Abstract
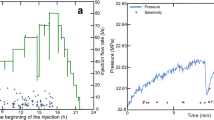
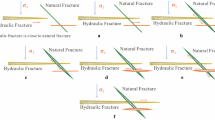
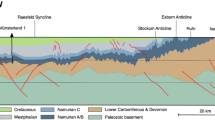
— We addressed effects of in situ stress on the formation of flow pathways in fractured rocks in geothermal reservoirs, especially for HDR projects. Here we focused on fractures which are critically-stressed, causing shear slip in a current stress field. The sliding is likely to break sealing in the fractures and, as a result, to increase their permeability. Such a mechanism is possibly significant under high-temperature conditions at geothermal fields because of temperature enhancement on chemical reactions for the sealing. We present a procedure to estimate the orientation of the critically-stressed fractures relative to axes of in situ principal stress with the aid of the Mohr diagram. The procedure allows us to evaluate intuitively how the orientation changes with factors such as magnitude of in situ principal stresses and pore pressure. We applied the procedure to estimate possible orientations of the critically-stressed fractures in major HDR test sites. Results show that overall alignments of microseismicity during hydraulic stimulation are within predicted ranges for possible orientations of the critically-stressed fractures. Furthermore, it was found that if the state of in situ stress is not favorable to cause sliding of natural fractures, it tends to lead a high wellhead pressure at hydraulic stimulation and a high recovery rate at circulation. On the other hand, if the state of in situ stress is favorable for sliding, it tends vice versa to lead a low wellhead pressure at hydraulic stimulation and a low recovery rate at circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
(Received January 31, 2001, revised July 3, 2001, accepted August 1, 2001)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, T., Hayashi, K. Role of Stress-controlled Flow Pathways in HDR Geothermal Reservoirs. Pure appl. geophys. 160, 1103–1124 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012563
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012563