Abstract
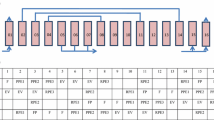
The operation of PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) processes is a highly nonlinear and challenging problem. We propose a systematic procedure to achieve the optimal operation of a PSA process. The model of the PSA process for CO2 separation and recovery is developed first and optimization is performed to identify optimal operating conditions based on the model. The effectiveness of the model developed is demonstrated by numerical simulations and experiments using CO2 and N2 gases and zeolite 13X. Breakthrough curves and temperature changes in the bed are computed from the model and the results are compared with those of experiments. The effects of the adsorption time and reflux ratio on the product purity and the recovery are identified through numerical simulations. The optimization problem is formulated based on nonlinear equations obtained from simulations. The optimal operating conditions identified are applied to experiments. The results show higher recovery of CO2 under optimal operating conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chue, K. T., Kim, J. N., Yoo, Y. J., Cho, S. H. and Yang, R. T., “Comparison of Activated Carbon and Zeolite 13X for CO2 Recovery from Flue Gas by Pressure Swing Adsorption”,Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,34, 591 (1995).
Farooq, S. and Ruthven, D. M., “Numerical Simulation of a Kinetically Controlled Pressure swing Adsorption Bulk Separation Process Based on a Diffusion Model”,Chem. Eng. Sci.,46, 2213 (1991).
Kikkinides, E. S. and Yang, R. T., “Simultaneous SO2/NOx Removal and SO2 Recovery from Flue Gas by Pressure Swing Adsorption”,Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,30, 981 (1991).
Kikkinides, E. S., Yang, R. T. and Cho, S. H., “Concentration and Recovery of CO2 from Flue gas by Pressure Swing Adsorption”,Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,32, 2714 (1993).
Kim, Y. C., Yeo, Y. K., Lee, H. U., Song, H. K, Chung, Y. S. and Na, B. K., “Simulation of PSA Process for CO2 Recovery from Flue Gas”,HWAHAK KONGHAK,36, 562 (1998).
Moon, I. S., Lee, D. I., Yang, J. H. and Ryu, H. W., “Air Separation by Adsorption on Molecular Sieve 5 A”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,3, 15 (1986).
Na, B. K., Koo, K. K. and Eum, H. M., “CO2 Recovery from Hue Gas by PSA Process using Activated Carbon”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 220 (2001).
Raghavan, N. S. and Ruthven, D. M., “Numerical Simulation of a PSA System”,AIChEJ.,31, 385 (1985).
Suzuki, M., “Adsorption Engineering”, Elsevier, England (1990).
Yang, J., Park, M. W. and Chang, J. W., “Effects of Pressure Drop in a PSA Process”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,15, 211 (1998).
Yang, R. T. and Doong, S. J., “Gas Separation by Pressure Swing Adsorption: A Pore-Diffusion Model for Bulk Separation”,AIChE J., 31, 1829 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, WK., Kwon, TI., Yeo, YK. et al. Optimal operation of the pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process for CO2 recovery. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 20, 617–623 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706897
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706897