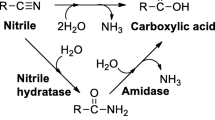
Abstract
Phenylglycine was obtained as the sole metabolite when α-aminophenylacetonitrile was ted to the culture broth ofAspergillus furmigatus. The isolated phenylglycine showed L-configuration with 80% optical purity. Examination of the hydrolysis, of the substrate to phenylglycine with cell free extracts, and the supernatant fraction and the particulate fraction both of which were obtained after ultracentrifugation of the cell free extract at 100,000g, indicated that the nitrile group hydrolyzing enzymes, nitrilase existed not only in cytoplasm, but in microsome fractions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Choi, S.Y.: Hydrolysis of the Nitrile Group in α-Aminophenylacetonitrile by Nitrilase, M.S. Thesis, Seoul National University (1985).
Esaki, N., Sida, K., Kumakai, H. and Yamada, H.:Biotechnol. Bioeng.,22, 127 (1980).
Fukumura, T.:Agric. Biol. Chem.,40, 1695 (1976).
Goo Y.M.: Antibiotics, Research and Development of Penicillin and Cephalosporin Antibiotics, pp. 184–193, Seoul National University Press, Seoul, Korea. (1983).
Goo, Y.M.:Kor. Biochem. J.,19, 67 (1986).
Hagino, H. and Nakayama, K.:Agric. Biol. Chem. 38, 157 (1974).
Hirose, Y. and Okada, H.:in: ‘Microbial Technology’ Ed. Peppler, H.J., and Perlman, D. pp. 211–240, Academic Press, N.Y. (1979).
Ingersoll, A.W. and Adams, R.:J. Am. Chem. Soc.,44, 2930 (1922).
Kanjaki, T., Kitano, K., Sumino, Y., and Okajaki, Y.:Nippon Rogei Kagaku Kaishi,46, 95 (1972).
Kitahara, K., Fukui, S. and Misawa M.:J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol.,5, 74 (1959).
Kisumi, M., Komatsubara, S. and Chibata, I.:J. Bacteriol. 106, 499 (1973).
Miozzari, G., Niederberger, P. and Hütter, R.:J. Bacteriol. 134, 48 (1978).
Nakazawa, H., Enei, H., Okumura, S., Yoshida, H. and Yamada, Y.:FEBS Lett. 25, 43 (1972).
Steiger, R.E.:Org. Synth. Col. Vol. III 84 (1955)
Sugimoto, S., Nakagawa, M., Tsuchida, T. and Shiio, I.,Agric. Biol. Chem. 37, 2327 (1973).
Terui, G.:in: ‘Microbial Production of Amino Acids’, Ed. Yamada, K., Kinoshita, S., Tsunoda, T. and Aida, K., p. 51. Halstead Press, N.Y. (1972).
Yamada, H. and Kumakai, H.:Adv. Appl. Microbiol.,19, 249 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S.Y., Goo, Y.M. Hydrolysis of the nitrile group in α-aminophenylacetonitrile by nitrilase; Development of a new biotechnology for stereospecific production ofS-α-phenylglycine. Arch. Pharm. Res. 9, 45–47 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857706
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857706