Abstract
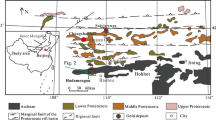
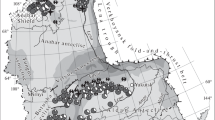
The Jiaodong Peninsula is the largest repository of gold in China based on the production in history. It covers less than 0.2% of China’s territory, but production of gold accounts for about one fourth of the whole country. Thus, the Jiaodong Peninsula is a typical area or case of large-scale metallogenesis and a large clusters of mineral deposits in China. It is characterized by the large clusters of gold deposits in large scale, high reserve and short mineralizing stage. In this study, we suggest that the eastern boundary of the large clusters of gold deposits is as same as that of North China Block, the gold deposits are hosted by Archean metamorphic rocks or Mesozoic granites, and the age of gold mineralization is 121.6 to 122.7 Ma. Gold and related ore-forming materials are derived from multisources, i.e. Archean metamorphic rocks, granites and intermediate-mafic dikes, especially, intermediate-mafic dikes and calc-alkaline granites. The metallogenic geodynamic process is constrained by the tectonic evolution of eastern North China Block during Late Mesozoic, and it is the result of the interaction between mantle and crust as the boundary plates are playing role on the block.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tu, G. C., The unique nature in ore deposition, geological background and metallogenic mechanism of non-conventional superlarge ore deposits: A preliminary discussion, Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. D, 1998, 41 (sup.): 1–6.
Pei, R. F., Qiu, X. P., Yin, B. C. et al., The Explosive anomaly of ore-forming processes and super-accumulation of metals, Mineral Deposits (in Chinese), 1999, 18(4): 333–340.
Zhai, Y. S., De, J., Li, X. B., Essentials of Metallogeny (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999: 1–288.
Mao, J. W., Hua, R. M., Li, X. B., A preliminary study of large-scale metallogenesis and large clusters of mineral deposits, Mineral Deposits (in Chinese), 1999, 18(4): 291–298.
Zhang, C. H., Gu, D. L., Study on the microstructure and deformation mechanism of the sinistral slick ductile shear zone in the middle of the northern Jiaonan uplift, in Tectonic and Geological Evolution of the Northern Jiaonan Uplift (in Chinese) ((eds. Gu, D. L., Zhang, C. H.), Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press, 1996, 96–104.
Zhai, M. G., Guo, J. H., Wang, Q. C. et al., Division of geological-tectonic units in the northern Sulu ultra-high pressure zone: An example of thick-skin thrust of crystalline units, Scientica Geologica Acta (in Chinese), 2000, 35(1): 16–26.
Zhai, M. G., Guo, J. H., Cong, B. L. et al., Sm-Nd geochronolgy and petrography of garnet pyroxene granulites in the northern Sulu region and their geotectonic implication, Scientica Geologica Acta (in Chinese), 1999, 34(3): 301–310.
Zhai, M. G., Cong, B., Guo, J., Sm-Nd geochronology and petrography of garnet pyroxene granulites in the northern Sulu region of China and their geotectonic implication, Lithos, 2000, 52: 23–33.
Jahn, B. M., Geochemical and isotopic study of UHP terrain in China (abstract), in First Workshop on UHP Metamorphism and Tectonics, Stanford: Stanford University, 1994, A71–74.
Li, S. G., Jagoutz, E., Xiao, Y. L. et al., Chronology of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the Dabie mountain and Su-Lu terrane: I. Sm-Nd isotope system, Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. D, 1996, 26(6): 597–609.
Ye, K., Guo, J. H., Zhai, M. G., The discovery and geological significance of coesite in the intercrystal of eclogite in Yangkou, Qingdao, Chinese Science Bulletin, 1996, 41(15): 1407–1408.
Liu, W. J., Zhai, M. G., Li, Y. G., Metamorphism of the high-pressure basic granulites in Laixi, eastern Shandong, China, Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1998, 14(4): 449–459.
Li, Y. G., Guo, J. H., Zhai, M. G., Geochemical differences of basement felsic gneisses in Shandong peninsula and its significance to the boundary between North China plate and Sulu UHP belt, Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1999, 15(4): 557–563.
Guo, W. K., Duan, C. J., The gold deposits in Linglong area, Zhaoyuan County, eastern Shandong Province, Geological Review (in Chinese), 1951, 16(1): 112–113.
Yu, H. M., Study on the isotope chronology of the rocks in the northwestern Jiaodong district, Shandong Province, Geology of Shandong (in Chinese), 1987, 3(1): 75–88.
Yao, F. L., Liu, L. D., Kong, Q. C. et al., The Lode Gold Deposits in Northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1990, 1–234.
Li, Z. L., Yang, M. Z., The Geology-Geochemistry of Gold Deposits in Jiaodong Region (in Chinese), Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 1993, 1–300.
Wang, H. N., Wang, Y., The relationships of migmatite, granite and gold mineralization, Journal of Nanjing University (in Chinese), 1984, (supp.): 29-40.
Li, H. Q., Liu, J. Q., Wei L., The Isochronology of Inclusions of Hydrothermal Deposits and its Geological Application (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993, 1–126.
Zhang, Z. H., Zhang, J. X., Ye, S. Z., The Isotopic Age of Gold Deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula (in Chinese), Beijing: Seismology Press, 1994, 1–56.
Luo, W. C., Wu, Q. S., Dating of the mineralizing age of gold deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula using the alteration minerals, Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 1987, 32(16): 1245–1248.
Farmer, G. L., DePaolo, D. J., Nd and Sr isotope study of hydrothermally altered granites at San Manud, Arizona: Implications for element migration paths during formation of porphyry copper ore deposits, Economic Geology, 1987, 82: 1142–1151.
Qiu, H. N., Peng, L., Chronology of40Ar/39Ar and Dating of Fluid Inclusions (in Chinese), Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 1997, 206–223.
Yang, J. H., Zhou, X. H., Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of pyrites: Implications for the age and genesis of lode deposits, Geology, 2001 (in press).
Chen, G. Y., Shao, W., Sun, D., Genetic Mineralogy of Gold Deposits in Jiaodong Region with Emphasis on Gold Prospecting (in Chinese), Chongqing: Chongqing Publishing House, 1989: 1–452.
Lüders, V., Ziemann, M., Possibilities and limits of infrared light microthermometry applied to studies of pyrite-hosted fluid inclusions, Chemical Geology, 1999, 154(1–4): 169–178.
Yang, J. H., Ma, H. M., Zhou, X. H. et al., Genesis and significance of component zones in pyrites from Penglai gold deposit, Shandong Province, Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2000, 35(2): 168–174.
Guan, K., Luo, Z. K., Miao, L. C. et al., SHRIMP in zircon chronology for Guojialing suite granite in Jiaodong district, Scientia Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1998, 33: 318–328.
Wang, L. G., Qiu, Y. M., McNaughton, N. J. et al., Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the Northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids, Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13: 275–291.
Yang, J. H., Age and metallogenic dynamics of gold mineralization in Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China-Constraints on the interaction of mantle/crust and metallogenesis/lithospheric evolution, Ph. D. Thesis, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2000, 1–133.
Zhu, F. S., The preliminary study on the metallogenesis of migmatization hydrothermal gold deposits, Geology and Prospecting (in Chinese), 1980, 16(7): 1–9.
Zhai, J. P., Xu, G. P., Hu, K., Formations and ore-forming fluid and isotope characteristics of the Qixia gold deposit and their implications, Mineral Deposits (in Chinese), 1998, 17(4): 307–313.
Lu, H. Z., Yuan, W. C., Zhang, G. P. et al., Stable isotopes studies and age dating of gold deposits and Linglong granites in Linglong-Jiaojia area, Shandong, China, Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology (in Chinese), 1999, 19(1): 1–8.
Sun, F. Y., Shi, Z. L., Feng, B. Z., Gold Ore Geology, Lithogenesis and Metallogenesis Related to the Differentiation of Mantle-Derived-C-H-O Fluids in Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China (in Chinese), Changchun: Jilin People’s Press, 1995, 1–170.
Ji, H. Z., Zhao, Y. Y., Lu, B. et al., On the relation of lamprophyre to gold ore in the Jiaodong area, Geology and Prospecting (in Chinese), 1992, 28(2): 15–18.
Sun, J. G., Relations of gold abundance in geological bodies to genesis of gold deposits, Jiaodong, Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research (in Chinese), 1999, 14(2): 43–54.
Boyle, R. W., The geochemistry of gold and its deposits, Geological Survey Canada Bulletin, 1979, 280.
Michard, A., Rare earth element systematics in hydrothermal fluids, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53: 745–750.
Voicu, G., Bardoux, M., Stevenson, R. et al., Nd and Sr isotope study of hydrothermal scheelite and host rocks at Omai, Guiana Shield: Implications for ore fluid source and flow path during the formation of orogenic gold deposits, Mineralium Deposita, 2000, 35: 302–314.
Hu, S. X., Zhao, Y. Y., Hu, Z. L. et al., Evolution and development of tectonics and magmatism at the active continental margin of the east China (E 106ü) during Mesozoic and Cenozoic, Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1994, 10(4): 370–381.
Deng, J. F., Zhao, H. L., Mo, X. X. et al., Continental Roots-Plume Tectonics of China (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publication House, 1996, 110–112.
Chen, Y. J., Guo, G. J., Li, X., Metallogenic geodynamic background of Mesozoic gold deposits in granite-greenstone terrains of North China Craton, Science in China, Ser. D, 1998, 41(2): 113–120.
Chi, J. S., Lu, F. X., Kimberlites and Palaeozoic Mantle beneath the North China Platform (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1996, 292–293.
Fan, Q. C., Hooper, P. R., The Cenozoic basaltic rocks of Eastern China: petrology and chemical composition, Journal of Petrology, 1991, 32: 765–810.
Menzies, M. A., Fan, W. M., Zhang, M., Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archean litho-sphere, Sino-Korean craton, China, in Magmatic Processes and Plate Tectonics (eds. Prichard, H. M. et al.), Geological Society Special Publication, 1993, 76: 71-81.
Fan, W. M., Menzies, M. A., Destruction of aged lower lithosphere and asthenosphere mantle beneath eastern China, Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1992, 16: 171–179.
Ren, J. S., Niu, B. G., Zheng, J., Tectonic frame and geodynamic evolution of eastern China, Geological Research (in Chinese), 1997, 29-30: 43–55.
Shao, J. A., Mou, B. L., Zhang, L. Q., Deep geological process and its shallow response during Mesozoic transfer of tectonic frameworks in eastern North China, Geological Review (in Chinese), 2000, 46(1): 32–39.
Ma, Z. J., Wang, G. Q., Plate slip divisions of the structure of lithosphere in the eastern China at present, Geological Journal of Universities (in Chinese), 1999, 5(1): 7–16.
Zhang, Q., Qian, Q., Wang, E. Q. et al., An east China plateau in Mid-late Yanshanian period: Implication from adakites, Chinese Journal of Geology (in Chinese), 2001, 36(2): 248–255.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, M., Yang, J. & Liu, W. Large clusters of gold deposits and large-scale metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 44, 758–768 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907205
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907205