Abstract
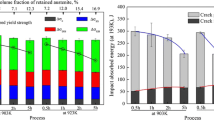
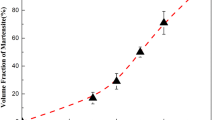
In an attempt to understand the role of retained austenite on the cryogenic toughness of a ferritic Fe-Mn-AI steel, the mechanical stability of austenite during cold rolling at room temperature and tensile deformation at ambient and liquid nitrogen temperature was investigated, and the microstructure of strain-induced transformation products was observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The volume fraction of austenite increased with increasing tempering time and reached 54 pct after 650 °C, 1-hour tempering and 36 pct after 550 °C, 16-hour tempering. Saturation Charpy impact values at liquid nitrogen temperature were increased with decreasing tempering temperature, from 105 J after 650 °C tempering to 220 J after 550 °C tempering. The room-temperature stability of austenite varied significantly according to the(α + γ) region tempering temperature;i.e., in 650 °C tempered specimens, 80 to 90 pct of austenite were transformed to lath martensite, while in 550 °C tempered specimens, austenite remained untransformed after 50 pct cold reductions. After tensile fracture (35 pct tensile strain) at -196 °C, no retained austenite was observed in 650 °C tempered specimens, while 16 pct of austenite and 6 pct of e-martensite were observed in 550 °C tempered specimens. Considering the high volume fractions and high mechanical stability of austenite, the crack blunting model seems highly applicable for improved cryogenic toughness in 550 °C tempered steel. Other possible toughening mechanisms were also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Jin, J.W. Morris, Jr., and V.F. Zackay:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 141–49.
S.K. Hwang, S. Jin, and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 2015–21.
C.K. Syn, S. Jin, and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1827–32.
P. Pahuta, Z. Janik, L. Hyspecka, and K. Mazanec:Trans. ISIJ, 1986, vol. 26, pp. 649–54.
J.I. Kim, C.K. Syn, and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 93–103.
J.D. Bolton, E.R. Petty, and G.B. Allen:Metall. Trans. A, 1971, vol. 2A, pp. 2915–23.
M.J. Schanfein, M.J. Yokota, V.F. Zackay, E.R. Parker, and J.W. Morris, Jr.: ASTM STP 579, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1975, pp. 361–77.
S.K. Hwang and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 545–55.
M. Niikura and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 1531–40.
S.W. Lee and H.-C. Lee:Advan. Cryogenic Eng., 1990, vol. 36B, pp. 1347–54.
Z. Nishiyama:Martensitic Transformation, Academic Press, New York, NY, 1978, p. 49.
C.K. Syn, B. Fultz, and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 1635–40.
P.M. Kelly:Acta Metall., 1965, vol. 13, pp. 635–46.
J.S. Bowles and J.K. Mackenzie:Acta Metall., 1954, vol. 2, pp. 129–37.
H.M. Otte:Acta Metall., 1957, vol. 5, pp. 614–27.
B. Cina:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1954, vol. 177, pp. 406–22.
J.A. Venables:Phil. Mag., 1962, vol. 7, pp. 35–44.
R. Lagneborg:Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12, pp. 823–43.
J.F. Breedis and W.D. Robertson:Acta Metall., 1962, vol. 10, pp. 1077–88.
H. Schumann:Arch. Eisenhuttenwes., 1969, vol. 40, pp. 1027–37.
L.I. Lysak, I.B. Goncharenko, and B.I. Nikolin:Fiz. Metall. Metalloved., 1973, vol. 36 (1), pp. 97–101.
P.C.J. Gallagher:Metall. Trans. A, 1970, vol. 1A, pp. 2429–61.
T. Ericsson:Acta Metall., 1966, vol. 14, pp. 853–65.
H.J. Rack and David Kalish:Metall. Trans. A, 1971, vol. 2A, pp. 3011–20.
C.N. Ahlquisf.Acta Metall., 1975, vol. 23, pp. 239–43.
H. Haga:Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1973, vol. 13, pp. 141–44.
K.J. Kim and L.H. Schwartz:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 33, pp. 5–20.
B. Fultz and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 2251–56.
D. Frear and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 243–52.
B. Fultz, J.I. Kim, Y.H. Kim, G.O. Fior, and J.W. Morris, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 2237–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Graduate Student, Seoul National University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.W., Lee, HC. The mechanical stability of austenite and cryogenic toughness of ferritic Fe-Mn-AI Alloys. Metall Trans A 24, 1333–1343 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668201
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668201