Abstract
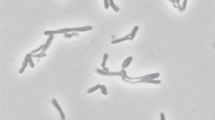
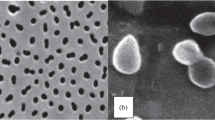
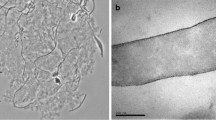
The cellular characteristics of a new methylotrophic, acidogenic, anaerobic bacterium that was first isolated from a sewage digestor in Marburg, Federal Republic of Germany, is described. The Marburg strain is a mesophilic, Gram-positive, nonmotile, pleomorphic rod that performs homoacetic, homobutyric, or heteroacidic fermentations. Cell morphology varies from single or paired straight rods to rudimentary branched rods, club-shaped cells, or oval refractile cells. Cell heat resistance correlated with the presence of a few refractile cells. Electron micrographs of thin sections revealed a thick monolayered cell wall and an atypical spore structure. The DNA base composition was 48.8±0.2 mol% guanosine plus cytosine. Growth required factors in yeast extract; methanol, H2/CO2, glucose, fructose, lactate, and pyruvate were fermented as energy sources. Corrinoid levels varied from 0.35±0.16 to 7.9±1.6 μg/mg cell dry weight when cells 0.1% yeast extract, N2/CO2, 100 mM methanol, and 50 mM Na acetate displayed a 20h doubling time, finalA 540 of 0.9, butyric acid yield of 25 mM, and ≈stoichiometry of 3 mol butyrate formed per 10 mol methanol fermented. The nameButyribacterium (emend.)methylotrophicum sp. nov. is proposed for the Marburg strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Andreesen, J. R., Gottschalk, G., Schlegel, H. G. 1970.Clostridium formicoaceticum nov. spec. Isolation, description and distinction fromClostridium aceticum. Archiv für Mikrobiologie72:154–174.
Balch, W. E., Schoberth, S., Tanner, R. S., Wolfe, R. S. 1977.Acetobacterium, a new genus of hydrogen-oxidizing, carbon dioxide-reducing, anaerobic bacteria. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology27:355–361.
Barker, H. A. 1944.Butyribacterium, a new genus of grampositive nonsporulating anaerobic bacteria of intestinal origin. Journal of Bacteriology47:301–305.
Buchanan, R. E., Gibbons, N. E. 1974. Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
Cho, K. Y., Doy, C. H. 1973. Ultrastructure of the anaerobic bacteriaClostridium kluyveri andC. acetobutylicum. Australian Journal of Biological Science26:547–58.
Daniels, L., Fuchs, G., Thauer, R. K., Zeikus, J. G. 1977. Carbon monoxide oxidation by methanogenic bacteria. Journal of Bacteriology132:118–128.
De Ley, J. 1970. Reexamination of the association between melting point, buoyant density, and chemical base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid. Journal of Bacteriology101:738–754.
Florent, J., Ninet, L. 1979. Vitamin B12, pp. 497–517. In: Peppler, H. J., Perlman, D. (eds.), Microbial technology, 2nd ed., vol. 1. New York: Academic Press.
Fontaine, F. E., Peterson, W. H., McCoy, E., Johnson, M. J., Ritter, G. J. 1942. A new type of glucose fermentation byClostridium thermoaceticum n. sp. Journal of Bacteriology43:701–715.
Kamikuvo, T., Hayashi, M., Nishio, N., Nagai, S. 1978. Utilization of non-sugar sources for vitamin B12 production. Applied and Environmental Microbiology35:971–973.
Krzycki, J., Zeikus, J. G. 1980. Quantification of corrinoids in methanogenic bacteria. Current Microbiology3:243–245.
Marmur, J. 1961. A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. Journal of Molecular Biology3:208–218.
Nelson, D. R., Zeikus, J. G. 1974. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous products of anaerobic metabolism. Applied and Environmental Microbiology28:258–261.
Quayle, J. R. 1972. The metabolism of one-carbon compounds in microorganisms. Advances in Microbial Physiology7:118–203.
Takagi, A., Kawata, T., Yamamoto, S. 1960. Electron microscopic studies of ultra thin sections of spores of theClostridium group with special reference to the sporulation and germination process. Journal of Bacteriology80:37–46.
Tanner, R. S., Wolfe, R. S., Ljungdahl, L. G. 1978. Tetrahydrofolate enzyme levels inAcetobacterium woodii and their implication in the synthesis of acetate from CO2. Journal of Bacteriology134:668–670.
Weimer, P. J., Zeikus, J. G. 1978. One-carbon metabolism in methanogenic bacteria: Cellular characterization and growth ofMethanosarcina barkeri. Archives of Microbiology119:49–57.
Weimer, P. J., Zeikus, J. G. 1978. Acetate metabolism inMethanosarcina barkeri. Archives of Microbiology119:175–182.
Wells, R. D., Blair, J. E. 1967. Studies on polynucleotides, LXXI. Sedimentation and buoyant density of some DNA-like polymers with repeating nucleotide sequences. Journal of Molecular Biology27:273–288.
Wieringa, K. T. 1940. The formation of acetic acid from carbon dioxide and hydrogen by anaerobic spore-forming bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Journal of Microbiology and Serology6:251–262.
Zeikus, J. G. 1977. Biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriological Reviews41:514–541.
Zeikus, J. G., Bowen, V. G. 1975. Fine structure ofMethanospirillum hungatii. Journal of Bacteriology121:373–380.
Zeikus, J. G., Hegge, P. W., Anderson, M. A. 1979.Thermoanaerobium brockii gen. nov. and sp. nov. a new chemoorganotrophic, caldoactive, anaerobic bacterium. Archives of Microbiology122:41–48.
Zeikus, J. G., Henning, D. L. 1975.Methanobacterium arbophilicum sp. nov. An obligate anaerobe isolated from wetwood of living trees. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Journal of Microbiology and Serology41:543–552.
Zeikus, J. G., Wolfe, R. S. 1972.Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. Journal of Bacteriology 109:707–713.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeikus, J.G., Lynd, L.H., Thompson, T.E. et al. Isolation and characterization of a new, methylotrophic, acidogenic anaerobe, the marburg strain. Current Microbiology 3, 381–386 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02601907
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02601907