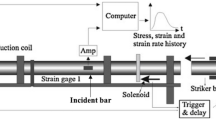
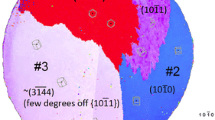
Abstract
The deformation behavior and substructure evolution of unalloyed-Ta and Ta-10W under quasistatic conditions have been compared to their respective responses when shock prestrained to 20 GPa at 25 °C as well as to unalloyed-Ta shocked to 7 GPa at 25 °C, 200 °C, and 400 °C. The reload yield behavior of shock-prestrained Ta and Ta-10W did not exhibit enhanced shock hardening when compared to their respective quasistatic stress-strain response at an equivalent strain level. In addition, the reload yield behavior of Ta shock prestrained to 7 GPa at 200 °C or 400 °C was found to exhibit increased hardening compared to the shock prestraining at 25 °C. The quasistatic substructure evolution and shock-hardening responses of Ta and Ta-10W were investigatedvia transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The dislocation substructures in both materials and at each strain rate condition and temperature were similar and consisted primarily of long, straight, ( α/2) 〈111〉 type screw dislocations. The propensity for long, straight screw dislocations, irrespective of the loading condition, supports the theory of strong Peierls stress control on defect generation and defect storage. The substructure evolution and mechanical behavior of Ta and Ta-10W are discussed in terms of defect storage mechanisms and compared to the mechanisms operative in face-centered cubic (fcc) metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.E. Dieter:Response of Metals to High Velocity Deformation, Interscience Publishers, New York, NY, 1961, pp. 409–45.
L.E. Murr: inShock Waves and High Strain Rate Phenomena in Metals, M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 607–73.
G.T. Gray: inHigh Pressure Shock Compression of Solids, J.R. Asay and M. Shahinpoor, eds., Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1993, pp. 187–215.
W.C. Leslie:Metallurgical Effects at High Strain Rates, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, p. 571.
S. Mahajan:Phys. Status Solidi A, 1970, vol. 2, pp. 187–201.
M.A. Mogilevsky and P.E. Newman:Phys. Rep., 1983, vol. 97, pp. 357–93.
G.T. Gray and P.S. Follansbee: inImpact Loading and Dynamic Behavior of Materials, C.Y. Chiem, H.-D. Kunze, and L.W. Meyer, eds., Deutsche Gesellschaft fuer Metallkunde, Oberursel, Germany, 1988, vol. 2, pp. 541–48.
P.S. Follansbee and G.T. Gray:Int. J. Plasticity, 1991, vol. 7, pp. 651–60.
R.G. McQueen and S.P. Marsh:J. Appl. Phys., 1960, vol. 31, pp. 1253–69.
V. Vitek:Dislocations and Properties of Real Materials, Institute of Metals, London, 1985, vol. 323, pp. 30–50.
J.W. Christian:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1237–56.
G.T. Gray, S. Bingert, S.I. Wright, and S.R. Chen: inHigh-Temperature Suicides and Refractory Alloys, C.L. Briant, J.J. Petrovic, B.P. Bewlay, A.K. Vasudevan, and H.A. Lipsitt, eds., Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1994, vol. 322, pp. 407–12.
G.T. Gray and A.D. Rollett: inHigh Strain Rate Behavior of Refractory Metals and Alloys, R. Asfahani, E. Chen, and A. Crowson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 303–15.
W. Kock and P. Paschen:J. Met., 1989, vol. 41, p. 33.
R.J. Arsenault and A. Lawley: inWork Hardening, J.P. Hirth and J. Weertman, eds., Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York, NY, 1968, vol. 46, pp. 283–309.
J.B. Clark, J.R.K. Garrett, T.L. Jungling, and R.I. Asfahani:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2959–68.
J.B. Clark, J.R.K. Garrett, T.L. Jungling, and R.I. Asfahani:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2183–91.
S.I. Wright, G.T. Gray, and A.D. Rollett:Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 1025–31.
CM. Lopatin, C.L. Wittman, J.P. Swensen, and P.F. Perron: inHigh Strain Rate Behavior of Refractory Metals and Alloys, R. Asfhani, E. Chen, and A. Crowson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 241–47.
A.M. Rajendran, J.R.K. Garrett, J.B. Clark, and T.L. Jungling:J. Mater. Shaping Technol, 1991, vol. 9, pp. 7–20.
A.M. Rajendran and J.R.K. Garrett: inHigh Strain Rate Behavior of Refractory Metals and Alloys, R. Asfahani, E. Chen, and A. Crowson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 289–302.
D.H. Lassila and G.T. Gray:3rd Int. Conf. on Mechanical and Physical Behavior of Materials under Dynamic Loading, J.D.P. IV, ed., 1991, vol. 1, pp. C3-19-C3-26.
C.L. Wittman, J.R.K. Garrett, J.B. Clark, and C.M. Lopatin: inShock- Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Materials, M.A. Meyers, L.E. Murr, and K.P. Staudhammer, eds., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY 1992, pp. 925–33.
G.T. Gray:High-Pressure Science and Technology—1993 AIP Conf. Proc, S.C. Schmidt, J.W. Shaner, G.A. Samara, and M. Ross, eds., American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1994, vol. 309, pp. 1103–06.
J.N. Johnson, R.S. Hixson, D.L. Tonks, and G.T. Gray:High-Pressure Science and Technology—1993 AIP Conf. Proc, S.C. Schmidt, J.W. Shaner, G.A. Samara, and M. Ross, eds., American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1994, vol. 309, pp. 1095–98.
D.L. Tonks, R.S. Hixson, J.N. Johnson, and G.T. Gray:High-Pressure Science and Technology—1993 AIP Conf. Proc, S.C. Schmidt, J.W. Shaner, G.A. Samara, and M. Ross, eds., American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1994, vol. 309, pp. 997–1000.
M.D. Furnish, L.C. Chhabildas, and D.J. Steinberg:High-Pressure Science and Technology—1993 AIP Conf. Proc, S.C. Schmidt, J.W. Shaner, G.A. Samara, and M. Ross, eds., American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1994, vol. 309, pp. 1099–1102.
P.S. Follansbee: inMetals Handbook, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1985, vol. 8, pp. 198–203.
P.S. Follansbee and U.F. Kocks:Acta Metall, 1988, vol. 36, pp. 81–93.
G.T. Gray: inModeling the Deformation of Crystalline Solids, T.C. Lowe, A.D. Rollert, P.S. Follansbee, and G.S. Daehn, eds., TMS- AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1991, pp. 145–58.
K.S. Vecchio and G.T. Gray:High-Pressure Science and Technology—1993 AIP Conf. Proc, S.C. Schmidt, J.W. Shaner, G.A. Samara, and M. Ross, eds., American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1994, vol. 309, pp. 1213–16.
G.T. Gray, P.S. Follansbee, and C.E. Frantz:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1989, vol. A111, pp. 9–16.
D.I. Bolef:J. Appl. Phys., 1961, vol. 32, p. 100.
R.W. Anderson and S.E. Bronisz:Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, pp. 645–46.
C.S. Barrett and R. Bakish:Trans. AIME, 1958, vol. 212, pp. 122–23.
G.T. Gray: inHigh Pressure Shock Compression of Solids, J.R. Asay and M. Shahinpoor, eds., Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1993, pp. 187–215.
S.-R. Chen and G.T. Gray: Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM, unpublished research, 1994.
U.F. Kocks: inThe Mechanics of Dislocations, E.C. Aifantis and J.P. Hirth, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1985, pp. 81–83.
J.N. Johnson:High-Pressure Science and Technology—1993 AIP Conf. Proc, S.C. Schmidt, J.W. Shaner, G.A. Samara, and M. Ross, eds., American Institute of Physics, New York, NY, 1994, vol. 309, pp. 1145–48.
Z.S. Basinski, M.S. Duesbery, and R. Taylor:Phil. Mag., 1970, vol. 21, pp. 1201–21.
U.F. Kocks: inUnified Constitutive Equations for Creep and Plasticity, A.K. Miller, ed., Elsevier Press, New York, NY, vol. 1987, pp. 1-88.
J.R. Low and A.M. Turkalo:Acta Metall., 1962, vol. 10, pp. 215–27.
W.G. Johnston and J.J. Gilman:J. Appl. Phys., 1960, vol. 31, pp. 632–43.
J.R. Low and R.W. Guard:Acta Metall, 1959, vol. 7, pp. 171–79.
D.K. Bowen, J.W. Christian, and G. Taylor:Can. J. Phys., 1967, vol. 45, pp. 903–38.
W.A. Spitzig and T.E. Mitchell:Acta Metall, 1966, vol. 14, pp. 1311–23.
U.F. Kocks:Proc. Conf. on Dislocations and Properties of Real Materials, The Institute of Metals, London, 1985, vol. 323, p. 125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation made in the symposium “Dynamic Behavior of Materials,” presented at the 1994 Fall Meeting of TMS/ASM in Rosemont, Illinois, October 3-5, 1994, under the auspices of the TMS-SMD Mechanical Metallurgy Committee and the ASM-MSD Flow and Fracture Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, G.T., Vecchio, K.S. Influence of peak pressure and temperature on the structure/property response of shock- loaded Ta and Ta-10W. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 2555–2563 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669413
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669413