Abstract
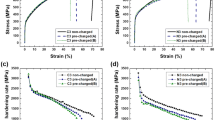
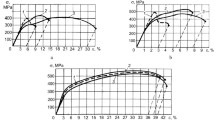
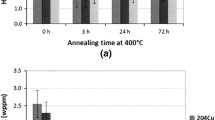
Hydrogen embrittlement of AISI 304-type austenitic stainless steels has been studied with special emphasis on the effects of the nitrogen content of the steels. Hydrogen charging was found to degrade the mechanical properties of all the steels studied, as measured by a tensile test. The fracture surfaces of hydrogen charged specimens were brittle cleavage-like whereas the uncharged specimens showed ductile, dimpled fracture. In sensitized materials transgranular cleavage mode of fracture was replaced by an intergranular mode of fracture and the losses of mechanical properties were higher. Nitrogen alloying decreased the hydrogen-induced losses of mechanical properties by increasing the stability of austenite. In sensitized steels the stability of austenite and nitrogen content were found to have only a minor effect on hydrogen embrittlement, except when sensitization had causedα′-martensite transformation at the grain boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.B. Whiteman and A. R. Troiano:Corrosion, 1965, vol. 21, pp. 53–66.
R. Lagneborg:J. Iron and Steel Inst., 1969, vol. 207, pp. 363–66.
M.R. Louthan, Jr., G.R. Caskey, Jr., J.A. Donovan, and D.E. Rawl, Jr.:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1972, vol. 10, pp. 357–68.
H. Hänninen and T. J. Hakkarainen:Advances of Fracture Research, D. Francoiset al., eds., Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 1081–88.
R. Liu, N. Narita, C. Altstetter, H. Birnbaum, and N. Pugh:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11 A, pp. 1563–74.
D. Eliezer, D. Chakrapani, C. Altstetter, and N. Pugh:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 935–41.
R. Latanision, O. Gastine, and C. Compeau:Environment-sensitive Fracture of Engineering Materials, Z. A. Foroulis, ed., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979, pp. 48–70.
H. Hänninen, S.-P. Hannula, and S. Tähtinen:Environmental Degradation of Engineering Materials in Hydrogen, M. R. Louthan, Jr., R.P. McNitt, and R.D. Sisson, Jr., eds., Virginia Polytechnic Inst., Blacksburg, VA, 1981, pp. 347–56.
A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein:Advances in Corrosion Science and Technology, M. G. Fontana and R.W. Staehle, eds,, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1980, vol. 7, pp. 53–175.
B.C. Odegard, J. A. Brooks, and A. J. West:Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials, A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1976, pp. 116–25.
C.L. Briant:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 181–89.
C. L. Briant:Hydrogen Effects in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 527–40.
A.I. West and J. H. Holbrook:Hydrogen Effects in Metals, I. M.Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, pp. 607–18.
N. Narita and H.K. Birnbaum:Scripta Met., 1981, vol. 14, pp. 1355–58.
J.K. Tien, A. W. Thompson, I.M. Bernstein, and R.J. Richards:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 821–29.
P. R. Swann:Corrosion, 1963, vol. 19, pp. 102t-12t.
D. Douglas, G. Thomas, and W. R. Roser:Corrosion, 1964, vol. 20, pp. 15t-28t.
G.R. Cskey, and R.D. Sisson, Jr.:Scripta Met., 1981, vol. 15, pp. 1187–90.
F. B. Pickering:Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels, Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London, 1978, p. 229.
R.E. Schramm and R.P. Reed:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1345–51.
E.P. Butler and M.G. Burke:Solid-Solid Phase Transformations, H.I. Aaronson, D.E. Laughlin, R. F. Sekerka, and C.M. Wayman, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 1403–07.
R.A. Mulford, E. L. Hall, and C.L. Briant:Corrosion, 1983, vol. 39, pp. 132–43.
C. DeCasa, V. B. Nileshwar, and D. A. Melford:J. Iron and Steel Inst., 1969, vol. 207, pp. 1325–32.
S. -P. Hannula: unpublished research, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 1983.
H. Thier, A. Bäumel, and E. Schmidtmann:Arch. Eisenhüttenwesen, 1969, vol. 40, pp. 333–39.
C.L. Briant, R.A. Mulford, and E. L. Hall:Corrosion, 1982, vol. 38, pp. 468–77.
H. Hänninen and T. Hakkarainen:Corrosion, 1980, vol. 36, pp. 47–51.
J.A. Venables:Phil. Mag., 1962, vol. 7, pp. 35–52.
N. Narita, C.J. Altstetter, and H.K. Birnbaum:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1355–65.
P.D. Pitcher: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wales, 1979.
S.-P. Hannula:Scripta Met., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 509–13.
S. -P. Hannula: Licentiate Thesis, Helsinki University of Technology, 1982.
J. Ovejero Garcia, J. Chene, and M. Aucouturier:Trans. Japan Inst. Metals, 1980, vol. 21, pp. 525–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly with Helsinki University of Technology, Laboratory of Physical Metallurgy, SF-02150 Espoo 15, Finland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hannula, SP., Hänninen, H. & Tähtinen, S. Influence of nitrogen alloying on hydrogen embrittlement in AISI 304-type stainless steels. Metall Trans A 15, 2205–2211 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647103
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647103