Abstract
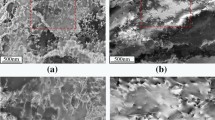
Adiabatic shear bands, formed in a hollow AISI 4340 steel cylinder subjected to dynamic expansion by means of an explosive charge placed in its longitudinal axis, were characterized. The adiabatic shear bands formed in this quenched and tempered steel were of the classical “transformed” type. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of etched surfaces revealed that alignment of the lamellae along the direction of shear seems to be the event that precedes shear localization. The transmission electron microscopy of a “white”-etching shear band having undergone a shear strain of approximately 4 revealed that it containedX (Fe5C2) carbides in a martensitic structure. These carbides were observed to form on (112) internal microtwins. Grains could not be resolved inside of the shear band, but they could be observed in the surrounding matrix material. A traverse of the shear band was made, and there existed no definite boundary between the matrix and the shear band. No evidence of a transformation to austenite was observed. Heat transfer calculations were conducted to help explain the features observed inside of the shear band. It is concluded that the “white”-etching bands, commonly referred to in the literature as “transformed” bands, do not exhibit a transformation at values of shear strain of up to 4. The enhanced reflectivity is an etching artifact and is possibly due to microstructural changes, a very small grain size, and carbide redissolution in the bands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.M. Trent:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1941, vol. 143, pp. 401–12.
C. Zener and H.H. Hollomon:J. Appl. Phys., 1944, vol. 9, pp. 22–32.
H.C. Rogers:Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1979, vol. 9, pp. 283–311.
H.C. Rogers: inMaterial Behavior Under High Stress and Ultrahigh Loading Rates, J. Mescall and V. Weiss, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1983, pp. 101–18.
R.C. Glenn and W.C. Leslie:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2945–47.
A.L. Wingrove:J. Aust. Inst. Met., 1971, vol. 16, pp. 67–70.
A.L. Wingrove:A Note on the Structure of Adiabatic Shear Bands in Steel, Department of Supply, Australian Defense Scientific Service, Defense Standard Laboratories, Tech. Memo. 33, 1971.
D.C. Erlich, L. Seaman, D.A. Shockey, and D. Curran:Development and Application of Computational Shear Band Model, Final Report, Contract ARBDL-CR-00416, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA, Mar. 1980, PRB-15.
D.R. Curran:Computational Model for Armor Penetration, Annual Report, Contract DAAK 11-78-C-0115, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA, Nov. 1979.
Y.K. Lee and J.L. Swedlow:Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 1984, vol. 20, pp. 409–21.
Y.K. Lee and J.L. Swedlow:Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 1984, vol. 20, pp. 423–45.
S. Kuriyama and M.A. Meyers:Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 443–50.
D.R. Curran and L. Seaman: inShock Waves in Condensed Matter, Y.M. Gupta, ed., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1986, pp. 315–20.
G.L. Moss: inShock Waves and High Strain Rate Phenomena in Metals: Concepts and Applications, M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 299–312.
Y. Meunier, L. Sangoy, and G. Pont: inImpact Loading and Dynamic Behavior of Materials, C.Y. Chiem, H.D. Kunze, and L.W. Meyer, eds., DGM Verlag, Federal Republic of Germany, 1988, pp. 711–18.
H.C. Rogers and C.V. Shastry: inShock Waves and High Strain, Rate Phenomena in Metals: Concepts and Applications, M.A. Meyers and L.E. Murr, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1981, pp. 285–98.
M.A. Meyers and H.-r. Pak:Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 2493–99.
K.H. Jack and S. Wild:Nature (London), 1966, vol. 212, pp. 248–50.
F.E. Werner, B.L. Averbach, and M. Cohen:Trans. ASM, 1956, vol. 49, pp. 823–41.
Y. Ohmori and S. Sagusava:Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1971, vol. 12, p. 170.
Y. Ohmori:Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1972, vol. 13, p. 119.
P.J. Fullingham, H.J. Leary, and L.E. Turner: inElectron Microscopy and Structure of Metals, G. Thomas, ed., University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1972, pp. 163–72.
G.Y. Lai, W.E. Wood, R.A. Clark, V.F. Zackay, and E.R. Parker:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1663–70.
H.S. Carslaw and J.C. Jaeger:Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed., Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1959, pp. 54–57.
R.C. Ruhl and M. Cohen:Trans. AIME, 1969, vol. 245, pp. 241–45.
S. J. Donachie and G.S. Ansell:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1863–75.
G.R. Speich and A. Szirmae:Trans. AIME, 1968, vol. 245, pp. 1063–74.
S.P. Timothy:Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 301–06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly with the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, Socorro, NM 87801.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wittman, C.L., Meyers, M.A. & Pak, H.R. Observation of an adiabatic shear band in AISI 4340 steel by high-voltage transmission electron microscopy. Metall Trans A 21, 707–716 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02671941
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02671941