Abstract
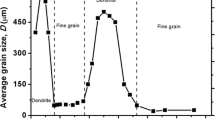
The microstructure of rapidly solidified laser molten or electron beam molten Al-4.5 wt pct Cu alloyed surfaces has been investigated. A variety of electron microscopy techniques was employed. The epitaxially resolidifying melt undergoes three different solidification modes: about 3 μm to 5 μm of material near the fusion line resolidify in a plane front mode. The next bulk resolidifies in a cellular dendritic mode, which then turns dendritic. The major impact of resolidification is refinement of the surface microstructure, which by itself shows various characteristics for the different resolidification modes. Particularly, the validity of the relationship of secondary interdendritic arm spacing, as inversely dependent on the one-third power of the average local cooling rate, was verified for cooling rates up to 106 K per second.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Jones:Aluminum, 1978, vol. 54, p. 274.
N.J. Grant:Fizika, 1970, vol. 2, Suppl. 2, paper 16.
H. Ahlbom and D. Merz:Aluminum, 1971, vol. 47, p. 671.
H. Ahlbom and D. Merz:Aluminum, 1974, vol. 50, p. 583.
M. Lebo and N.J. Grant:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 1547.
K. D. Krishnanamd and R. W. Cahn:Rapidly Quenched Metals, N.J. Grant and P.C. Giessen, eds., MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1976, p. 67.
H. Kaneko and J. Ikeuchi:Proc. 1st International Conf. on Electro- discharge Machining, Tokyo, Japan, 1965, p. 23.
E. Scheil and Y. Masuda:Aluminum, 1955, vol. 31, p. 51.
B. P. Bardes and M. C. Flemings:Trans. AFS, 1966, vol. 74, p. 406.
P. Ramachandraro and M. Laridjani:J. Mater. Sci., 1974, vol. 9, p. 434.
R. Mehrabian, S. Kou, S.C. Hsu, and A. Munitz:Laser-Solid Inter- actions and Laser Processing, 1978, AIP Conference Proceedings, No. 50, American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1979, p. 129.
R. Mehrabian, S. C. Hsu, S. Kou, and A. Munitz:ASM Conference Proceedings on Application of Lasers in Materials Processing, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1980.
A. Munitz:Metall. Trans. B, 1980, vol. 11B, p. 563.
S.J.B. Reed:Electron Microprobe Analysis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1977, pp. 175–97.
J. W. Cowley:Analytical Microscopy, Report of a Specialist Work- shop, 1st ed., Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 1976, p. 189.
L. F. Mondolfo:Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties, Butter- worths, London, 1st ed., 1976, pp. 253–78.
M.G. Scott and J. A. Leake:Acta Metall., 1975, vol. 23, p. 503.
G.J. Davies and J. G. Garland:Inter. Met. Reviews, 1975, vol. 20, p. 83.
W. W. Mullins and R.F. Sekerka:J. Appl. Phys., 1964, vol. 35, p. 444.
R.F. Sekerka:Crystal Growth: an Introduction, Amsterdam, North- Holland, 1973, p. 403.
W. A. Tiller, K. A. Jackson, J.W. Rutter, and B. Chalmers:Acta Metall., 1953, vol. 1, p. 428.
M. C. Flemings:Solidification Processing, New York, NY, McGraw- Hill, 1974, p. 38.
T. F. Bower, H.D. Brody, and M.C. Flemings:Trans. AIME, 1966, vol. 236, p. 624.
J.G. Garland and G.J. Davies:Metal Construction, 1970, vol. 2, p. 171.
T. R. Anthony and H.E. Cline:J. Appl. Phys., 1977, vol. 48, p. 3888.
S.M. Copley. D. Beck, O. Esqivel. and M. Bass:ibid., p. 161.
H.S. Gurev and R.D. Stout:Weld. J., 1963, vol. 42, p. 298.
B.A. Morchan and A. Abitdnar:Automat. Weld. (USSR), 1968, vol. 21, p. 4.
A.T. D’Annessa:Weld. J., 1970, vol. 49, p. 41.
C.R. Loper:Weld. J., 1969, vol. 48, p. 171.
J. Waring:Australian Weld. J., 1967, vol. 11, p. 15.
M. Kato:Trans. Japan Weld. Soc, 1972, vol. 2, p. 59.
B.G. Lewis and P.R. Strutt:J. Metals, Nov. 1982, p. 37.
B. A. Joyce:Rep. Prog. Phys., 1974, vol. 37, p. 363.
P.A. Joly and R. Mehrabian:J. Mater. Sci., 1974, vol. 9, p. 1446.
S.C. Hsu, S. Kou, and R. Mehrabian:Metall. Trans. B, 1981, vol. 12B, p. 33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munitz, A. Microstructure of rapidly solidified laser molten AI-4.5 Wt Pct cu surfaces. Metall Trans B 16, 149–161 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657500
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02657500