Abstract
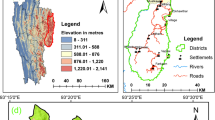
The present study was aimed to identify and delineate the groundwater potential areas in parts of Western Ghats, Kottayam, covering the upper catchment of Meenachil river. The study area is composed rocks of Archaean age and Charnockite dominated over others. The information on lithology, geomorphology, lineaments, slope and land use/land cover was generated using the Resourcesat (IRS P6 LISS III) data and Survey of India (Sol) toposheets of scale 1:50,000 (surveyed in 1969) and integrated them with raster based Geographical Information System (GIS) to identify the groundwater potential of the study area. Thus, a GIS-based model which takes account of local condition/variations has been developed specifically for mapping groundwater potential. On the basis of hydrogeomorphology, three categories of groundwater potential zones namely good, moderate and poor were identified, and delineated. The high potential zones correspond to the fracture valleys, valley fills, pediments and denudational slope, which coincide with the low slope and high lineaments density areas. The low zone mainly comprise structural hills and escarpments and these act as run-off zones. The derived panchayath-wise groundwater potentiality information could be used for effective identification of suitable locations for extraction of potable water for rural populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahuguna, I.M., Shailesh Nayak, Tamilarasan, V. and Moses, J. (2003). Groundwater prospective zones in basaltic terrain using remote sensing.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,31(2): 101–105.
Basudeo Rai, Tiwari, A. and Dubey, V.S. (2005). Identification of groundwater prospective zones by using remote sensing and geoelectrical methods in Jaria and Raniganj coalfields, Dhanbad district, Jharkhand state.J. of Earth System Sciences,114(5): 515–522.
Jagadeeswara Rao, P., Harikrishna, and Suryaprakasa Rao, B. (2004). An integrated study on groundwater resources of Pedda Gedda watershed.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,32(3): 307–311.
Khan, M.A., Pratap Narain and Moharana, P. C. (2006). Prospecting groundwater resources using RS-GIS-a case study from arid westrn Rajasthan of India.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,34(2): 171–179.
Krishnamurthy, J. and Srinivas, G. (1996). Demarcation of geological and geomorphological features of parts of Dharwar Craton, Karnataka, using IRS LISS-II data.International J. of Remote Sensing,17(16): 3271–3288.
Lokesha, N., Gopalakrishna, G.S., Honne Gowda, H. and Gupta, A.K. (2005). Delineation of groundwater potential zones in a hard rock terrain of Mysore district, Karnatak using IRS data and GIS techniques.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,33(3): 405–412.
Murthy, K.S.R., Amminedu, V. and Venkateswara Rao, V. (2003). Integration of thematic maps through GIS for identification of groundwater potential zones.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,31(3): 197–210.
National Remote Sensing Agency (1995). Integrated Mission for Sustainable Development (IMSD). Technical guidelines, National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad.
National Remote Sensing Agency (2000). Technical guidelines for preparation of groundwater prospect map, Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission, National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad.
Pradeep Jain K. (1998). Remote sensing techniques to locate groundwater potential zones in upper Urmil river basin, distict Chhatarpur - central India.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,26(3): 135–147.
Ravindran, K.V. and Jeyaram, A. (1997). Groundwater prospectus of Shahba Teshil, Baran district, eastern Rajasthan: A remote sensing approach.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,25(4): 239–246.
Sankar, K. (2002). Evaluation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing data in upper Vaigai river basin, Tamil Nadu, India.J. of Indian Society of Remote Sensing,30(3): 119–128.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Vijith, H. Groundwater potential in the hard rock terrain of western ghats: A case study from Kottayam district, Kerala using resourcesat (IRS-P6) data and GIS techniques. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 35, 163–171 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990780
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990780