.
G. W. Roper and D. P. Whittle:Met. Sci., 1980, vol. 14, pp. 21–28.
D. Tu: Ph.D. Dissertation, SUNY, Stony Brook, NY, 1982.
T. Yamamoto, T. Takashima, and K. Nishida:Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1980, vol. 21, pp. 601–08.
M.M.P. Janssen:Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 1623–33.
S. Shankar and L. L. Seigle:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 1467–76.
W. Gust, M. B. Hintz, A. Lodding, H. Odelius, and B. Predel:Phys. Stat. Sol. A, 1981, vol. 64, pp. 187–94.
R.A. Swalin and A. Martin:Trans. AIME, 1956, vol. 206, pp. 567–72.
Y.E. Ugaste:Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 1967, vol. 24, pp. 442–49.
A. Davin, V. Leroy, D. Coutsouradis, and L. Habraken:Mem. Sci. Rev. Metall., 1963, vol. 60, pp. 275–84.
A.V. Pawar and D.R. Tenney:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 2139–43.
J. A. Nesbitt and R. W. Heckel: NASA Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, OH, 1987, vol. 18A, pp. 2075-86.
C.A. Barrett and C. E. Lowell:Oxid. Met., 1977, vol. 11, pp. 199–223.
S.R. Levine:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 1237–50.
K. F. J. Heinrich, R. L. Myklebust, H. Yakowitz, and S. D. Rasberry: NBS Technical Note 719, National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, 1972.
J.A. Nesbitt: NASA TM-83738, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, DC, 1984.
M.A. Dayananda:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1851–58.
J.A. Nesbitt and R.W. Heckel: inHigh-Temperature Protective Coatings, S.C. Singhai, ed., TMS-AIME, New York, NY, 1982, pp. 75-91.
J. S. Kirkaldy: inAdvances in Materials Research, H. Herman, ed., Wiley, New York, NY, 1970, vol. 4, pp. 55–100.
J. S. Kirkaldy, D. Wichert, and Zia-Ul-Haq:Can. J. Physics, 1963, vol. 41, pp. 2166–73.
A. Taylor and R. W. Floyd:J. Inst. Met., 1952, vol. 81, pp. 451–64.
S. M. Merchant, M. R. Notis, and J. I. Goldstein: inMicrobeam Analysis 1984, A.D. Romig, Jr. and J.I. Goldstein, eds., San Francisco Press, San Francisco, CA, 1984, pp. 315–18.
H. Yakowitz: inPractical Scanning Electron Microscopy, J.I. Goldstein and H. Yakowitz, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1975, pp. 327–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nesbitt, J.A., Heckel, R.W. Interdiffusion in Ni-Rich, Ni-Cr-Al alloys at 1100 and 1200 °C: Part I. Diffusion paths and microstructures. Metall Trans A 18, 2061–2073 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647078
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647078