Abstract
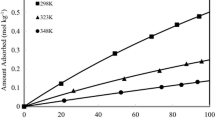
The adsorption characteristics of H2O on zeolite 13X were measured by a gravimetric method. The adsorption isotherm showed type II isotherm and was fitted by using both the excess surface work (ESW) model and Langmuir-Freundlich model. The results predicted by the Langmuir-Freundlich model were much smaller than the experimental results at higher-pressure region. However, the ESW model agreed well with the experimental data over the whole pressure region. In this case, a plot of the change in chemical potential versus the amount adsorbed gave two linear regions due to secondary effects such as capillary condensation. The experimental uptake curves were well fitted by several LDF models and solid diffusion model with the error range of 1.5-3.5%. Unlike the expectation that the more rigorous solid diffusion model would fit better, Nakao-Suzuki model showed the best agreement with experimental uptake data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs, J. and Setzer, M. J., “A Model to Describe Adsorption Isotherms”,J. Colloid and Interface Sci.,180, 70 (1996).
Adolphs, J. and Setzer, M. J., “Energetic Classification of Adsorption Isotherms”,J. Colloid and Interface Sci.,184,443 (1996).
Adolphs, J. and Setzer, M. I, “Description of Gas Adsorption on Porous and Dispersed Systems with the Excess Surface Work Model”,J. Colloid and Interface Set,207,349 (1998).
Do, D. D., “Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics”, Imperial College Press, London (1998).
IMSL MATH/LIBRARY, “FORTRAN Subroutine for Mathematical Application Ver. 1.1 User’s Manual”, IMSL Inc. (1989).
Karger, J. and Ruthven, D. M., “Diffusion in Zeolite and other Microporous Solids”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York (1992).
Kim, W G., Yang, J., Han, S., Cho, C, Lee, C. H. and Lee, H. I, “Experimental and Theoretical Study on H2/CO2 Separation by a Five-Step One-Column PSA Process”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,12,5 (1995).
Ruthven, D. M., Farooq, S. and Knabel, K. S., “Pressure Swing Adsorption”, VCH Publishers, Inc., New York (1994).
Ruthven, D. M., “Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Processes”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York (1984).
Sircar, S. and Hurton, J. R., “Why Does the Linear Driving Force Model for Adsorption Kinetics Work”,Adsorption,6,137 (2000).
Suzuki, M., “Adsorption Engineering”, Kodansha Ltd., Tokyo (1990).
Yang, R. T., “Gas Separation by Adsorption Processes”, Butterworths, Boston (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, Y.K., Lee, S.J., Kim, J.W. et al. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of H2O on zeolite 13x. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 18, 525–530 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698301
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698301