Abstract
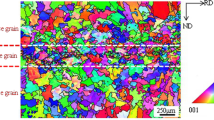
A centrifugal water-cooling casting method was used to cast a 7075 alloy with the aim of refining the grain and inclusion size and improving mechanical properties in the wrought condition. Con-ventional ingot casting methods were also used and investigated for comparison with the centrifugal casting method. The results show that by the centrifugal casting method, a small equiaxed grain size, 17 μm, is obtained in as-cast condition. Only 50 minutes are required for material homogenization. After rolling to obtain sheet, a grain size of 15 × 8 × 6 μm and an inclusion size of 2 to 3 μm are achieved. Fine-grained centrifugal-cast 7075 alloy exhibits higher strength than the ingot-cast one in the early stages of aging but poorer in the latter stages. However, its ductility and combination of strength and ductility is superior to the ingot-cast ones at all aging times. The reduction in strength in the latter aging stages for the fine-grained structure arises from its higher volume fraction of soft precipitate free zones. The improved ductility is attributed to the higher fraction of transgranular fracture, higher transgranular fracture strain, and intergranular fracture strain. Fine-grained 7075 alloy also displays significant improvements in the exfoliation corrosion resistance. These improvements are related to the increased density of attacking sites on the surface and the increased turns for crack propagation along grain boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Church, P. Wieser, and J.F. Wallace:Modem Casting, 1966, vol. 49, pp. 129–44.
J.J. Burke and V. Weiss:Ultrafine-Grain Metals, Syracuse University Press, New York, NY, 1970.
M.C. Flemings:Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1974, pp. 341–44.
G.S. Cole and G.F. Boiling:Ultrafine-Grain Metals, J.J. Burke and V. Weiss, eds., Syracuse University Press, New York, NY, 1970, pp. 31–69.
G.S. Cole, K.W. Casey, and G.F. Boiling:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 1413–16.
L. Backerud:Light Metal Age, 1983, vol. 10, p. 6.
W.C. Johnston, G.R. Kolter, and W.A. Tiller:Trans. TMS-A1ME, 1963, vol. 227, pp. 890–96.
S. O'Hara and W.A. Tiller:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 497–501.
G.S. Cole and G.F. Boiling:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 1824–35.
J.D. Hunt and K.A. Jackson:J. Appl. Phys., 1966, vol. 37, pp. 254–57.
J.R. Picken:J. Mater. Sci., 1981, vol. 16, pp. 1437–57.
W.E. Quist and R.E. Lewis:Rapidly Solidified Powder Aluminum Alloys, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1984, pp. 7–30.
R.E. Maringer and C.E. Mobley:Rapid Solidification Process Principle and Technologies, Proc. Int. Conf. on Rapid Solidification Processing, Claitor's Publishing Division, Baton Rouge, LA, 1977, pp. 208–21.
R.M. German:Powder Metallurgy Science, Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1984.
P.K. Domalavage, N.J. Grant, and Y. Gefen:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1599–1606.
J.W. Yeh and S.H. Jong:Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 643–50.
Metals Handbook, 9th eds, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1979, vol. 2, pp. 63–139.
ASTM Standard G34-79(EXCO), ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1979.
M.C. Flemings:Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York, NY, 1974, pp. 328–38.
R.H. Van Stone, R.H. Merchant, J.R. Low, Jr.: ASTM STP 556, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1974, pp. 93–124.
J. Waldman, H. Sulinski, and H. Markus:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 573–84.
J.A. Wert, N.E. Panton, C.H. Hamilton, and M.W. Mahoney:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1267–76.
N.E. Panton, C.H. Hamilton, J. Wert, and M. Mahoney:J. Met, 1982, Aug., pp. 21-27.
J.A. Wert:Microstructural Control in Aluminum Alloys, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 67–94.
M.A. Meyers and K.K. Chawla:Mechanical Metallurgy, Prentice-Hall, Inc., New York, NY, 1984, pp. 494–506.
J.W. Martin:Micromechanisms in Particle-Hardened Alloys, The Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1980, pp. 91–94.
T. Kawabata and O. Izumi:Acta Metall, 1976, vol. 24, pp. 817–25.
N. Ryum:Acta Metall., 1968, vol. 16, pp. 327–32.
A.J. Cornish and M.K.B. Day:J. Inst. Met., 1971, vol. 99, pp. 377–84.
M. Abe, K. Asano, and A. Fujiwara:Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 1499–1505.
I. Kirman:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 1761–70.
J.W. Yeh and K.S. Liu:Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met, 1986, vol. 27(7), pp. 504–11.
B.I. Edelson and W.M. Baldwin, Jr.:Trans. ASM, 1962, vol. 55, pp. 230–50.
N. Ryum, B. Haegland, and T. Lindtveit:Z. Metallkd., 1967, vol. 58, pp. 28–31.
N. Ryum and K. Baardseth:J. Inst. Met, 1968, vol. 96, pp. 92–93.
E. Hornbogen and M. Gräf:Acta. Metall, 1977, vol. 25, pp. 877–81.
J.D. Embury and E. Nes:Z. Metallkd., 1974, vol. 65, pp. 45–55.
T. Kawabata and O. Izumi:J. Mater. Sci., 1979, vol. 14, pp. 1071–79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
SHANG-HAW JONG, formerly Graduate Student with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, National Tsing Hua University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, JW., Jong, SH. & Liu, WP. The improved microstructures and properties of 7075 alloys produced by a water-cooling centrifugal casting method. Metall Mater Trans A 27, 1933–1944 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651943
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651943