Abstract
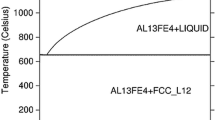
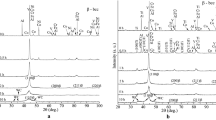
The structural evolution in mechanically alloyed binary aluminum-iron powder mixtures containing 1, 4, 7.3, 10.7, and 25 at. pct Fe was investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and electron microscopic techniques. The constitution (number and identity of phases present), microstructure (crystal size, particle size), and transformation behavior of the powders on annealing were studied. The solid solubility of Fe in Al has been extended up to at least 4.5 at. pct, which is close to that observed using rapid solidification (RS) (4.4 at. pct), compared with the equilibrium value of 0.025 at. pct Fe at room temperature. Nanometer-sized grains were observed in as-milled crystalline powders in all compositions. Increasing the ball-to-powder weight ratio (BPR) resulted in a faster rate of decrease of crystal size. A fully amorphous phase was obtained in the Al-25 at. pct Fe composition, and a mixed amorphous phase plus solid solution of Fe in Al was developed in the Al-10.7 at. pct Fe alloy, agreeing well with the predictions made using the semiempirical Miedema model. Heat treatment of the mechanically alloyed powders containing the supersaturated solid solution or the amorphous phase resulted in the formation of the Al3Fe intermetallic in all but the Al-25 at. pct Fe powders. In the Al-25 at. pct Fe powder, formation of nanocrystalline Al5Fe2 was observed directly by milling. Electron microscope studies of the shock-consolidated mechanically alloyed Al-10.7 and 25 at. pct Fe powders indicated that nanometer-sized grains were retained after compaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.H. Shingu: inFirst Int. Conf. on Processing Materials for Properties, H. Henein and T. Oki, eds. TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 1275–80.
F.H. Froes, C. Suryanarayana, K. Russell, and C.G. Li:Int. J. Mechanochem. Mech. Alloying, 1994, vol. 1, pp. 112–24.
J.S. Benjamin:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2943–51.
C.C. Koch: inProcessing of Metals and Alloys, R.W. Cahn, ed., VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, F.R. Germany, 1991, Materials Science and Engineering—A Comprehensive Treatment, pp. 193–245.
D. Maurice and T.H. Courtney:Metall. Trans. A., 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 289–303.
C. Suryanarayana and F.H. Froes:Mater. Sci. Forum, 1992, vol. 88–90, pp. 445–52.
C. Suryanarayana and F.H. Froes:Metall. Trans. A., 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 1071–81.
C.C. Koch:Nanostructured Mater., 1993, vol. 2, pp. 109–29.
Dispersion Strengthened Aluminum Alloys, Y.W. Kim and W.M. Griffith, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988.
Mechanical Alloying for Structural Applications, J.J. deBarbadillo, F.H. Froes, and R. Schwarz, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993.
T.B. Massalski:Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1986, vol. 1, pp. 147–49.
C. Suryanarayana:Bull. Mater. Sci., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 307–46.
C. Suryanarayana, F.H. Froes, D.K. Mukhopadhyay, G. Cizmich, G.H. Chen, Z. Peng, and J. Mishurda: inProcessing and Fabrication of Advanced Materials III, V.A. Ravi, T.S. Srivatsan, and J.J. Moore, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1994, pp. 567–84.
M.A. Morris and D.G. Morris:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1991, vol. 136, pp. 59–70.
D.K. Mukhopadhyay, C. Suryanarayana, and F.H. Froes:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 31, pp. 333–38.
Metallic Glasses, T.R. Anantharaman, ed., Trans Tech Pub., Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1984.
C. Suryanarayana and F.H. Froes:Nanostructured Mater., 1993, vol. 3, pp. 147–53.
B. Huang: Ph.D. Thesis, Kyoto University, Japan, 1990.
B. Huang, N. Tokijane, K.N. Ishihara, P.H. Shingu, and S. Nasu:J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1990, vol. 117/118, pp. 688–91.
I.S. Polkin, E.J. Kaputkin, and A.B. Borzov: inStructural Applications of Mechanical Alloying, F.H. Froes and J.J. deBarbadillo, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1990, pp. 251–56.
Y. Dong, W.H. Wang, L. Lin, K.Q. Xiao, S.H. Tong, and Y.Z. He:Mater Sci. Eng. A, 1991, vol. 134, pp. 867–71.
G. Wang, D. Zhang, H. Chen, B. Lin, W. Wang, and Y. Dong:Phys. Lett. A, 1991, vol. 155, pp. 57–61.
G. Korth: inAdvanced Synthesis of Engineered Structural Materials, J.J. Moore, E.J. Lavernia, and F.H. Froes, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993, pp. 81–86.
B.D. Cullity:Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, Addison-Wesley Pub. Co., Reading, MA, 1976.
S.K. Pradhan, T. Chakraborty, S.P. Sengupta, C. Suryanarayana, A. Frefer, and F.H. Froes:Nanostructured Mater., 1995, vol. 5, pp. 53–61.
G. Falkenhagen and W. Hofmann:Z. Metallkd., 1952, vol. 43, p. 69.
A. Fontaine and A. Guinier:Phil. Mag., 1971, vol. 31, p. 70.
M. De Sanctis, A.P. Woodfield, and M.H. Loretto:Int. J. Rapid Solidification, 1988, vol. 4, pp. 53–74.
A. Kamio, H. Tezuka, T. Sato, T.T. Long, and T. Takahashi:J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met., 1986, vol. 36, pp. 72–80.
P. Furrer and H. Warlimont:Z. Metallkd., 1973, vol. 64, pp. 236–48.
A. Tonejc and A. Bonefacic:J. Appl. Phys., 1968, vol. 40, pp. 419–20.
K.F. Kobayashi, N. Tachibana, and P.H. Shingu:J. Mater. Sci., 1990, vol. 25, pp. 801–04.
K.F. Kobayashi, N. Tachibana, and P.H. Shingu:J. Mater. Sci., 1990, vol. 25, pp. 3149–54.
M.D. Zdujic, K.F. Kobayashi, and P.H. Shingu:J. Mater. Sci., 1991, vol. 26, pp. 5502–08.
M.D. Zdujic, K.F. Kobayashi, and P.H. Shingu:Z. Metallkd., 1990, vol. 81, pp. 380–85.
H. Jones:Rapid Solidification of Metals and Alloys, Institution of Metallurgists, London, 1982.
R.B. Schwarz, R.R. Petrich, and C.K. Saw:J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1985, vol. 76, pp. 281–302.
A.K. Messen, F.R. de Boer, R. Boom, P.F. de Chatel, W.C.M. Martens, and A.R. Miedema:CALPHAD, 1983, vol. 7, pp. 51–70.
T. Koyano, T. Takizawa, T. Fukunaga, U. Mizutani, S. Kamizuru, E. Kita, and A. Tasaki:J. Appl. Phys., 1993, vol. 73, pp. 429–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, D.K., Suryanarayana, C. & FROES, F.H.(. Structural evolution in mechanically alloyed Al-Fe powders. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 1939–1946 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670665
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670665