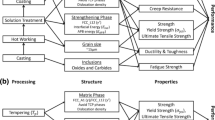
Abstract
A systems approach to the design of materials involves modeling the interactions of the processing-structure-property links. This approach leads to total optimization of properties both within and beyond the limits of any empirical approach. The design of precipitation-strengthened, high-strength, high-electrical-conductivity alloys provides a unique opportunity for demonstrating the efficiency of this approach. Using this computer-aided design, a new class of alloys with improved strength-conductivity combinations can be designed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SCM Metal Products (Alloys C15715, 15725, 15760), Cleveland, OH.
H.L. Marcus, Z. Eliezer, and M.E. Fine, U.S. patent 5,338,374 (16 August 1994).
Y. Sakai, K. Inoue, and H. Maeda,Acta Metall. Mater., 43 (1995), p. 1517.
J. Bevk, J.P. Harbison, and J.L. Bell,J. Appl. Phys., 49 (1979), p. 6031.
K.R. Karasek and J. Bevk,Scripta Metall., 13 (1979), p. 259.
K.R. Karasek and J. Bevk,Scripta Metall., 14 (1980), p. 431.
K.R. Karasek and J. Bevk,J. Appl. Phys., 52 (1981), p. 1370.
J. Miyake and M.E. Fine,Acta Metall. Mater., 40 (1992), p. 733.
C.S. Smith,A Search for Structure, (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1981).
G.B. Olson,Innovations in Ultrahigh-Strength Steel Technology, ed. G.B. Olson, M. Azrin, and E.S. Wright (1990), p. 3.
G.B. Olson,Morris E. Fine Symposium, ed. P.K. Liaw et al. (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1991), p. 41.
M.F. Ashby,Symposium on Materials Design, ed. J.D. Embury, (Materials Park, OH: ASM, 1989).
M.F. Ashby,Materials Selection in Mechanical Design (Tarrytown, NY: Pergamon 1992).
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.O. Andersson,CALPHAD, 9 (1985), p. 153.
A. Engstrom, L. Hoglund, and J. Agren,Metall. Mater. Trans., 25A (1994), p. 1127.
P.L. Rossiter,The Electrical Resistivity of Metals and Alloys (Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 1987).
V.L. Nordheim,Ann. Phys. 5 (1931), p. 642.
N.F. Mott and H. Jones,The Theory of the Properties of Metals and Alloys, (New York: Dover Publications, 1958).
T. Muto,Sci. Papers Inst. Phys. Chem. Res., 34 (1938), p. 377.
J.K. Stanley,Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Metals (Metals Park, OH: ASM, 1963), p. 53.
P.W. Taubenblatt, W.E. Smith, and A.R. Graviano,High Conductivity Copper and Aluminum Alloys, ed. E. Ling and P.W. Taubenblatt. (Warrendale, PA: TMS, (1984), p. 19.
R.B. Dingle,Proc. Royal Soc. London A, 201 (1950), p. 545.
E.H. Sondheimer,Adv. Phys., 1 (1952), p. 1.
R.A. Brown,J. Phys. F: Met. Phys., 7 (1977), p. 1269.
R.A. Brown,J. Phys. F: Met. Phys., 7 (1977), p. 1283.
T. Brown,Proc. Phys. Soc., London B, 65 (1952), p. 871.
Z.S. Basinski and S. Saimoto,Can. J. Appl. Phys., 45 (1967), p. 1161.
T.H. Blewitt, R.R. Coltman, and J.K. Redman,Defects in Crystalline Solids, (London: Physical Soc., 1955), p. 369.
L.M. Clareborough, M.C. Hargreaves and M.H. Loretto,Phil. Mag., 7 (1962), p. 115.
Z.S. Basinski, J.S. Dugdale, and A. Howie,Phil. Mag., 8 (1963), p. 1989.
J.G. Rider and C.T.B. Foxon,Phil. Mag., 16 (1967), p. 1133.
A. Seeger,Dislocations and Mechanical Properties of Crystals, ed. J.C. Fisher et al. (New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1957), p. 347.
A. Seeger,Can. J. Phys., 34 (1956), p. 1219.
J.W. Christian and J. Spreadborough,Phil. Mag., 1 (1956), p. 1069.
J.D. Verhoeven et al.,J. Appl. Phys., 65 (1989), p. 1293.
D.K. Crampton, H.L. Berghoff, and J.T. Stacy,Trans. AIME, 137 (1940), p. 354.
V.N. Fedorov et al.,Russian Metall., 6 (1971), p. 128.
M.G. Corson,Proc. Inst. Metals Div. (1927), p. 435.
M. Hansen,Constitution of Binary Alloys, (New York: McGraw Hill, 1958).
P.R. Subramanian and D.E. Laughlin,Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 9 (1988), p. 322.
R.P. Elliott,Constitution of Binary Alloys, First Supplement (New York: McGraw Hill, 1965).
C. Zener,Thermodynamics in Physical Metallurgy (Metals Park, OH: ASM, 1950), p. 16.
W.L. Fink and H.R. Freche,Trans. Am. Soc. Metall. Engrs., 111 (1934), p. 304.
Copper Alloys Guide (Illinois: Olin Corp., 1992).
Olin HSM Copper (Alloy 194), technical data (Illinois: Olin Corp.).
T. Mura,Micromechanics of Defects in Solids (Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1987).
C. Wagner,Z. Electrochem., 65 (1961), p. 581.
M.F. Ashby:Oxide Dispersion Strengthening, Metall. Soc. Conf. New York: Gordon and Breach, 1968).
J.W. Martin,Micromechanism in Particle-Hardened Alloys. (Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 1980).
I.F. Lifshitz and V.V. Slyozov,J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 19 (1961), p. 35.
D. Hull and D.J. Bacon,Introduction to Dislocations (Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1989), p. 243.
J.G. Byrne, M.E. Fine, and A. Kelly,Phil. Mag., 6 (1961), p. 1119.
J. Miyake and M.E. Fine,Scripta Metall., 25 (1991), p. 191.
Additional information
G. Ghosh earned his Ph.D. in physical metallurgy from the Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi, India, in 1986. He is currently a research assistant professor at Northwestern University.
J. Miyake earned his Ph.D. in materials science and engineering from Northwestern University in 1990. He is currently a senior research metallurgist for Nippon Mining and Metals Company in Japan.
M.E. Fine earned his Ph.D. in metallurgy from the University of Minnesota in 1943. He is currently an emeritus professor at Northwestern University. Dr. Fine is a member of TMS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, G., Miyake, J. & Fine, M.E. The systems-based design of high-strength, high-conductivity alloys. JOM 49, 56–60 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914659
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914659