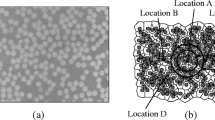
Abstract
Automated serial sectioning is presented as an attractive experimental technique for producing an accurate, large-scale three-dimensional (3-D) digital microstructural model of an extruded discontinuously reinforced aluminum composite material. The model is used as input for an elastic-plastic 3-D finite-element analysis that simulates tensile loading of the microstructure. The 3-D visualization and characterization of the resultant deformation structures within the composite microstructure has allowed some of the critical microstructural features that control the tensile response to be identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Alkemper and P.W. Voorhees,J. Microscopy, 201 (2001), pp. 388–394.
J.E. Spowart, H.M. Mullens, and B.T. Puchala,JOM, 55 (10) (2003), pp. 35–37.
J.E. Spowart,Mat. Sci. Engr. A, A425 (2006), pp. 225–237.
J.E. Spowart and D.B. Miracle,Mat. Sci. Eng. A, A357 (2003), pp. 111–123.
V.V. Ganesh and N. Chawla,Mat. Sci. Engr. A, A391 (2005), pp. 342–353.
B. Maruyama et al.,Scripta Materialia, 54 (2006), pp. 1709–1713.
J.E. Spowart,Scripta Materialia, 55 (2006), pp. 5–10.
ABAQUS/Standard, version 6.4-5 (Pawtucket, RI: ABAQUS, Inc., 2006).
T.W. Clyne and P.J. Withers,An Introduction to Metal Matrix Composites (Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press, 1993).
J.D. Eshelby,Proc. Roy. Soc. London, Ser. A, A241 (1957), pp. 376–396.
J.D. Eshelby, “Elastic Inclusions & Inhomogeneities,”Prog. Solid Mech., ed. I.N. Sneddon and R. Hill (1961), vol. 2, pp. 89–140.
J.C. Russ,The Image Processing Handbook (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1995).
H. Shen and C.J. Lissenden,Mat. Sci. Engr. A, A338 (2002), pp. 271–281.
J.E. Spowart, B. Maruyama, and D.B. Miracle,Mat. Sci. Eng. A, A307 (2001), pp. 51–66.
A. Tewari et al.Acta Materialia, 52 (2004), pp. 307–331.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spowart, J.E. The 3-D analysis of discontinuously reinforced aluminum composite microstructures. JOM 58, 29–33 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02748492
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02748492