Abstract
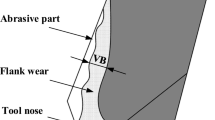
A new wear criterion, namely, the flank wear area, has been employed to indicate the severeness of drill wear condition. This new wear criterion is much better than the conventional criterion and is justified by experimental results. A computer vision approach has been adopted to measure the flank wear area, which is very difficult to measure using conventional techniques.
Thresholding technique is used for image processing and analysis of the flank wear area. In order to distinguish the worn drill from the usable drill, a threshold has been established based upon a minimum risk principle. Experiments show that the threshold is a reliable indicator for shop floor quality control of the drill.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.I. Liu: Development of Crankshaft Multifacet Drill and On-line Drill Wear Monitoring,” Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1987.
ISO/TC 29/WG22, 1972.
J.W. Lee: “Force Analysis of Drill Point Geometry for Optimal Design and Wear Prediction,” Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1986.
M.C. Shaw:Metal Cutting Principles pp. 224–250, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1984.
T.J. Drozda, C. Wick:Tool and Manufacturing Engineer’s Handbook, Vol. 1:Machining, 4th Ed., pp. 9-4–9-67, SME, 1983.
K. Subramanian and N.H. Cook: ASMEJournal of Engineering for Industry, 1977, pp. 295–301.
B.G. Batchelor, D.A. Hill, and D.C. Hodgson:Automated Visual Inspection, pp. 329–400, IFS Publications, U.K., 1985.
J.T. Barczak and J.T. Merchant: MVA/SME Vision ’86 Conference, 1986.
S.N. Lapidus: MVA/SME Vision ’86 Conference, 1986.
W.B. Green:Digital Image Processing, 2nd Ed., pp. 29–63, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1989.
F.L. Skaggs: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers’ 3rd International Conference on Robot Vision and Sensor Control, 1983.
Q. Ma: “Development of a Model-Based Vision System for Drill Quality Control in CIM,” Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1987.
G.R. Cooper, C.D. Mcgillem:Probabilistic Methods of Signal and System Analysis, pp. 35–73, Holt, Rinehart, and Winnston, New York, 1971.
A.J. Duncan:Quality Control and Industrial Statistics, 5th ed., pp. 79–119, Irwin, Inc., Illinois, 1986.
H. Gitlow, S. Gitlow, A. Oppenheim, and R. Oppenheim:Tools and Methods for the Improvement of Quality, pp. 290–378, Irwin, Inc., Illinois, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T.I. A computer vision approach for drill wear measurements. J. Mater. Shaping Technol. 8, 11–16 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834788
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834788