Abstract
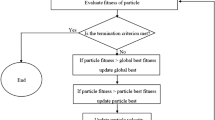
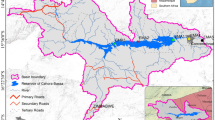
The rainfall-runoff relationship is one of the most complex hydrological phenomena. In recent years, hydrologists have successfully applied backpropagation neural network as a tool to model various nonlinear hydrological processes because of its ability to generalize patterns in imprecise or noisy and ambiguous input and output data sets. However, the backpropagation neural network convergence rate is relatively slow and solutions can be trapped at local minima. Hence, in this study, a new evolutionary algorithm, namely, particle swarm optimization is proposed to train the feedforward neural network. This particle swarm optimization feedforward neural network is applied to model the daily rainfall-runoff relationship in Sungai Bedup Basin, Sarawak, Malaysia. The model performance is measured using the coefficient of correlation and the Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient. The input data to the model are current rainfall, antecedent rainfall and antecedent runoff, while the output is current runoff. Particle swarm optimization feedforward neural network simulated the current runoff accurately with R = 0.872 and E2 = 0.775 for the training data set and R = 0.900 and E2= 0.807 for testing data set. Thus, it can be concluded that the particle swarm optimization feedforward neural network method can be successfully used to model the rainfall-runoff relationship in Bedup Basin and it could be to be applied to other basins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour, M.; Rahmani, A. M.; Teshnehlab, M., (2005). Carbon monoxide prediction using novel intelligent network. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 1 (4), 257–264 (8 pages).
Al-kazemi, B.; Mohan, C. K., (2002). Training feedforward neural network using multi-phase particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of the 9th. International Conference on Neural Information Processing, New York.
Ashlock, D., (2006). The evolutionary computation for modeling and optimization. Springer. Germany.
Bandyopadhyay, G.; Chattopadhyay, S., (2007). Single hidden layer artificial neural network models versus multiple linear regression model in forecasting the time series of total ozone. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (1), 141–150 (10 pages).
Bessaih, N.; Mah, Y. S.; Muhammad, S. M.; Kuok, K. K.; Rosmina, A. B., (2003). Artificial neural networks for daily runoff simulation. Faculty of Engineering, University Malaysia Sarawak, Charles River Media Inc.
Bishop, C. M., (1995). Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press. Chapter 7, 253–294.
Bong, S. K.; Bryan, W. K., (2006). Hydraulic optimization of transient protection devices using GA and PSO approaches. J. Water Res. PL-ASCE., 132 (1), 44–52 (10 pages).
Dastorani, M. T.; Wright, N. G., (2001). Artificial neural network based real-time river flow prediction. School of Civil Engineering, University of Nottingham, Nottingham NG7 2RD, UK.
DID, (2004). Hydrological Year Book. Department of Drainage and Irrigation Sarawak, Malaysia.
Eberhart, R.; Hu, X., (1999). Human tremor analysis using particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, CEC. Washington.
Eberhart, R.; Shi, Y., (2001). Particle swarm optimization: Developments, application and resources. IEEE., 1, 81–86 (6 pages).
Elshorbagy, A.; Simonovic, S. P.; Panu, U. S., (2000). Performance evaluation of artificial neural networks for runoff prediction. J. Hydrologie Eng., 5 (4), 424–427 (4 pages).
Ferguson, D., (2004). Particle swarm. University of Victoria, Canada.
Fukumaya, Y.; Takamaya, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yoshida, H., (1999). A particle swarm optimization for reactive power and voltage control in electric power systems. Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Orlando, Florida, USA.
Garcia-Bartual, R., (2002). Short term river flood forecasting with neural networks. Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain, 160–165.
Gautam, M. R.; Watanabe, K.; Saegusa, H., (2000). Runoff analysis in humid forest catchment with artificial neural networks. J. Hydrol., 235 (1–2), 117–136(20 pages).
Gies, D.; Rahmat-Samii, Y, (2003). Particle swarm optimization for reconfigurable phase-differentiated array design. Micro. Opt. Tech. Lett., 38 (3), 168–175 (8 pages).
Gudise, V. G.; Venayagamoorthy, G K., (2003). Evolving digital circuits using particle swarm. Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks.
Harun, S.; Kassim, A. H.; Van, T. N., (1996). Inflow estimation with neural networks. 10th. Congress of the Asia and Pacific Division of the International Association for Hydraulic Research, 150-155.
Haza, N.,(2006). Particle swarm optimization for neural network learning enhancement. M.Sc. Thesis, University Technology of Malaysia.
Imrie, C. E.; Durucan, S.; Korre, A., (2000). River flow prediction using artificial neural networks: Generalization beyond the calibration range. J. Hydrol., 233, 138–153 (16 pages).
Jain, S. K.; Chalisgaonkar, C., (2000). Setting up stage-discharge relations using ANN. J. Hydro. Eng., 5 (4), 424–433 (10 pages).
Jones, M. T., (2005). AI application programming. 2nd. Ed. Hingham, Massachusetts.
Jupem (1975). Jabatan ukur dan pemetaan Malaysia. Scale 1, 50,000.
Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. C., (1995). Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE Press. 1942–1948.
Lee, J. S.; Lee, S.; Chang, S.; Ahn, B. H., (2005). A comparison of GA and PSO for excess return evaluation in stock markets. Springer-Verlag, 221-230.
Lisa, A. O.; Kaylan, V., (2004). Optimal scheduling in sensor network using swarm intelligence. CISS, Princeton, New Jersey.
Lisa, A. O.; Veeramachaneni, K.; Varshney, P., (2003). Adaptive multimodel biometric fusion algorithm using particle swarm. Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 5099.
Nishimura, S.; Kojiri, T., (1996). Real-time rainfall prediction using neural network and genetic algorithm with weather radar data, 10th. Congress of the Asia and Pacific Division of the International Association for Hydraulic Research, 204-211 (8 pages).
Rajani, M.; Lisa, A. O., (2004). Decision making in a building access system using sensor using swarm intelligence and POSets. CISS, Princeton, New Jersey.
Rene, E. R.; Kim, J. H.; Park, H. S., (2008). An intelligent neural network model for evaluating performance of immobilized cell biofilter treating hydrogen sulphide vapors. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (3), 287–296 (9 pages).
Shi, Y., (2004). Particle swarm optimization. IEEE Neural Network Society: 8-13.
Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R. C., (1998). A modified particle swarm optimizer. Proceedings of the 105 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 69-73.
Song, M. P.; Gu, G. H., (2004). Research on particle swarm optimization: A Review. Proceedings of the 3rd. International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernectics. Shanghai, China.
Tokar, A. S; Johnson, P. A., (1999). Rainfall-runoff modeling using artificial neural networks. J. Hydro. Eng., 4 (3), 223–239 (17 pages).
Van den Bergh, F.; Engelbrecht, A. P., (1999). Particle swarm weight initialization in multi-layer perceptron artificial neural networks. ICAI Durban, South Africa.
Van den Bergh, F.; Engelbrecht, A. P., (2000). Cooperative learning in neural networks using particle swarm optimizers. S. Afr. Comput. J., 26, 84–90 (7 pages).
Van den Bergh, F., (2001). An analysis of particle swarm optimizers. Ph.D dissertation,University of Pretoria. South Africa.
Wright, N. G; Dastorani, M. T., (2001). Effects of river basin classification on artificial neural networks based ungauged catchment flood prediction, Proceedings of the 2001 International Symposium on Environmental Hydraulics.
Zhang, C.; Shao, H.; Li, Y., (2000). Particle swarm optimization for evolving artificial neural network. IEEE, 2487–2490 (4 pages).
Zweiri, Y. H.; Whidborne, J. F.; Sceviratne, L. D., (2003). A three-term backpropagation algorithm. Neurocomputing, 50, 305–318 (14 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuok, K.K., Harun, S. & Shamsuddin, S.M. Particle swarm optimization feedforward neural network for modeling runoff. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 67–78 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326118
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326118