Abstract
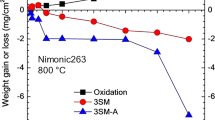
Hot corrosion is the accelerated oxidation of materials at elevated temperatures induced by a thin film of fused salt deposit. Because of its high thermodynamic stability in the mutual presence of sodium and sulfur impurities in an oxidizing gas, Na2SO4 is often found to be the dominant salt in the deposit. The corrosive oxyanion-fused salts are usually ionically conducting electrolytes that exhibit an acid/base chemistry, so that hot corrosion must occur by an electrochemical mechanism that may involve fluxing of the protective oxides. With the aid of high-temperature reference electrodes to quantify an acid/base scale, the solubilities for various metal oxides in fused Na2SO4 have been measured, and these show remarkable agreement with the theoretical expectations from the thermodynamic phase stability diagrams for the relevant Na-Metal-S-O systems. The solubilities of several oxides infused Na2SO4-NaVO3 salt solutions have also been measured and modeled. Such information is important both in evaluating the corrosion resistance of materials and in interpreting any oxide fluxing/reprecipitation mechanisms. Various electrochemical measurements have identified the S2O7 2− anion (dissolved SO3) as the oxidant that is reduced in the hot corrosion process. Electrochemical polarization studies have elucidated the corrosion reactions and clarified the corrosion kinetics of alloys. Mechanistic models for Type I and Type II hot corrosion are discussed briefly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.T. Reid, R.C. Corey, and BJ. Cross, Trans. ASME, 67 (1945), p. 279.
F.J. Wall and S.T. Michael, ASTM Spec. Tech. Publ. STP 421 (1967), p. 223.
E. Erdos, Deposition and Corrosion in Gas Turbines, ed. A.B. Hart and A.J.B. Cutler (London: Applied Science Publishers, 1973), p. 115.
K.J. Kohl et al., J. Electrochem. Soc., 126 (1979), p. 1054.
K.L. Luthra and H.S. Spacil, J. Electrochem. Soc., 129 (1982), p. 649.
E.L. Simons, G.V. Browning, and H.A. Liebhafsky, Corrosion, 11 (1955), p. 505.
A.U. Seybolt, Trans. AIME, 242 (1968), p. 1955.
N.S. Bornstein and M.A. DeCrescente, Trans. AIME, 245 (1969), p. 583.
N.S. Bornstein and M.A. DeCrescente, Met. Trans.,2 (1971), p. 2875.
J.A. Goebel and F.S. Pettit, Met. Trans., 1 (1970), p. 1943.
J.A. Goebel, F.S. Pettit, and G.W. Goward, Met. Trans., 4 (1973), p. 261.
J. Stringer, Annual Review of Materials Sci., 7, ed. R.A. Huggins (Palo Alto, CA: Annual Review Inc., 1977), p. 449.
J. Stringer, Materials Sci. Techn., 3 (1987), p. 482.
F.S. Pettit and C.S. Giggins, “Hot Corrosion,” Superalloys II, ed. C.T. Sims, N.S. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel (New York: Wiley Publ., 1987), p. 327.
R.A. Rapp, Corrosion, 42 (1986), p. 568.
R.A. Rapp, “Hot Corrosion of Materials,” Selected Topics in High Temperature Chemistry, ed. O. Johannesen and A.G. Andersen (Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1989), p. 291.
C.O. Park and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 133 (1986), p. 1636.
D. Inman and D.M. Wrench, Brit. Corros. J., 1 (1966), p. 246.
D.A. Shores and R.C. John, J. Appl. Electrochem., 10 (1980), p. 275.
P.P. Leblanc and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 139 (1992), p. L31.
P.P. Leblanc and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 140 (1993), p. L41.
D.K. Gupta and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 127 (1980), p. 2194 and 2656.
Y.S. Zhang and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 132 (1985), p. 734 and 2498.
Y.S. Zhang, J. Electrochem. Soc., 133 (1986), p. 655.
P.D. Jose, D.K. Gupta, and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 132 (1985), p. 735.
D.Z. Shi and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 133 (1986), p. 849.
M.L. Deanhardt and K.H. Stern, J. Electrochem. Soc., 128 (1981), p. 2577.
A.K. Misra, D.P. Whittle, and W.L. Worrell, J. Electrochem. Soc., 129 (1982), p. 1840.
M.L. Deanhardt and K.H. Stern, J. Electrochem. Soc., 129 (1982), p. 2228.
N.S. Jacobson and J.L. Smialek, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 68 (1985), p. 432.
N.S. Jacobson, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 76 (1993), p. 3.
Y.S. Hwang and R.A. Rapp,J. Electrochem. Soc., 137 (1990), p. 1276.
Y.S. Zhang and R.A. Rapp, Corrosion, 43 (1987), p. 348.
Y.S. Hwang and R.A. Rapp, Corrosion, 45 (1989), p. 933.
R.A. Rapp and Y.S. Zhang, “Electrochemical Studies of Hot Corrosion of Materials,” Proc Intern. Corr. Conf. (Merida, Mexico: 1993)
R.L. Jones, D.B. Nordman, and S.T. Gadomski, Met. Trans., 16A (1985), p. 303.
R.L. Jones, S.R. Jones, and C.E. Williams, J. Electrochem. Soc., 132 (1985), p. 1499.
R.L. Jones, C.E. Williams, and S.R. Jones, J. Electrochem. Soc., 133 (1986), p. 227.
R.L. Jones and D. Mess,J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 75 (1992), p. 1818.
R.L. Jones, High Temp. Tech., 6 (1988), p. 187.
M. Seiersten and P. Kofstad, Mater. Sci. Tech., 3 (1987), p. 576.
A.S. Nagelberg, J. Electrochem. Soc., 132 (1985), p. 2502.
F. Mansfeld and J.V. Kenkel, Corr. Sci., 16 (1976), p. 111.
F. Mansfeld and J.V. Kenkel, Corrosion, 33 (1977), p. 238.
R. Andresen, J. Electrochem. Soc., 126 (1979), p. 328.
D.A. Shores and W.C. Fang,J. Electrochem. Soc., 128 (1981), p. 346.
W.C. Fang and R.A. Rapp,J. Electrochem. Soc., 130 (1983), p. 2335.
H. Numata, A. Nishikata, and S. Haruyama, Proc. JIMIS-3, Trans. Japan Inst. Suppl. (1983), p. 303.
X. Zheng and R.A. Rapp,J. Electrochem. Soc., 140 (1993), p. 2857.
H. Numata and S. Haruyama, Corrosion, 44 (1988), p. 7249.
J. Kupper and R.A. Rapp, Werkstoffe und Korrosion, 38 (1987), p. 674.
J.C. Nava, D.Z. Shi, and R.A. Rapp, “Electrochemical Reactions of NaVO3 and Na2CO4 Solutes in Na2SO4,” High Temperature Materials Chemistry IV (Pennington, NJ: Electrochem. Soc., 1987), p. 1.
D.Z. Shi and R.A. Rapp, Werkstoffe und Korrosion, 41 (1990), p. 215.
D.A. Shores, Corrosion, 31 (1975), p. 434.
A. Rahmel, M. Schmidt, and M. Schorr, Oxid. Metals, 18 (1982), p. 195.
W.T. Wu, A. Rahmel, Oxid. Metals, 19 (1983), p. 201.
W.T. Wu, A. Rahmel, and M. Schorr, Oxid. Metals, 22 (1984), p. 59.
W.T. Wu, J. Zhang, and Y. Niu, Proc 11th Intern. Cong. Mater. Corr. (Florence, Italy, April 2–6,1990), p. 1475.
Y. Niu, J. Zhang, and W.T. Wu, High Temperature Corrosion and Protection, ed. H. Guan, W.T. Wu, J. Shen, and T. Li (Shenyang, China: Liaoning Sci. Techn. Publ. House, 1990), p. 201.
R.A. Rapp and K.S. Goto, “Hot Corrosion of Metals by Molten Salts,” Molten Salts I, ed. J. Braunstein and J.R. Selman (Pennington, NJ: Electrochem. Soc., 1981), p. 159.
D.A. Shores, “New Perspective on Hot Corrosion Mechanisms,” High Temperature Corrosion, NACE-6, ed. R.A. Rapp (Houston, TX: NACE, 1983), p. 493.
N. Otsuka and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 137 (1990), p. 46.
Y.M. Wu and R.A. Rapp, J. Electrochem. Soc., 138 (1991), p. 2683.
Y.S. Zhang and R.A. Rapp, “Solubility of CeO2 in Molten Na2SO4-10 mol.% NaVO3 salt solution at 900°C” (Paper to be presented at 9th Intern. Symp. Molten Salts, San Francisco, 22–27 May 1994).
G.C. Fryburg et al., J. Electrochem. Soc., 129 (1982), p. 571.
G.C. Fryburg, F.J. Kohl, and C.A. Stearns, J. Electrochem. Soc., 131 (1984), p. 2985.
K.L. Luthra and D.A. Shores, J. Electrochem. Soc., 127 (1980), p. 2202.
K.L. Luthra, High Temperature Corrosion, NACE-6, ed. R.A. Rapp (Houston, TX: NACE, 1983), p. 507.
K.L. Luthra, Met. Trans., 13A (1982), pp. 1647,1843, and 1853.
K.L. Luthra,J. Electrochem. Soc., 132 (1985), p. 1293.
K.L. Luthra and J.H. Wood, Thin Solid Films, 119 (1984), p. 271.
Y.S. Zhang, L.Q. Shi, and S.T. Shih,J. Chin. Soc. Corr. Protec., 12 (1992), p. 189.
Y.S. Zhang, X.M. Li, L.Q. Shi, and S.T. Shih, J. Chin. Soc. Corr. Protec, 11 (1991), p. 17.
L.Q. Shi, Y.S. Zhang, and S.T. Shih, Corr. Sci., 33 (1992), p. 1427.
L.Q. Shi, Y.S. Zhang, and S.T. Shih, Oxid. Metals, 38 (1992), p. 385.
Y.S. Zhang, X.M. Li, T.L. Cao, and S.T. Shih, Corr. Sci. Protec Tech., 4 (1992), p. 9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rapp, R.A., Zhang, YS. Hot corrosion of materials: Fundamental studies. JOM 46, 47–55 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222665
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222665