Abstract
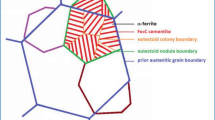
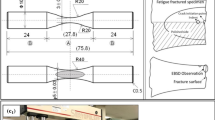
The effect of microstructure on the fatigue crack initiation of fully pearlitic steels was studied through independent variation of the prior austenite grain size, pearlite colony size, and the pearlite interlamellar spacing. Increasing yield strength (controlled by decreasing the pearlite interlamellar spacing) was seen to increase the smooth and notched-bar crack initiation endurance limit. Grain and colony size variations, at constant yield strength, were seen to exhibit no effect on crack initiation. Scanning Electron Microscopy revealed smooth-bar cracks to have initiated at surface inclusions. The influence of the pearlite interlamellar spacing, reflecting a change in the effective slip length, and the differences between notched and smooth-bar fatigue specimens for studying the effects of microstructure on crack initiation are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. E. Fine and R. O. Ritchie:Fatigue and Microstructure, 1978 ASM Materials Science Seminar, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1979, pp. 245-78.
R. C. Gibson, H. W. Hayden, and J. H. Brophy:Trans. ASM, 1968, vol. 61, pp. 85–93.
P. G. Forrest and A. E. L. Tate:J. Inst. Metals, 1964–1965, vol. 93, pp. 438–44.
A. W. Thompson and W. A. Backofen:Acta Metall., 1971, vol. 19, pp. 597–606.
M. Klesnil, M. Holzmann, P. Lukas, and P. Rys:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, pp. 47–53.
W. L. Philips and R. W. Armstrong:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1969, vol. 17, pp. 265–70.
R. M. Pelloux:Ultra-Fine Grain Metals, Syracuse University Press, Syracuse, NY, 1970, pp. 231–43.
A. Puskar:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7, pp. 1529–33.
S. Taira, K. Tanaka, and M. Hoshina:Fatigue Mechanisms, ASTM STP 675, Amer. Soc. Testing Mater., Philadelphia, PA, 1979, pp. 135–73.
G. Luetjering, T. Hamajima, and A. Gysler:Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Fracture, D.M.R. Taplin, ed., Pergamon Press, 1977, vol. 2, pp. 7–16.
G. Luetjering and A. Gysler:Proc. 1st Int. Sym. Aluminum Trans- formation Techn. and Appl., C. A. Pamillo, H. Biloni, and D.E. Embury, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1980, pp. 171–210.
J.J. Lucas and P.P. Konieczny:Metall. Trans. A, 1971, vol. 2, pp. 911–12.
A. Gysler, J. Lindigkeit, and G. Luetjering:Proc. 5th Int. Conf. Strength of Metals and Alloys, Pergamon Press, 1979, vol. 2, pp. 1113–18.
M. Peters, A. Gysler, and G. Luetjering:Titanium 80, Science and Technology, H. Kimura and O. Izumi, eds., AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1980, vol.’3, pp. 1777–86.
N.E. Paton, J.C. Williams, J.C. Chesnutt, and A. W. Thompson:Alloy Design for Fatigue and Fracture Resistance, AGARD Conf. Proc, AGARD-CP-185, NATO-AGARD, 1975.
A. W. Bowen and C. A. Stubbington:Titanium Science and Tech- nology, Jaffee and Burte, eds., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1973, vol. 3, pp. 2097–108.
C.A. Stubbington and A.W. Bowen:J. Mat. Sci., 1974, vol. 9, pp. 941–47.
J. D. Grozier and J. H. Bucher:J. Mater., 1967, vol. 2, pp. 393–407.
G. E. Dieter, R. F. Mehl, and G. T. Home:Trans. ASM, 1955, vol. 47, pp. 423–39.
Y. H. Kim, T. Mura, and M. E. Fine:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9, pp. 1679–83.
A. Querales and J.G. Byrne:Fat. Eng. Mats. Struc, 1979, vol. 1, pp. 371–82.
J.P. Benson and D. V. Edmonds:Met. Sci., 1978, vol. 12, pp. 223–32.
P.O. Kettunen:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1964, vol. 203, pp. 209–15.
S. Marich:Proc. Seminar on Vanadium in Rail Steels, Vanitec, 1979, pp. 23–40.
D. V. Wilson:Met. Sci., 1977, vol. 11, pp. 321–31.
J.M. Hyzak and I.M. Bernstein:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1217–24.
G. T. Gay, III, A.W. Thompson, J.C. Williams, and D.H. Stone:Can. Met. Quart., 1982, vol. 21, pp. 73–78.
G. T. Gay, III, J. C. Williams, and A. W. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 421–33.
A.W. Thompson and J.C. Chesnutt :Metall. Trans. A, vol. 10A, pp. 1193–96.
G. Birkbeck, A. E. Inckle, and G. W. J. Waldron:J. Mat. Sci., 1971, vol. 6, pp. 319–23.
J. Schijve:Fatigue Crack Propagation, ASTM STP 415, Amer. Soc. Testing Mater., Philadelphia, PA, 1967, pp. 415–59.
P.S. Maiya and D.E. Busch:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1761–66.
G.R. Leverant, B.S. Langer, A. Yuen, and S.W. Hopkins:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 251–57.
M.E. Fine:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 365–79.
G.J. Fowler: Ph.D. Thesis, 1976, University of California at Los Angeles, CA.
C. Laird:Fatigue Crack Propagation, ASTM STP 415, Amer. Soc. Testing Mater., Philadelphia, PA, 1967, pp. 131–81.
T. Yokobori, Y. Sawaki, S. Shono, and A. Kumasai:Trans. Japan Inst. Metals, 1976, vol. 17, pp. 1–10.
G. J. Fowler:Mat. Sci. Eng., 1979, vol. 39, pp. 121–26.
S. Marich: Bulletin 663, Amer. Railway Eng. Assoc., 1977, pp. 594–610.
A.R. Rosenfield, E. Votava, and G. T. Hahn:Trans. ASM, 1968, vol. 61, pp. 807–12.
A.R. Rosenfield, G.T. Hahn, and J. D. Embury:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 2797–804.
P. Lukas and M. Klesnil:Mat. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 34, pp. 61–66.
M. Klesnil and P. Lukas:Eng. Frac. Mech., 1972, vol. 4, pp. 77–92.
C. Laird:Mat. Sci. Eng., 1976, vol. 22, pp. 231–36.
N.E. Frost:J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 1960, vol. 2, pp. 109–19.
N.E. Frost, K.J. Marsh, and L.P. Pook:Metal Fatigue, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1974, pp. 149–56.
N.E. Dowling:Fat. Eng. Mat. Struc., 1979, vol. 2, pp. 129–38.
S. Suresh and R. O. Ritchie:Int. Metals Reviews, 1984, vol. 29, pp. 445–76.
B. N. Leis, M. F. Kanninen, A. T. Topper, J. Ahmad, and D. Broek:A Critical Review of the Short Crack Problem in Fatigue, Report AFWAL-TR-83-4019, Air Force Systems Command, WPAFB, OH, January 1983.
H. Tada, P. Paris, and G. Irwin:The Stress Analysis of Cracks Hand- book, Del Research Corporation, 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly with Carnegie-Mellon University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, G.T., Thompson, A.W. & Williams, J.C. Influence of microstructure on fatigue crack initiation in fully pearlitic steels. Metall Trans A 16, 753–760 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814826
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814826