Abstract
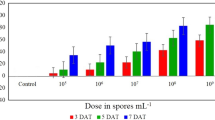
The interaction effects of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Kurstaki and HaSNPV on the survival of second instars of Plutella xylostella were evaluated under laboratory conditions. The exposure of second instars to the combination of HaSNPV (2.3×103, 3.8×104, 6.6×105 occlusion bodies (OB) ml−1) and B. thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki (2.4×101, 3.4×103, 4.7×105 spores ml−1), indicated an additive effect in the toxicity of most combinations. Synergism occurred when the lowest concentration of the combination of B. thuringiensis (2.4×10−1 spores ml−1) and HaSNPV (2.3×103 OB ml−1) was applied. When the larvae were fed on leaf discs contaminated with both B. thuringiensis and HaSNPV, their growth and developmental rates were decreased and a reduction in their pupation rate, pupal weight as well as the emergence rate of adults was observed. The LT50 values correlated negatively with B. thuringiensis and HaSNPV concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS, 1925. A method of computing the effectiveness of insecticides. J Econ Entomol 18, 265–267.
Bohorova N, Maciel AM, Brito RM, Aguilart L, Ibarra JE & Hoisington D, 1996. Selection and characterization of mexican isolates of Bacillus thuringiensis active against four major lepidopteran maize pests. Entomophaga 4, 153–165.
Bonsall MB, 2004. The impact of diseases and pathogens on insect population dynamics. Physiol Entomol 29, 223–236.
Brar S, Verma M, Tyagi RD & Valero JR, 2006. Recent advances in downstream processing and formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides. Process Biochem 41, 323–342.
Bravo A, Gill SS & Soberon M, 2007. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxin 49, 423–435.
Chang JH, Choi JY, Jin BR, Roh JY, Olszewski JA, Seo SJ, O‘Reilly DR & Je YH, 2003. An improved baculovirus insecticide producing occlusing bodies that contains Bacillus thuringiensis insect toxin. J Invertebr Pathol 84, 30–37.
Duffield S & Jordan SL, 2000. Evaluation of insecticides for the control of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) and Helicoverpa punctigera (Wallengren) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on soybean, and the implications for field adoption. Aust J Entomol 39, 322–327.
Farrar RR, Shapiro M & Shepard M, 2007. Relative activity of baculoviruses of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). BioControl 52, 657–667.
Huang DF, Zhang J, Song FP & Lang ZH, 2007. Microbial control and biotechnology research on Bacillus thuringiensis in China. J Invertebr Pathol 95, 175–180.
Kim JS, Choi JY, Chang JH, Shim HJ, Roh JY & Jin BR, 2005. Characterization of an improved recombinant baculovirus producing polyhedra that contain Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac crystal protein. J Microbiol Biotechnol 15, 710–715.
Liu XX, Zhang QW, Xu B & Li J, 2006. Effects of Cry1Ac toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis and nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Helicoverpa armigera Hubner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on larval mortality and pupation. Pest Manage Sci 62, 729–737.
Luttrell RG, Young SY, Yearian WC & Horton DL, 1982. Evaluation of Bacillus thuringiensis sprays adjuvant viral insecticide combinations against Heliothis spp. (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Environ Entomol 11, 783–787.
Mansour NA, Eldefrawi ME, Toppozada A & Zeid M, 1966. Toxicological studies on the Egyptian cotton leafworm, Prodenia litura Vl potentiation and antagonism of carbamate insecticide. J Econ Entomol 59, 307–311.
Marzban R, 2012. Midgut pH profile and energy differences in lipid, protein and glycogen metabolism of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin and cypovirus-infected Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Entomol Res Soc 14, 45–53.
Marzban R, He Q, Liu X & Zhang Q, 2009. Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac and cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (HaCPV) on cotton bollworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Invertebr Pathol 101, 71–76.
Matter MM & Zohdy NM, 1981. Biotic efficiency of Bacillus thuringiensis Berl. and a nuclear-polyhedrosis virus on larvae of the American bollworm, Heliothis armigera Hbn. (Lep.: Noctuidae). J Appl Entomol 92, 336–343.
Moscardi F, 1999. Assessment of the application of baculo-viruses for control of Lepidoptera. Annu Rev Entomol 44, 257–289.
Raymond B, Sayyed AH & Wright D, 2006. The compatibility of a nucleopolyhedrosis virus control with resistance management for Bacillus thuringiensis: Co-infection and cross-resistance studies with the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J Invertebr Pathol 93, 114–120.
Reddy GVP & Manjunatha M, 2000. Laboratory and field studies on the integrated pest management of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) in cotton, based on pheromone trap catch threshold level. J Appl Entomol 124, 213–221.
Salama HS, Sharaby A & Eldin MM, 1993. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis and nuclear polyhedrosis virus in the larvae of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd). Insect Sci Appl 14, 483–488.
Sarfraz M, Keddie AB & Dosdall LM, 2005. Biological control of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella: A review. Biocon Sci Technol 15, 763–789.
SAS Institute, 1999. SAS Online Doc®. Version 8. Cary, NC.
Shang JN, Zhu JQ & Ye GY, 1999. Mixed experiments of the nuclear polyhedrosis virus from Ectropis obliqua prout with some insecticides. J Tea 25, 80–82.
SPSS, 1998. SPSS User‘s Guide. SPSS, Inc, Chicago, IL.
Tabashnik BE, Cushing NL, Finson N & Johnson MW, 1990. Field development of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 83, 1671–1676.
Trang T & Chaudhari S, 2002. Bioassay of nuclear polyhe-drosis virus (NPV) and in combination with insecticide on Spodoptera litura (Fab). Omonrice 10, 45–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magholli, Z., Marzban, R., Abbasipour, H. et al. Interaction effects of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki and single nuclear polyhedrosis virus on Plutella xylostella. J Plant Dis Prot 120, 173–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356471
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356471