Abstract
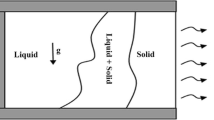
An analysis is given of interdendritic flow behavior during solidification of castings and ingots, assuming resistance to flow is as in other types of porous media. Driving forces for the flow are solidification contractions and gravity acting on a fluid of variable density. Detailed flow calculations are given for horizontal, unidirectional, steady-state solidification, using aluminum-copper alloys as examples. Conditions are quantitatively described under which gravity induced convection becomes an important contributory cause of macrosegregation. A critical condition of flow is shown to produce local melting with resulting formation of “channel-type” segregates. Qualitative examples are given of application of the ideas presented to interpretation of macrosegregation in commercial ingots, with specific reference to centerline segregation and “channel-type” segregation, including “V” segregates, “A” segregates and “freckles”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. C. Flemings and G. E. Nereo:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 1449–61.
M. C. Flemings, R. Mehrabian, and G. E. Nereo:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol.242, pp. 41–49.
M. C. Flemings and G. E. Nereo:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 50–55.
R. Mehrabian and M. C. Flemings:Trans. Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 455–64.
R. J. McDonald and J. D. Hunt:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1969, vol. 245, pp. 1993–97.
S. M. Copley, A. F. Giamei, S. M. Johnson, and M. F. Hornbecker:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, in press.
M. Muskat:Flow of Homogeneous Fluids through Porous Media, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1937; J. W. Edwards, Inc., Ann Arbor, 1946.
A. E. Scherdegger:The Physics of Flow through Porous Media, University of Toronto Press, 1957.
R. E. Collins:Flow of Fluids through Porous Materials, Reinhold Publishing Co., 1961.
E. Scheil:Metallforschung: 1947, vol. 2, p. 69.
J. Preston: International Transactions Vacuum Metallurgy Conference, E.L. Foster, ed., American Vacuum Society, New York, 1968.
E. C. Ellwood and J. M. Silcock:J. Inst. Metals, 1948, vol. 74, p. 457.
V. E. Gebhardt, M. Becker, and S. Dorner:Aluminum, 1955, vol. 31, p. 315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrabian, R., Keane, M. & Flemings, M.C. Interdendritic fluid flow and macrosegregation; influence of gravity. Metall Trans 1, 1209–1220 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900233
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900233