Abstract
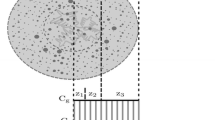
In nodular cast iron, ferrite forms around the graphite nodules and growth proceeds until pearlite nucleates and consumes the remaining austenite. In order to simulate the structure, it is therefore necessary to have accurate models for the ferrite growth. Some investigators have proposed that the growth is completely governed by carbon diffusion through the ferrite shell. In the present work, it is shown that the ferrite growth in nodular cast iron can be divided into three different stages where the growth initially is governed by carbon diffusion in the austenite until the graphite nodule is entirely enveloped by a ferrite shell. During the second stage, it is proposed that the growth is controlled by the incorporation rate of carbon atoms on the graphite nodule. During the later stages of the transformation, the diffusion distance has increased considerably, and therefore, the diffusion of carbon through the ferrite shell will determine the growth rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
area (m2)
- C c α/gr :
-
carbon solubility in ferrite in equilibrium with graphite
- C c α/γ :
-
carbon solubility in ferrite in equilibrium with austenite
- C c γ/α :
-
carbon solubility in austenite in equilibrium with ferrite
- Cskc/γ :
-
carbon content in bulk austenite
- iCkc/α :
-
carbon content in ferrite at graphite interface
- C p :
-
specific heat (J/g/K)
- D c α :
-
diffusion coefficient for carbon in ferrite (m2/s)
- D c γ :
-
diffusion coefficient for carbon in austenite (m2/s)
- f t :
-
fraction transformed austenite (0 <-f, ≤ 1)
- f gr :
-
fraction of graphite
- f real :
-
fraction of graphite and ferrite
- f fict :
-
fictitious fraction of graphite and ferrite
- f α :
-
fraction of ferrite
- f αprim :
-
fraction of ferrite formed by primary growth
- ΔH :
-
latent heat (kJ/kg)
- 1 α :
-
thickness of ferrite shell (m)
- n :
-
number of moles of carbon
- M c :
-
mole weight of carbon (g/mole)
- N a :
-
area nodule count (m−2)
- N v :
-
unit volume nodule count (m−3)
- P :
-
number of ferrite grains/graphite nodule
- r g :
-
graphite nodule radius (m)
- R α :
-
r g+ lα (m)
- S α :
-
thickness of primary ferrite shell (m)
- t :
-
time (s)
- T r :
-
reference temperature (K)
- T s :
-
sample temperature (K)
- T o :
-
start temperature for transformation (K)
- T 1 :
-
temperature at maximum transformation rate (K)
- T 2 :
-
end temperature for transformation (K)
- T kLα :
-
lower stable eutectoid temperature (K)
- T u α :
-
upper stable eutectoid temperature (K)
- V :
-
volume (m3)
- y :
-
coordinate in the plane of the graphite surface (m)
- ρ :
-
specific density (g/m3)
- μ :
-
interface coefficient (m/s)
References
J.M. Schissler, D. Le Dily, and J.P. Chobaut:Proc. 54th Int. Foundry Congr., CIATF, New Delhi, India, 1987, paper no. 23.
R. Boeri and F. Weinberg:Cast Met., 1993, vol. 6, pp. 153–57.
J.E. Rehder:AFS Trans., 1965, vol. 73, pp. 473–87.
M. Wessen and I.L. Svensson:Modeling of Casting, Welding & Advanced Solidification Processes VI, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 71–78.
D.M. Stefanescu and C. Kanetkar:Proc. Computer Simulation of Microstructural Evolution, TMS, Warrendale, Toronto, 1985, pp. 171–88.
D.M. Stefanescu and C. Kanetkar:Proc. 54th Int. Foundry Congr., CIATF, New Delhi, India, 1987, paper no. 19.
D.M. Stefanescu, G. Upadhya, D. Bandyopadhyay, and I.G. Chen:JOM, 1989, Feb., pp. 22–25.
D. Venugopalan:Proc. Physical Metallurgy of Cast Iron IV, Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1990, pp. 271–78.
D. Venugopalan:Metall Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 913–18.
E. Lundbäck: Ph.D. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, 1991.
E. Lundbäck: Lic. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, 1989.
S. Chang, D. Shangguan, and D.M. Stefanescu:Metall Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 1333–46.
H. Fredriksson and I.L. Svensson:Proc. Physical Metallurgy of Cast Iron III, Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1984, pp. 273–84.
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.-O. Andersson:CALPHAD, 1985, vol. 9, pp. 153–90.
T. Noguchi and K. Nagaoka:AFS Trans., 1985, vol. 93, pp. 115–22.
M. Castro: Ph.D. Thesis, INPL, Nancy, France, 1991.
C. Charbon: Ph.D. Thesis, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Laussane, Switzerland, 1995.
J. Lacaze and G. Lesoult:Proc. COST 504—Advanced Casting and Solidification Technology, Espoo, Finland, 1994, pp. 5–34.
P.G. Shewmon:Diffusion in Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1963.
MAGMASOFT, MAGMA Gmbh, Aachen, Germany.
I.L. Svensson and M. Wessen:Proc. Physical Metallurgy of Cast Iron—SCI5, Nancy, France, 1994.
A. de Sy:AFS Trans., 1959, vol. 67, pp. 321–28.
A. Hultgren:Trans. Am. Soc. Met., 1947, vol. 39, pp. 915–87.
M. Hillert:The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystal Solids, Institute of Metals, London, 1969, p. 231.
M. Hillert:Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc, 1983, vol. 19, p. 295.
H. Fredriksson:Proc. Physical Metallurgy of Cast Iron—SCI5, Nancy, France, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wessén, M., Svensson, I.L. Modeling of ferrite growth in nodular cast iron. Metall Mater Trans A 27, 2209–2220 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651875
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651875